

Barrel scaling in chemical reactions occurs when unwanted deposits or build-up form on the inner walls of a reaction vessel, resembling the appearance of scales on a barrel. This scaling can occur due to various factors such as the presence of impurities in the reactants, the temperature and pressure conditions of the reaction, and the nature of the chemical reaction itself. The formation of barrel scaling can hinder the efficiency of the reaction and may even lead to equipment damage if left unaddressed.
Several factors contribute to barrel scaling in chemical reactions. One of the main factors is the presence of impurities in the reactants or the reaction vessel. These impurities can react with the chemicals involved in the reaction, leading to the formation of solid deposits on the inner walls of the vessel. Additionally, the temperature and pressure conditions of the reaction can also influence barrel scaling. Higher temperatures can accelerate the formation of scales, while higher pressures can promote the deposition of solid particles. The nature of the chemical reaction, such as the types of reactants and the reaction kinetics, can also play a role in barrel scaling.
Have you ever tried to install a screw or bolt, only for the threads to become misaligned? A phenomenon known as cross-threading, it’s a serious problem that can leave the fastened parts loose and vulnerable to damage. Threaded fasteners like … Read More The post How to Avoid Cross-Threading Fasteners appeared first on OneMonroe.
Posted by on 2024-03-08
If you’re going to fasten two or more objects together with a machine screw, you should consider using a machine screw nut. Nuts, of course, are used in conjunction with screws and bolts. They feature interior threading that mates with … Read More The post What Are Machine Screw Nuts? appeared first on OneMonroe.
Posted by on 2024-02-16
Toggle wing wall anchor Read More The post Toggle Wing Anchors vs Traditional Wall Anchors: What’s the Difference? appeared first on OneMonroe.
Posted by on 2024-01-22
Nuts are one of the most common types of threaded fasteners. They are typically used in conjunction with a bolt to join two or more parts. Nuts feature internal threading, whereas bolts feature external threading. After driving a bolt through … Read More The post Barrel Nuts vs Traditional Threaded Nuts: What’s the Difference? appeared first on OneMonroe.
Posted by on 2024-01-15
Have you ever tried to remove a screw, only for your screwdriver to spin freely in the screw’s head? Most screws have a recess in the head. You can tighten or loosen them by placing a screwdriver in this recess … Read More The post What Causes Stripped Screws? appeared first on OneMonroe.
Posted by on 2024-01-12
While it may not be possible to completely prevent barrel scaling in chemical reactions, there are measures that can be taken to minimize its occurrence. One approach is to ensure the purity of the reactants and the reaction vessel by using high-quality materials and conducting thorough purification processes. Controlling the temperature and pressure conditions within optimal ranges can also help reduce scaling. Additionally, regular cleaning and maintenance of the reaction vessel can help remove any existing scales and prevent their further accumulation.
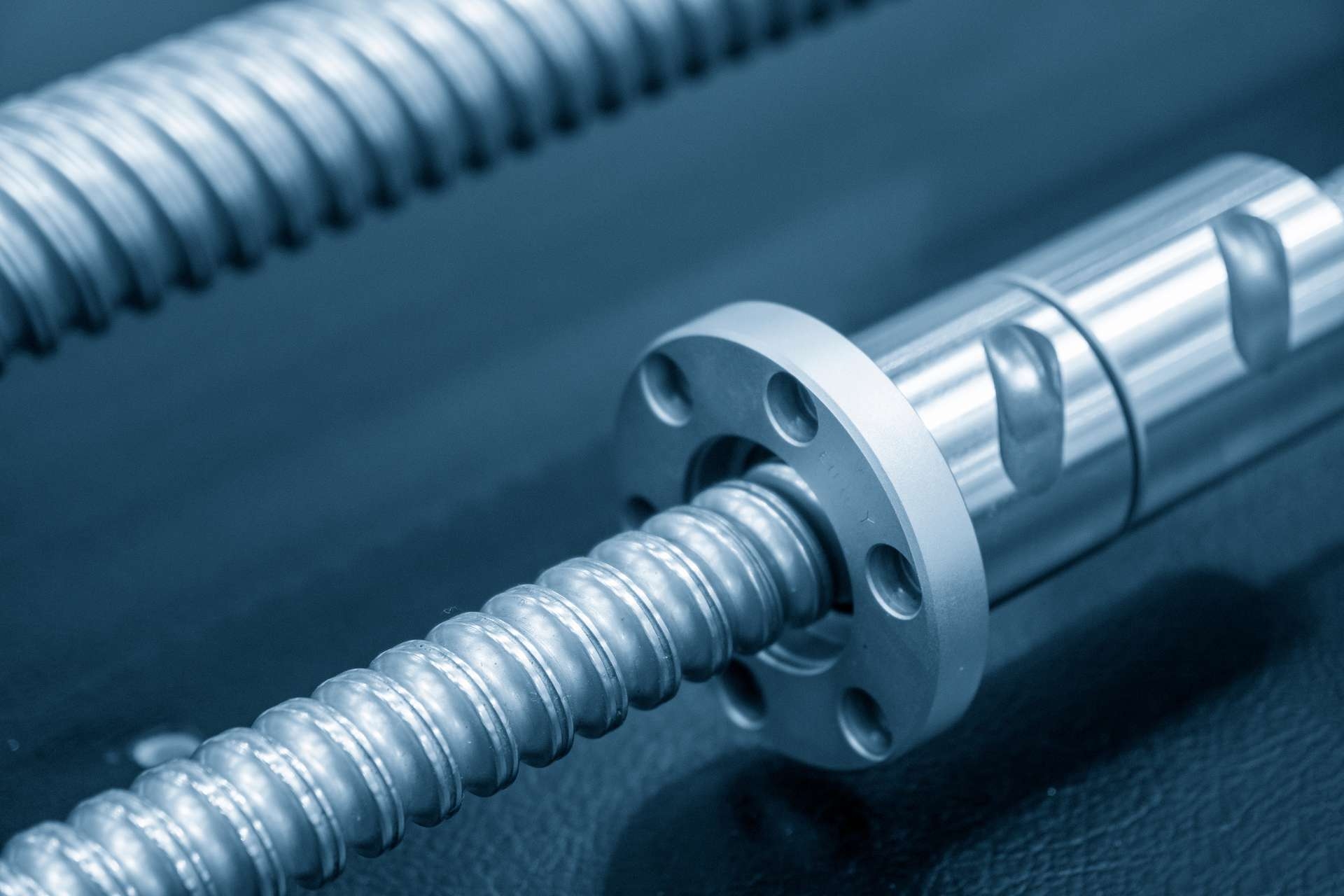
The consequences of barrel scaling in chemical reactions can be significant. Firstly, it can lead to a decrease in the efficiency of the reaction, as the presence of scales can hinder the contact between the reactants and the reaction vessel, slowing down the reaction rate. This can result in longer reaction times and lower yields of the desired products. Furthermore, barrel scaling can also cause equipment damage, as the build-up of solid deposits can lead to clogging, corrosion, or even structural integrity issues in the reaction vessel. These consequences can result in increased costs, decreased productivity, and potential safety hazards.
While barrel scaling can occur in various types of chemical reactions, certain reactions are more prone to this phenomenon. Reactions involving substances that have a tendency to form solid precipitates or insoluble products are more likely to experience barrel scaling. For example, reactions involving metal ions that can form insoluble salts or reactions that produce solid byproducts can be particularly susceptible to scaling. Additionally, reactions that require high temperatures or pressures, such as those involving catalytic processes, can also be more prone to scaling due to the increased likelihood of solid deposition.

Temperature plays a significant role in barrel scaling in chemical reactions. Higher temperatures can accelerate the formation of scales by increasing the rate of chemical reactions and promoting the deposition of solid particles. This is because higher temperatures provide more energy for the reactant molecules to collide and react, leading to the formation of more solid products. Additionally, elevated temperatures can also affect the solubility of certain substances, causing them to become less soluble and more likely to precipitate out of solution, contributing to barrel scaling.
There are methods and techniques available to remove barrel scaling in chemical reactions. One common approach is to use cleaning agents or solvents that can dissolve or remove the scales from the inner walls of the reaction vessel. These cleaning agents can be selected based on the nature of the scales and the materials of the reaction vessel to ensure effective removal without causing damage. Mechanical methods, such as scrubbing or scraping, can also be employed to physically remove the scales. In some cases, it may be necessary to disassemble and clean the reaction vessel thoroughly. Regular maintenance and cleaning practices can help prevent the build-up of scales and ensure the smooth operation of chemical reactions.
Common Issues in Industrial Screws and Barrels and How Professionals Repair Them

The best methods for removing abrasive fillers to prevent erosion include mechanical methods such as scraping, grinding, and sandblasting, as well as chemical methods like using solvents or acids to dissolve the fillers. Additionally, thermal methods such as heat treatment or burning can also be effective in removing abrasive fillers. It is important to consider the specific type of filler being removed and the surface it is adhered to when choosing the most appropriate method. Proper protective equipment and safety measures should be used when employing these methods to prevent any potential hazards. Regular maintenance and inspection of surfaces can also help identify and address any potential erosion caused by abrasive fillers.
To prevent barrel corrosion when processing acidic materials, it is crucial to implement effective corrosion prevention measures. Firstly, selecting the appropriate barrel material is essential. Opting for corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel, titanium, or high-density polyethylene (HDPE) can significantly reduce the risk of corrosion. Additionally, applying protective coatings or linings to the barrel's interior can provide an extra layer of defense against acidic substances. Regular inspection and maintenance of the barrels are also vital to identify any signs of corrosion early on and take necessary corrective actions. Implementing proper cleaning procedures, including thorough rinsing and drying after each use, can help remove any residual acidic materials that may contribute to corrosion. Furthermore, monitoring and controlling the pH levels of the processed materials can aid in preventing excessive acidity that could accelerate corrosion. Overall, a comprehensive approach that combines appropriate material selection, protective coatings, regular maintenance, and pH monitoring can effectively prevent barrel corrosion when processing acidic materials.
Barrels that are exposed to chemicals require materials that are corrosion-resistant to prevent damage and ensure longevity. Some of the most effective materials for this purpose include stainless steel, titanium, and high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Stainless steel is a popular choice due to its high resistance to corrosion and its ability to withstand high temperatures. Titanium is also a strong option as it is highly resistant to corrosion and is lightweight, making it ideal for transportation purposes. HDPE is a plastic material that is resistant to chemicals and is often used in the manufacturing of barrels for the storage of hazardous materials. Other materials that may be used include aluminum, fiberglass, and epoxy-coated steel, depending on the specific chemical exposure and the intended use of the barrel.
To minimize screw wear from high-temperature polymers, several strategies can be employed. Firstly, selecting a screw material with high resistance to wear and heat is crucial. Materials such as hardened steel or alloys like titanium can be considered. Additionally, using specialized coatings on the screw surface, such as ceramic or diamond-like carbon coatings, can provide an extra layer of protection against wear. It is also important to optimize the design of the screw, considering factors like the flight depth, pitch, and compression ratio, to ensure efficient polymer processing while minimizing wear. Regular maintenance and cleaning of the screw, as well as monitoring the temperature and pressure during operation, can help identify any potential issues and prevent excessive wear.