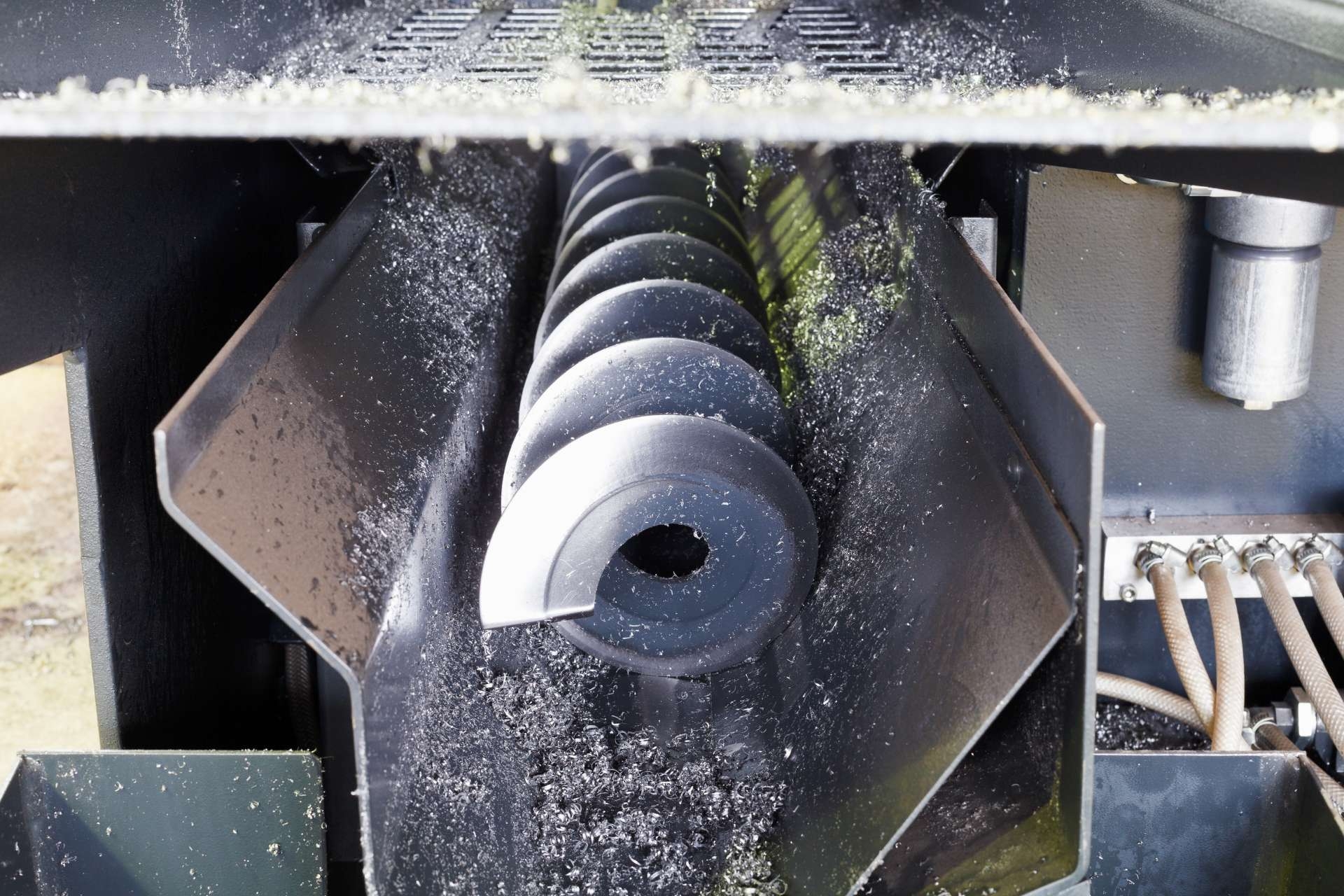


Common corrosive substances that can cause screw pitting include acids, such as hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, as well as saltwater and other chloride-containing solutions. These substances have the ability to react with the metal surface of screws, leading to the formation of pits or small cavities.
Common Issues in Industrial Screws and Barrels and How Professionals Repair Them
The presence of corrosive substances can lead to screw pitting through a process called corrosion. When a corrosive substance comes into contact with a screw's metal surface, it initiates a chemical reaction that causes the metal to deteriorate. This reaction can occur through various mechanisms, such as oxidation or acid attack, which ultimately result in the formation of pits on the screw's surface.
Have you ever tried to install a screw or bolt, only for the threads to become misaligned? A phenomenon known as cross-threading, it’s a serious problem that can leave the fastened parts loose and vulnerable to damage. Threaded fasteners like … Read More The post How to Avoid Cross-Threading Fasteners appeared first on OneMonroe.
Posted by on 2024-03-08
If you’re going to fasten two or more objects together with a machine screw, you should consider using a machine screw nut. Nuts, of course, are used in conjunction with screws and bolts. They feature interior threading that mates with … Read More The post What Are Machine Screw Nuts? appeared first on OneMonroe.
Posted by on 2024-02-16
Toggle wing wall anchor Read More The post Toggle Wing Anchors vs Traditional Wall Anchors: What’s the Difference? appeared first on OneMonroe.
Posted by on 2024-01-22
Nuts are one of the most common types of threaded fasteners. They are typically used in conjunction with a bolt to join two or more parts. Nuts feature internal threading, whereas bolts feature external threading. After driving a bolt through … Read More The post Barrel Nuts vs Traditional Threaded Nuts: What’s the Difference? appeared first on OneMonroe.
Posted by on 2024-01-15
Have you ever tried to remove a screw, only for your screwdriver to spin freely in the screw’s head? Most screws have a recess in the head. You can tighten or loosen them by placing a screwdriver in this recess … Read More The post What Causes Stripped Screws? appeared first on OneMonroe.
Posted by on 2024-01-12
There are several preventive measures that can be taken to avoid screw pitting from corrosive substances. One effective measure is to use corrosion-resistant materials for screws, such as stainless steel or other alloys that have a high resistance to corrosion. Additionally, applying protective coatings or finishes to the screws can provide an extra layer of protection against corrosive substances. Regular maintenance and cleaning of screws, especially in environments where corrosive substances are present, can also help prevent pitting.
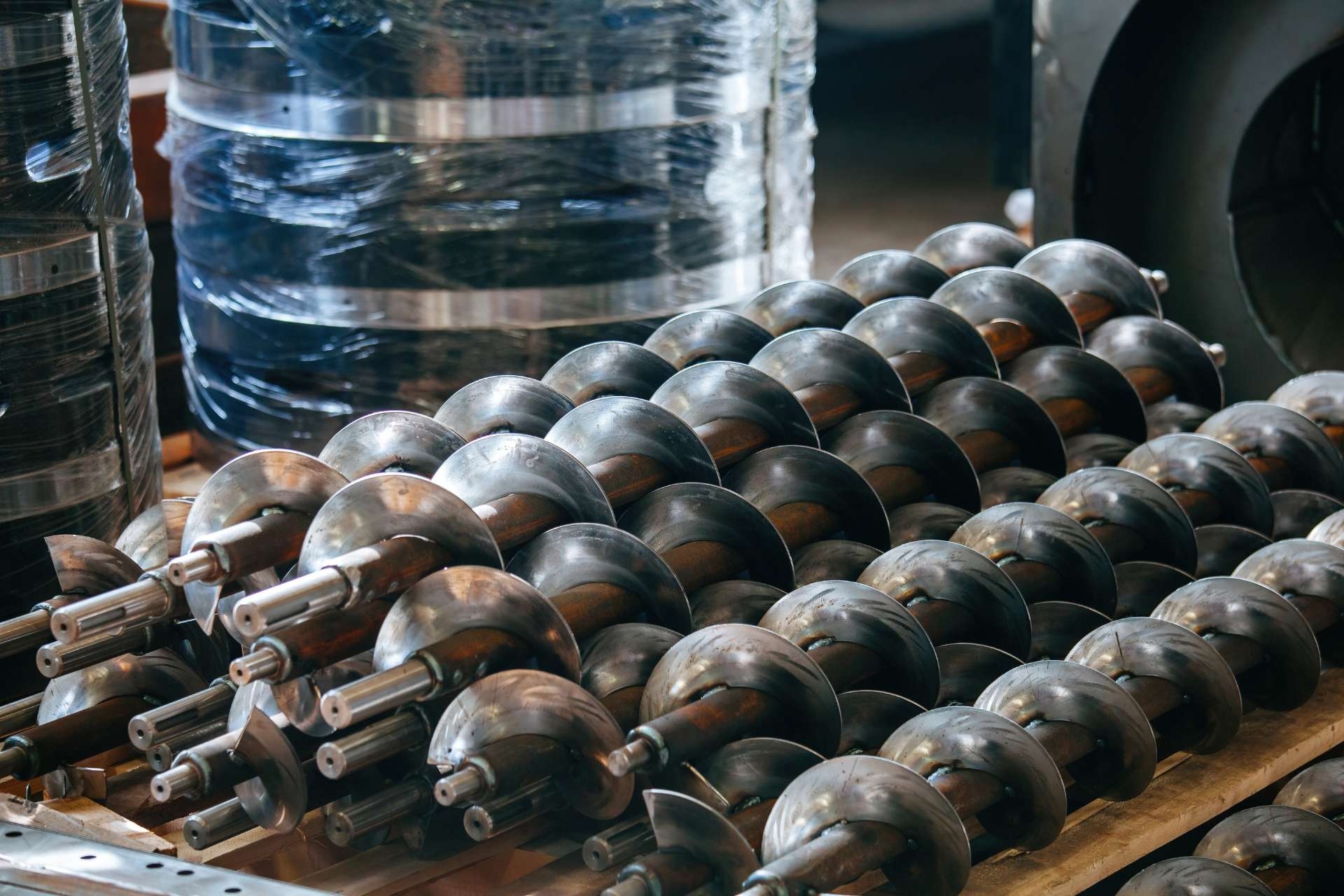

The signs and symptoms of screw pitting caused by corrosive substances can vary depending on the severity of the corrosion. In mild cases, the pitting may appear as small, shallow depressions on the screw's surface. However, in more severe cases, the pitting can become deeper and more extensive, leading to structural weakness and potential failure of the screw. Other signs may include discoloration, roughness, or the presence of rust on the screw's surface.
Unfortunately, screw pitting caused by corrosive substances cannot be repaired or reversed. Once the metal surface of a screw has been pitted, the damage is permanent. However, steps can be taken to prevent further corrosion and minimize the impact of the existing pitting. This may involve replacing the corroded screws with new ones, applying protective coatings, or implementing corrosion control measures in the environment where the screws are used.

Screw pitting from corrosive substances is more common in industries or environments where there is a high exposure to corrosive agents. For example, in industries such as chemical processing, marine, or wastewater treatment, where acids, saltwater, or other corrosive substances are present, the risk of screw pitting is elevated. Similarly, outdoor environments with high humidity or exposure to saltwater, such as coastal areas, can also increase the likelihood of screw pitting.
The long-term effects of screw pitting caused by corrosive substances can be detrimental to the overall performance of screws. Pitting can weaken the structural integrity of screws, making them more susceptible to failure or breakage. This can lead to operational issues, such as loosening or disassembly of components, reduced load-bearing capacity, or compromised safety. Additionally, the presence of pitting can create rough surfaces that promote further corrosion, accelerating the deterioration of the screws over time. Therefore, it is crucial to address screw pitting promptly and implement preventive measures to ensure the longevity and reliability of screws in corrosive environments.
To prevent barrel stress cracking, it is important to observe load thresholds within the recommended range. The load thresholds should be carefully monitored and maintained to ensure that the barrels are not subjected to excessive stress. It is crucial to consider factors such as weight distribution, pressure levels, and material strength when determining the appropriate load thresholds for the barrels. By adhering to these guidelines, the risk of barrel stress cracking can be significantly reduced, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of the barrels and ensuring safe and efficient operation. Additionally, regular inspections and maintenance can help identify any potential issues related to load thresholds and prevent barrel stress cracking from occurring.
Screw cold flow, also known as screw creep, is a phenomenon that occurs when the threads of a screw gradually deform and lose their original shape over time due to the application of external forces. This can be indicated by visible signs such as loosening of the screw, increased friction during rotation, or even complete failure of the screw joint. To mitigate screw cold flow, several measures can be taken. One effective approach is to use screws made from materials with high resistance to creep, such as stainless steel or titanium. Additionally, applying lubricants or coatings to the screw threads can help reduce friction and minimize the risk of cold flow. It is also important to ensure that the screws are properly tightened to the recommended torque specifications, as over-tightening can accelerate cold flow. Regular inspection and maintenance of the screw joints can help identify any signs of cold flow early on and take appropriate corrective actions.
To prevent screw wear from aggressive additives, it is crucial to implement effective preventive measures. One approach is to utilize protective coatings or surface treatments that can enhance the screw's resistance to wear. These coatings may include materials such as ceramic, carbide, or nitride, which possess high hardness and durability. Additionally, employing lubricants or additives specifically designed to mitigate the detrimental effects of aggressive substances can significantly reduce wear. These lubricants should possess properties like high viscosity, anti-wear additives, and corrosion inhibitors to provide optimal protection. Regular maintenance and inspection of the screws are also essential to identify any signs of wear or damage early on, allowing for timely repairs or replacements. By implementing these preventive strategies, the detrimental effects of aggressive additives on screw wear can be effectively minimized.
Proper maintenance procedures can significantly reduce screw wear caused by improper alignment. One effective method is to regularly inspect the alignment of the screw and its corresponding components, such as the nut or threaded hole. This can be done by using precision measuring tools to ensure that the screw is properly aligned and seated. Additionally, lubrication plays a crucial role in reducing wear. Applying a suitable lubricant to the screw and its mating surfaces can minimize friction and prevent excessive wear. Furthermore, implementing preventive maintenance practices, such as tightening loose screws and replacing worn-out components, can help maintain proper alignment and prolong the lifespan of the screw. By adhering to these maintenance procedures, the risk of screw wear from improper alignment can be significantly mitigated.
In harsh environments, certain materials exhibit resistance to corrosion. These materials include stainless steel, which is known for its high resistance to corrosion due to the presence of chromium and other alloying elements. Additionally, titanium alloys are highly resistant to corrosion in harsh environments, thanks to their protective oxide layer. Another material that demonstrates corrosion resistance is nickel-based alloys, which possess excellent resistance to both oxidizing and reducing environments. Furthermore, ceramics such as alumina and zirconia exhibit exceptional resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for use in harsh environments. Lastly, certain polymers like polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and polyethylene (PE) are also resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for applications in harsh environments.
Improper alignment can lead to screw wear, but there are several measures that can be taken to prevent this issue. Firstly, it is crucial to ensure accurate alignment during the installation process. This can be achieved by using precision tools and following the manufacturer's guidelines. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspections should be conducted to identify any misalignment and address it promptly. Utilizing alignment aids such as shims or spacers can also help maintain proper alignment. Furthermore, employing lubricants specifically designed for screw applications can reduce friction and minimize wear. Lastly, educating and training personnel on proper alignment techniques and the importance of maintaining alignment can contribute to preventing screw wear caused by improper alignment.