General Controls
Table of Contents
Overview
The general controls in Neutron can affect the entire plug-in or individual modules only.
The following general controls affect the entire plug-in:
The following controls affect individual modules:
Resize Window
You can resize the main window by clicking and dragging the bottom right corner of the plug-in window. The Neutron 4 mothership, Visual Mixer, and component plug-ins are all resizable.
Global Controls
The following controls are included in the header area of the Neutron 4 mothership plug-in:

- Plug-in Instance Name: Displays the name of the current instance as it appears in IPC lists in supported iZotope plug-ins.
- Assistant View: Opens the Assistant view. See the Assistant chapter for more information.
- Detailed View: Opens the Detailed View, allowing you to access deeper controls in the modules.
- Preset Manager: Opens the Preset Manager window. See the Presets chapter for more information.
- Undo History: Opens the Undo History window. Undo History allows you to compare settings you’ve adjusted. See the Undo History Controls section below for more information.
- Zero Latency: Enables Zero Latency processing. When enabled, some processing options will be automatically adjusted: Disables Limiter mode selection, disables the Sculptor module, disables the Unmask module, locks the crossover type in the multiband modules (Compressor 1 & 2, Transient Shaper, Exciter) to the “Zero Latency (Analog)” option.
- Options: Opens the Neutron Options window. See the Options chapter for more information.
- Help: Opens the Neutron help documentation in your default web browser.
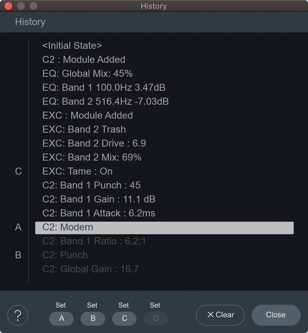
Undo History Controls
The Undo History window allows you to compare controls you’ve adjusted in the current Neutron instance. You can revert settings to audition a specific parameter change by clicking on one of the history list items. The following controls are available in the Undo History window:
| Controls | Description |
|---|---|
| CLEAR | Clears all events from the current history list. |
| CLOSE | Closes the History window. Processing resumes from the point you had last selected, so you can continue building on the History list from an earlier point. |
| SETS | You can assign up to four points in the History list to sets A, B, C, or D. This is useful for comparing a collection of different settings at once. To assign a History item to a Set: Select an item in the history list you want to capture. Click on the A, B, C, or D text labels to assign the selected history item to the button. Click on the assigned A, B, C, or D buttons to quickly toggle between set events in the history list. |
Signal Chain
You can add, rearrange, and move the following modules in the Signal Chain:

Signal chain limitations
Most modules can only be added to the Signal Chain once. If a module has been added to the Signal Chain already, the option in the module list will be greyed out. Only the Compressor module can be added to the Signal Chain twice.
Use the signal chain controls outlined in the table below to customize your Signal Chain.
| Icons | Control | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Add | Click the + button in the Signal Chain to open the module menu. Select a module from the list to add it to the last slot in the Signal Chain. |

|
Power Button | Click the power button the upper left corner of a module tile to bypass processing of that module. |

|
Module Presets | Opens the module preset manager for the associated module. See the Presets chapter for more information. |

|
Remove | Click to remove the associated module from the Signal Chain. |

|
Reorder | Click and drag a module panel left or right within the Signal Chain to change its order in the signal flow. |
|
Wet/Dry Mix | Adjust the slider to balance between the dry (unprocessed) and wet (processed) signals. |
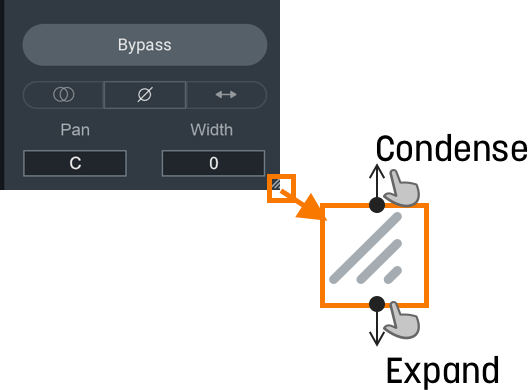
I/O Panel
The I/O (input/output) Panel allows you to monitor levels and adjust gain, stereo width and pan, limiter settings, and channel operations.
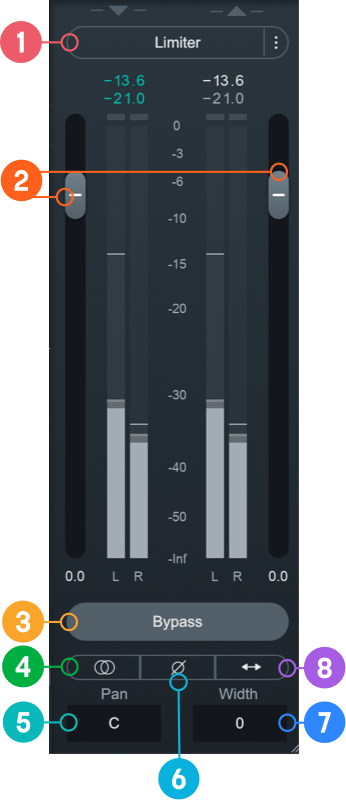
- Limiter: Enable to apply transparent limiting while preserving transients in the output. See Limiter section below for more information.
- Gain (Input/Output): Adjusts the input or output gain. Output gain level comes before the Limiter in the signal flow.
- Bypass: Toggle to either turn processing on (Bypass disabled) or off (Bypass enabled). When you toggle Bypass ON (processing disabled), you will not be able to modify module controls.
- Sum To Mono: Toggle on to sums the left and right channels from the stereo signal into a mono output signal.
- Pan: Pans the output signal to the left or right channel. Only functional in stereo instances of Neutron.
- Invert Phase: Enable to invert the polarity of the signal.
- Width: Adjusts the amount of stereo widening. Decreasing this control results in a narrowing effect (-100% is equivalent to mono), increasing this control widens the apparent stereo field. Only functional in stereo instances of Neutron.
- Swap Channels: Enable to route the left channel to the right channel output and the right channel to the left channel output.
Limiter
Enable to allow the BS.1770-2/3-compliant1 True Peak Limiter to process digital loudness maximization of your output signal while preventing True Peak overflows across all of your mono, stereo, and surround channels.

The limiter comes after the output gain slider in the signal flow. You can use the output gain slider to increase or decrease the level of the signal going into the limiter.
When the limiter is enabled, gain reduction activity is drawn in orange on top of the output meters.
The limiter includes the following controls:
When the Limiter is actively limiting audio, you will see the amount of gain reduction shown in orange from the top of the meter.
Ceiling
Determines the maximum output level of your audio. All peaks above this point will be limited. You can set the Ceiling of the Limiter via the Ceiling slider overlaid on the output meter, within a range of 0 to -20 dB.
There are two ways you can adjust the Ceiling slider:
- Click and drag the Ceiling slider UP or DOWN to the desired value.
- Hover over the Ceiling readout, and click and drag the mouse UP or DOWN to the desired value.
Limiter Style
You can choose from one of three user-definable character options for more direct control over the adaptive, transparent nature of the limiting algorithm.
| Character | Description |
|---|---|
| Clear | The Limiter will respond more quickly in order to better present fast-moving transient material in the mix. |
| Smooth | Smooth is the most common, best-sounding middle ground between Clear and Thick. It’s the most appropriate algorithm for the majority of program material, including most vocals and dialogue. |
| Thick | The Limiter will respond to audio more slowly, useful for louder, slower-moving sounds like a big explosion sound effect, or a bass/low-frequency swell, where you wouldn’t want an aggressive limiter to break the sound up. |
Limiter Mode
You can choose to optimize the Limiter in three different ways using the algorithms described in the table below. Each algorithm has a different sonic quality and latency requirement.
| Limiting Algorithm | Sonic Quality | Latency Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| IRC II | Transparency | Higher latency: 3772 samples at 48 kHz Ensures maximum transparency when hitting the limiter hard, particularly with low frequencies that you’d like to remain loud, without crunch or distortion. |
| IRC LL | Low Latency | Lower Latency: minimum is 120 samples at 48 kHz ensure efficient performance, yet still maintains a high level of sound quality and broadcast-standard True Peak performance. |
| Hard | Brickwall | Zero Latency Most latency-efficient algorithm. Final output level does not exceed the ceiling. Not True Peak compliant due to zero latency. |
NOTE: Low Latency is Important to Consider
Low latency is important to avoid lag or loss of sync when mixing to picture, dealing with limited latency compensation, or a control surface that needs to remain responsive.
Limiter LFE
Appears when Neutron is inserted on a 5.1 or 7.1 surround track. The limiter applies gain reduction equally to all channels when the peak level of any given channel exceeds the Ceiling value. It may be desirable to exclude the LFE channel from triggering gain reduction or from being affected by the limiter.
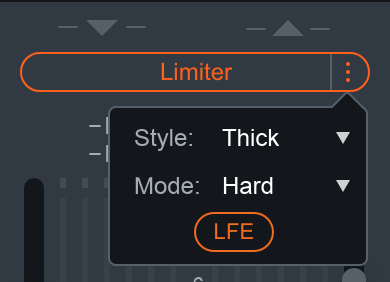
- Enabled: LFE channel is included in limiter input and will be processed by the limiter.
- Disabled: LFE channel is excluded from the limiter input and not affected by limiter gain reduction.
Vocal Unmask Controls
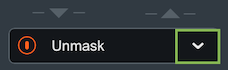
When Neutron is selected in the Vocal Unmask source menu in Nectar and masking is detected by Vocal Assistant, an EQ cut curve will be applied to the output of Neutron to unmask the vocal track. An Unmask control box will appear above the I/O meters in the Neutron interface that is unmasking the vocal track.
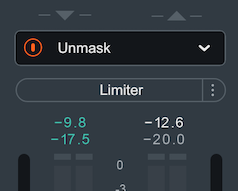
Depending on the edition of Nectar you are using, different Unmask controls will be available in Neutron:
- Using Nectar Standard edition: An Unmask EQ power button will appear in
the Neutron instance that is unmasking the vocal.
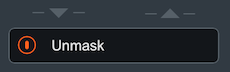
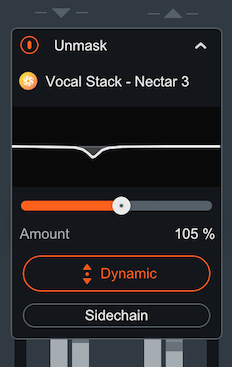
- Using Nectar Plus edition: The Unmask box in Neutron will include a
power button and an expandable advanced controls panel. The Advanced unmask controls panel includes: the
Nectar Plus instance name that Neutron is unmasking, an Unmask EQ curve
display, EQ amount control, Dynamic Unmask EQ on/off, and an external sidechain option when Dynamic mode is
enabled.
I/O Panel Meters
The Input and Output meters display Peak and RMS metering information.
- The current Peak value is displayed in white.
- The current RMS value is displayed in light grey.
The text readouts directly above the meters display the current Peak and RMS values.
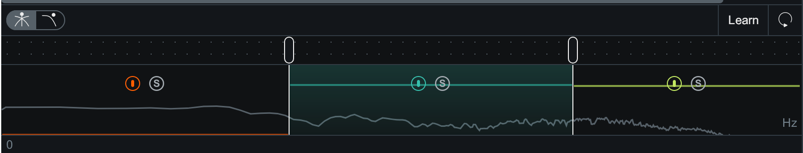
Multiband Crossover Spectrum View
You can use the Multiband Crossover Spectrum View to select, adjust, and audition processing bands in mulitband modules. The following modules include multiband processing: Compressor, Exciter, Gate, and Transient Shaper. Each multiband module supports up to three adjustable processing bands.
| Icons | Control | Description |
|---|---|---|

|
ADD | To add Crossover Cutoff nodes, hover over the Crossover Cutoff node bar and click on the + button that appears. You can add up to 3 crossover regions. |

|
REMOVE | To remove Crossover Cutoff nodes, hover over the band area and click the x button. |

|
POWER BUTTON | Toggle ON/OFF to enable/disable processing for the cutoff section. |

|
SOLO | Enable to hear only the band selected. |
Adjusting Crossover Cutoffs
You can manually adjust the multiband crossover points in the crossover spectrum view using the following methods:
- CLICK & DRAG CUTOFF HANDLES
- Hovering over the crossover handle.
- Left-click and drag the handle left or right to the desired position.
- Use the frequency readout at the bottom of the handle while dragging as a reference to where the crossover point is in relation to frequency.
- ENTER TEXT INPUT
- Double-click on a crossover handle to open the readout as a text edit field.
- Type the desired frequency value for the crossover cutoff into this field.
- Hit the enter or return key to update the value.
NOTE: Crossover cutoff points are per-module
Crossover cutoff points are not shared across multiband modules. Adjusting a crossover point in one module will not affect the crossover points in other multiband modules.
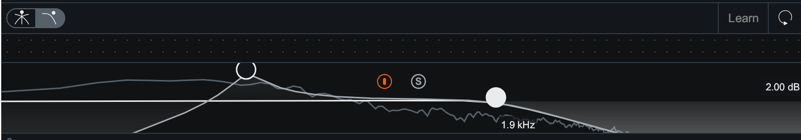
Detection Filter View
Enable the Detection Filter to adjust the frequency response of the detection circuit in the Compressor or Gate modules. When the Detection Filter is active, you can access the controls outlined below.
When enabled, the Detection Filter gives you access to the following controls:
| Icon | Control | Description |
|---|---|---|

|
Power Button | Toggle ON to enable the Sidechain Filter. By default the Detection Filter is OFF. |

|
Solo | Enable to audition the output of the Detection Filter. This can be useful to enable when adjusting the Detection Filter nodes. |
|
Resonant Filter Nodes | Adjusts gain and center frequency in lowpass bands and highpass bands. |
Resonant Filter Node Adjustments
The Resonant Filter Nodes are displayed within the the Detection Filter view. You can use these to tailor your frequency response:
- Click and drag the resonant filter nodes UP or DOWN to increase or decrease gain.
- Click and drag the resonant filter nodes LEFT or RIGHT to adjust the center frequency.
TIP: Compressor Detection Filter
- Making adjustments to the Detection Filter allows you to tailor the sensitivity of the Compressor to different frequencies. This is useful when using the Compressor in single band mode.
- For example: If you want the Compressor to react more to sibilant or harsh frequencies rather than low-frequency content, you can filter out low frequencies using the high-pass filter and boost sibilant frequencies using the resonant low-pass filter to adjust the signal that the Compressor treats as the input signal.
LFE (Low-frequency effects)
The LFE (Low-Frequency Effects) button only appears when Neutron is loaded on 5.1 or 7.1 surround
tracks. LFE For more information on surround sound support, see the Surround Sound section
below.
You can find the LFE button for modules in the module header.

- Enable to include LFE in the audio processing. This is the default setting.
- Disable the LFE button to exclude low frequencies when passing audio through the Low Frequency Effects (LFE) channel with the relative latency compensation.
LFE Rolloff Filter
If you are mixing to a surround sound specification that requires a band-limited LFE signal, the 24 dB/octave LFE rolloff filter helps you achieve this. You can enable the filter and select a cutoff slope value in the Options under the Metering Tab.
NOTE: LFE Rolloff Filter
This option only appears in the Options when Neutron is instantiated on a 5.1 or 7.1 surround track.
Surround Sound
Neutron supports the following surround sound formats in the following hosts. Neutron processes all channels equally unless LFE processing is bypassed in any particular module.
| DAW | Surround Format | Channel Configurations |
|---|---|---|
| Pro Tools | Film | 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 (LCR), 4.0 (Quad), 5.0, 5.1, 7.0, 7.1 |
| Logic Pro | DTS, ITU/SMPTE, SDDS | 1.0, 2.0, 4.0 (Quad), 4.0 (LCRS), 5.1 (ITU/SMPTE) |
| Cubase | ITU/SMPTE | 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 (LRC), 3.0 (LRS), 4.0 (Quad), 4.0 (LCRS), 5.0, 5.1 |
| Nuendo | DTS, ITU/SMPTE, SDDS | 1.0, 2.0, 4.0 (Quad), 4.0 (LRCS), 5.0, 5.1, 7.0 (cine), 7.0 (music), 7.1 (cine), 7.1 (music) |
Surround Sound configuration in Neutron will include LFE button and surround sound meters in the I/O panel as seen in the image below.
