What is a WAN Network?
A Wide Area Network (WAN) connects multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) across different geographical locations. WANs are used to facilitate communication between devices over long distances, such as between cities and countries.
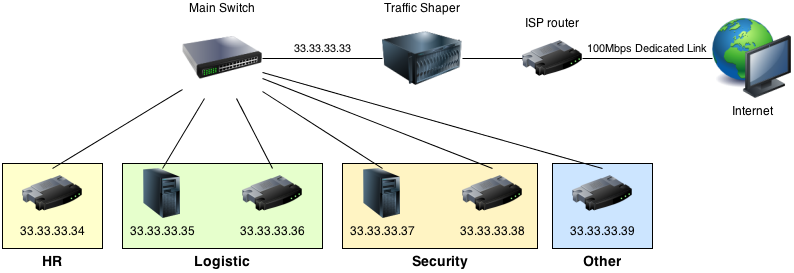
WAN networks are used by organizations to connect geographically dispersed locations, allowing for seamless communication and access to shared resources. This network topology can be integrated with the internet, allowing users to access data and applications from any location with an internet connection.
A WAN network consists of routers, gateways, switches, hubs, and other network elements that are interconnected to provide a high-speed data transfer rate between different nodes. With the help of advanced technologies such as MPLS, VPN, and leased lines, WAN networks provide secure and reliable communication between different locations.
The benefits of WAN networks include improved communication, centralized management, and reduced costs for infrastructure and management. Companies can share resources, information, and applications across multiple locations easily, making it ideal for multinational organizations with large infrastructures.
While setting up a WAN network can be an expensive process, the benefits far outweigh the cost. The implementation of a WAN network reduces the need for physical travel by allowing for virtual meetings, improved communication, shared resources, and access to critical information.
In conclusion, a WAN network is a vital component of modern communication, connecting disparate locations and facilitating communication and collaboration across the global workforce. It is the backbone of modern enterprises, providing seamless access to data and resources, allowing businesses to operate efficiently on a global scale.