K Means Grid Tutorial¶
The purpose of this tutorial is to walk the new user through a K-Means Grid analysis.
Those who have never used H2O before should see the quick start guide for additional instructions on how to run H2O.
Getting Started¶
This tutorial uses a publicly available data set that can be found
Seeds data set http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/seeds
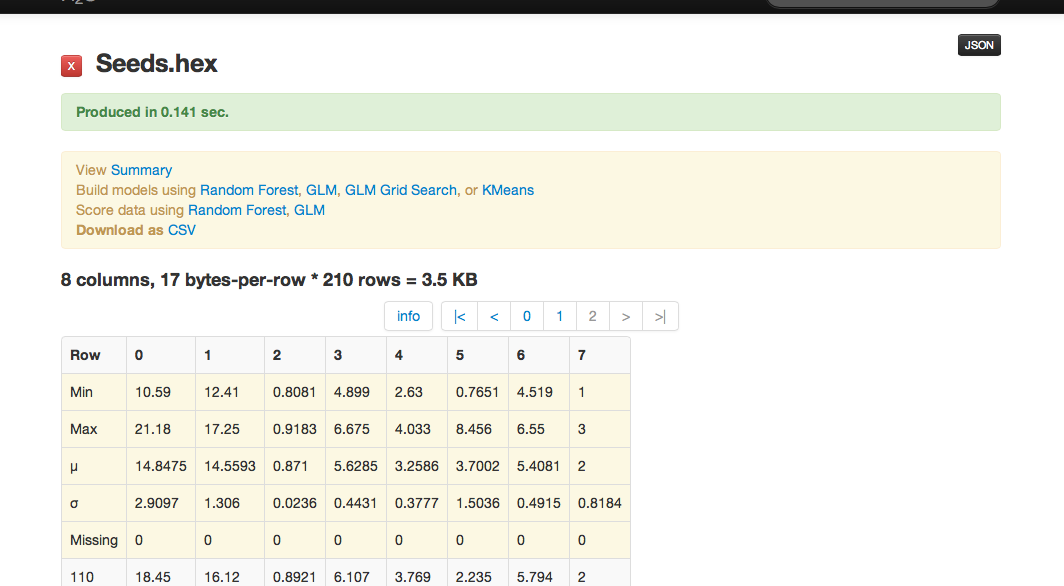
The data are composed of 210 observations, 7 attributes, and an priori grouping assignment. All data are positively valued and continuous. Before modeling, parse data into H2O as follows:
- Under the drop down menu Data select Upload and use the helper to upload data.
- User will be redirected to a page with the header “Request Parse”. Select whether the first row of the data set is a header. All other settings can be left in default. Press Submit.
- Parsing data into H2O generates a .hex key (“data name.hex”).
Building a Model¶
- Once data are parsed a horizontal menu will appear at the top of the screen reading “Build model using ... ”. Select K Means Grid here, or go to the drop down menu Model and select K-Means Grid there.
- In the field for Source Key enter the .hex key associated with the data set.
- Choose K. There is no hard and fast rule for how to do this. K-Means Grid is designed to allow users to examine many different values of K simultaneously. To consider K={2, 5, 10} for this analysis enter 2|5|10 into the K field.
- Note that data can be normalized, though it is not done for this analysis.
- Max iter allows the user to specify the maximum number of iterations the algorithm processes. To consider Max Iterations ={50, 100, 200} for this analysis enter 50|100|200 into the Max Iter field.
- Press submit.
The separator between alternative levels of K and Max Iter is the vertical bar or pipe. On a US keyboard it is found below the delete key on the right hand side of the keyboard by shift + (backslash).
K-Means Grid Output¶
Output is a table displaying basic information about each model generated. Because 3 levels of K, and 3 levels of iteration were requested, there are 9 total models presented in the output. To examine any one of these models click the link in the Model Key field of the table.
Each of the models was produced with the same seed, and each can be reproduced by entering that same seed.
THE END.