Cloning Protected Virtual Machines to the Remote Site
You might want to create a clone if you need to have a copy of the virtual machines saved to a specific point-in-time, for example, when a VPG enters a Replication Paused state, or when testing a VPG in a live DR test.
To clone a VPG:
1. In the Zerto User Interface, in the VPGs tab click the name of the VPG to be cloned.
A new tab is added to the Zerto User Interface, with the name of the VPG that you clicked. The tab displays data about the VPG.
Note: If the VPG was previously viewed, and the tab for this VPG is still displayed, you can access the details by selecting the tab.
2. Select the new tab and click MORE > Offsite Clone.
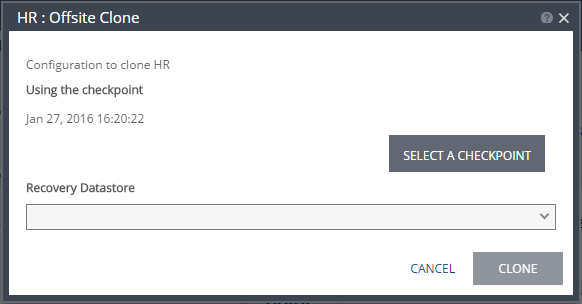
The {VPG-Name}: Offsite Clone dialog is displayed.
3. If you intend to use the last checkpoint, which is displayed in the dialog, go to step
8.
To select the checkpoint, click SELECT A CHECKPOINT.
The {VPG-Name}: Checkpoints dialog is displayed.
When selecting the point to recover to:
■ The refresh button is initially grayed out and is enabled for clicking after 5 seconds. It is also grayed out for 5 seconds after being clicked, before being re-enabled.
■ A Click the refresh button to view the latest checkpoints reminder is displayed 10 seconds after the refresh button is clicked to remind the user that there is a new Latest Checkpoint.
■ If the user has scrolled to, and selected, a checkpoint anywhere in the checkpoints list, clicking the refresh button will automatically return the user to the selected checkpoint in the list.
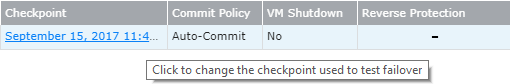
4. Select the checkpoint to use:
5. By default, the last checkpoint added to the journal is displayed in the Checkpoint column
■ To use this checkpoint, proceed to the next step.
■ To change the checkpoint, click the link that appears as the checkpoint.
A window appears, displaying a list of the VPGs’ checkpoints.
Latest: Recovery is to the latest checkpoint. This ensures that the data is crash-consistent for the recovery.
When selecting the latest checkpoint, the checkpoint used is the latest at this point.
If a checkpoint is added between this point and starting the failover, this later checkpoint is not used.
Latest Tagged Checkpoint: The recovery operation is to the latest checkpoint added in one of the following situations:
■ By a user.
■ When a failover test was previously performed on the VPG that includes the virtual machine.
■ When the virtual machine was added to an existing VPG after the added virtual machine was synchronized.
6. To use a checkpoint which is not the latest checkpoint, or the latest tagged checkpoint, choose Select from all available checkpoints. By default, this option displays all checkpoints in the system. You can choose to display only automatic, or tagged checkpoints, or any combination of these types.
7. Click OK.
8. Select the recovery datastore to use for the cloned virtual machines.
Note: All the cloned virtual machines use a single datastore, that is accessible by all the recovery site VRAs used by the VPG. In a vCD environment the datastore is selected from the list of available datastores that is accessible by all the recovery site VRAs and that has the most free space.
9. Click CLONE.
The cloning starts and the status is displayed in the VPG details tab.
The cloned machines are assigned the names of the protected machines with the addition of the timestamp of the checkpoint used for the clone. The cloned virtual machines are not powered on.
When cloning to VMware vSphere environments:
■ The cloned virtual machines are created in the ZertoRecoveryFolder folder, and not the recovery folder defined in the VPG.
■ The cloned virtual machines use a single datastore.
■ The VMDKs are renamed (1).vmdk, (2).vmdk, etc.
■ When the recovery site is VMware vCloud Director, the clone is created in vCenter Server and the virtual machines have to be manually imported into vCD.
■ If the protected virtual machine has RDMs attached, these disks are always cloned as thin-provisioned VMDKs to the datastore specified in the Recovery Datastore field in the Edit VM dialog in the REPLICATION step in the Edit VPG wizard.
When cloning to Microsoft Hyper-V environments:
■ The cloned virtual machines use a single storage.
■ The VHDs are renamed (1).vhdx, (2).vhdx, etc.