Partial Runs
A partial run is when only one section of a workspace is carried out. One way to do this is to disable objects in the canvas to only run certain enabled sections. Another method is to use a tool called Partial Runs, which is represented by pop-up options when a workspace is run with caching turned on.
The technique you use will depend on how large the workspace is, and how much of it you need to run. You may use one technique or the other - or you may use both!
Disabled Objects
If designed correctly, a large workspace should be made up of small sections. Isolating a section (or part of a section) for testing is possible by disabling connections to all other components.
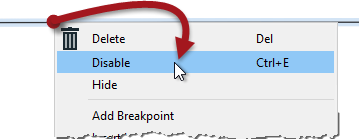
An object (connection or feature type) is disabled by right-clicking it and choosing the option to Disable (or selecting it and using the shortcut Ctrl+E):
A disabled connection is rendered inoperative in much the same way as if it had been deleted, and no features will pass through. The same disabling can be done to other canvas objects such as transformers and feature types. Even a reader/writer can be disabled through the Navigator window.
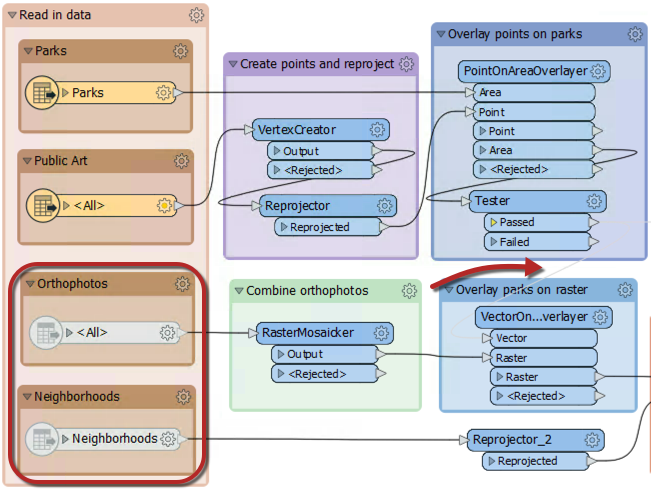
Here an author has disabled two connections (both from the Tester:Passed port) and two feature types:
With that setup the top part of the workspace will operate up until (and including) the Tester. The bottom portion will not run at all. No data will emerge from the disabled feature types, and no data is passed to it from the Tester.
With caching turned on, the author can inspect part of the workspace without having to run the entire translation. This feature is a significant advantage when (like here) the disabled section takes up most of the overall processing time.
Partial Runs
The technical aspect of partial runs has already been covered. However, using partial runs is an important part of workspace testing. You should use partial runs to develop your workspace incrementally, testing each new section to ensure it works.
A partial run is particularly useful in avoiding re-reading data from its source; especially when the data comes from a slow, remote location such as a web service. Creating a cache can help increase the development of your workspace.
Finally, caches can be saved with the workspace when it is saved as a template (File > Save As Template, check Include Feature Caches). That means the workspace can be re-run using the caches from a previous session or even from another author!