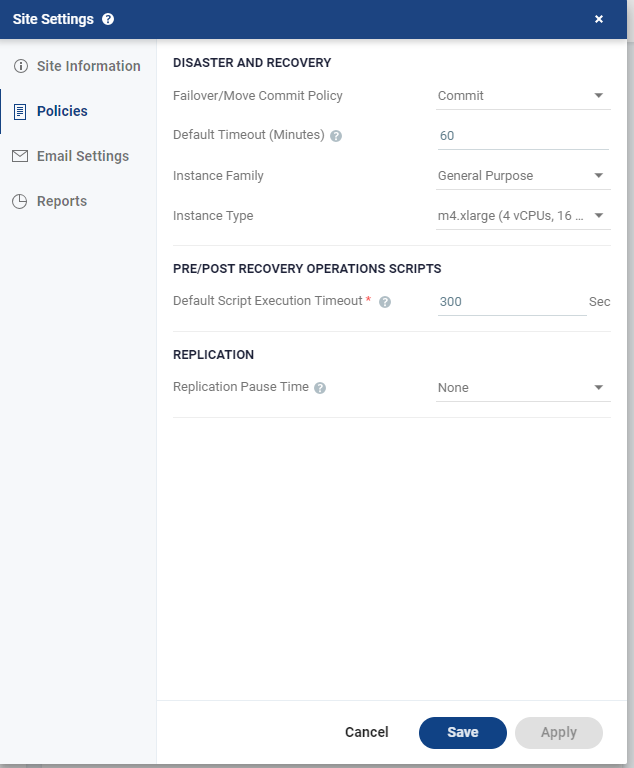
Defining Site Policies
You can set default recovery and replication policies.
Configuring Disaster Recovery Policies
To configure disaster recovery policies:
|
•
|
None: The failover or move operation must be manually committed or rolled back by the user. |
|
•
|
Commit: After the time specified in the Default Timeout field the failover or move operation is committed, unless manually committed or rolled back by the user before the time-out value is reached. During the specified time you can check the recovered VPG virtual machines. |
|
•
|
Rollback: After the time specified in the Default Timeout field the failover or move operation is rolled back, unless manually committed or rolled back by the user before the time-out value is reached. During the specified time you can check the recovered VPG virtual machines. |
The value set here applies as the default for all failover or move operations from this point on but can be changed when defining a failover or move operation.
|
3.
|
Specify the Default Timeout after which a Commit or Rollback commit policy is performed. A value of zero indicates that the system will automatically perform the commit policy, without waiting for any user interaction. |
|
4.
|
In the Pre/Post Recovery Operations Scripts area, specify the timeout in seconds for a script to run before or after a failover, move, or test failover in the Default Script Execution Timeout field. |
For information about scripts, see .
|
5.
|
In the Replication area: |
|
•
|
If the same site is to be used as both the protected and recovery site, select Enable Replication to Self. |
|
•
|
Choose the Replication Pause Time, which is the time to pause when the journal might have problems, resulting in the loss of all checkpoints. For example, when the datastore for the journal is almost full. |
|
•
|
Replication pause time is the amount of time that the transfer of data from the protected site to the journal on the recovery site is paused. |
|
•
|
This time can then be used by the administrator to resolve the issue, for example by cloning the virtual machines in the VPG, described in . |
|
•
|
The value defined here is applied to existing and new VPGs. |
|
•
|
The value defined here is applied to this site only. |
|
•
|
To pause the protection in both directions, for example to cover reverse protection back to the original site after a move operation, you must define Replication Pause Time on both sites. |
|
•
|
To preserve the BIOS UUID of the protected VM after recovery operations, in the recovery ZVM Site Settings window, select For incoming replication, copy the BIOS UUID of the protected VM to the recovered VM. |
|
•
|
Preserving of the BIOS UUID is not supported in Clone and Self-Replication recovery operations. |
|
•
|
Preserving of the BIOS UUID is not supported in Public Cloud. |
|
•
|
Cross replication is not supported. |
|
6.
|
Choose the Instance Family from which to select the type. AWS instance families are optimized for different types of applications. |
|
7.
|
Choose the Instance Type within the instance family, to assign to recovered instances. Different types within an instance family vary primarily in vCPU, ECU, RAM, and local storage size. The price per instance is directly related to the instance size. |
|
8.
|
Specify the Default Script Execution Timeout or a script running before or after the failover, move, or test failover. A value of zero indicates that there is no time out. Values can be between 300 to 6000 seconds. |
|
9.
|
Choose the Replication Pause Time, which is the time to pause when the journal might have problems, resulting in the loss of all checkpoints, for example, when the datastore for the journal is near to being full. |
The replication pause time is the amount of time that the transfer of data from the protected site to the journal on the recovery site is paused. This time can then be used by the administrator to resolve the issue, for example by cloning the virtual machines in the VPG, described in Cloning Protected Virtual Machines to the Remote Site. The value set here is applied to existing and new VPGs.
See also: