Imagine being able to connect multiple devices to a network, seamlessly transferring data from one point to the next with lightning-fast speed. Well, that's exactly what Ethernet network offers.
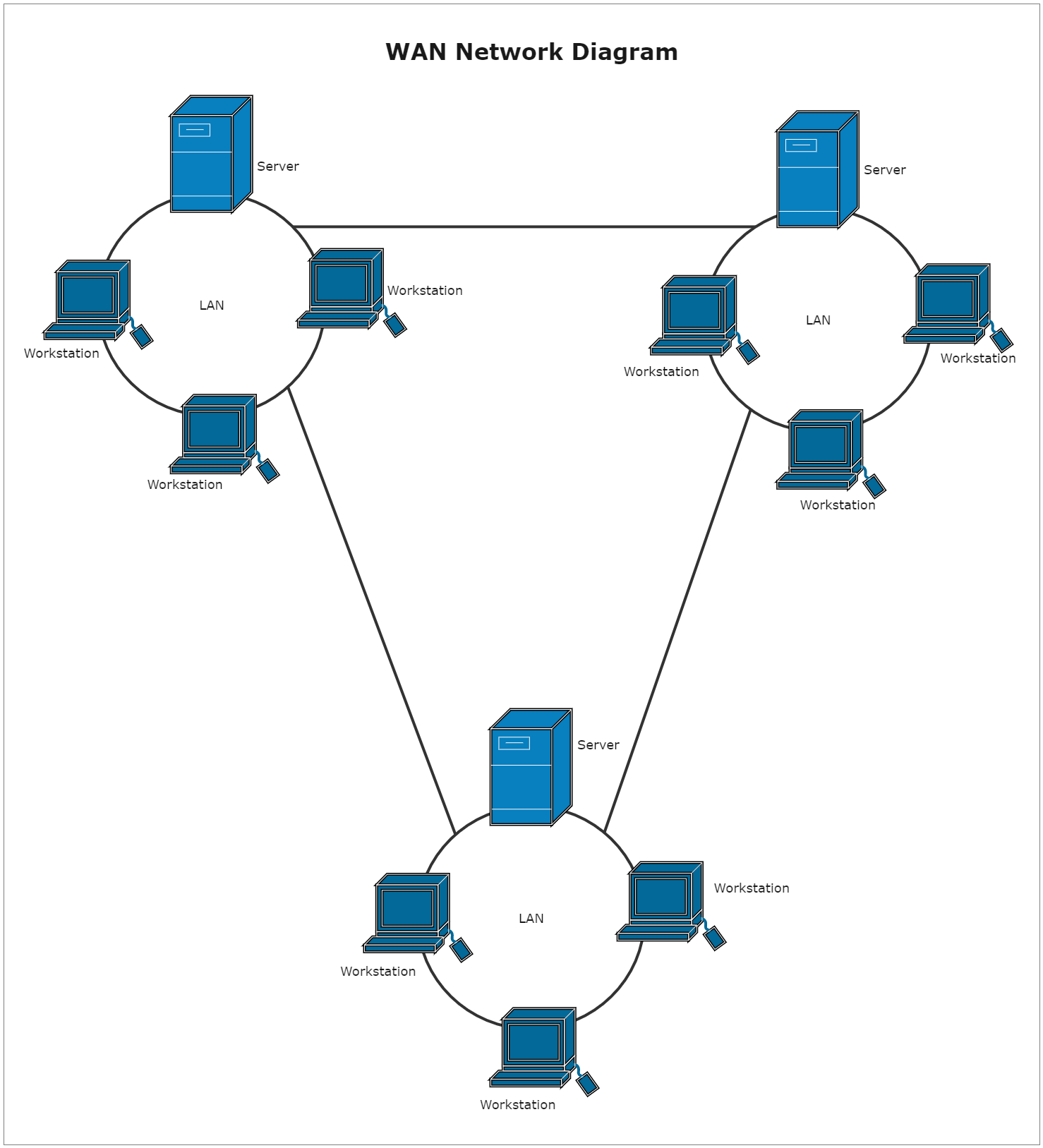
An Ethernet network is a wired network that uses twisted pair cables to transmit data. It is a popular choice for homes and businesses due to its reliability and cost-effectiveness.
History of Ethernet Network
The development of Ethernet network began in the early 1970s at the Xerox's Palo Alto Research Center (PARC). Robert Metcalfe, a research engineer, invented Ethernet network with the aim of connecting computers within a local area network (LAN). In 1983, Ethernet network became the standard protocol for LANs with the release of the Ethernet II specification by Digital, Intel, and Xerox (DIX).
How Ethernet Works
Each device on an Ethernet network has a unique MAC address that identifies it on the network. When a device wants to send data to another device on the network, it broadcasts a message containing the destination MAC address. The message is received by all devices on the network, but only the device with the matching MAC address accepts and processes the message.
Ethernet network supports various speeds, with Gigabit Ethernet being the most common in modern networks. Gigabit Ethernet can transfer data at speeds of up to 1000 megabits per second.
Furthermore, Ethernet network has evolved to support Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology, which enables devices to receive power over the Ethernet cable. This feature is ideal for powering devices like IP cameras, wireless access points, and VoIP phones.
In conclusion, Ethernet network provides a reliable, cost-effective, and easy-to-manage networking solution for homes, businesses, and organizations. Whether you're transferring large files, streaming videos, or powering devices, Ethernet network has got you covered.