Replication From a Protected Site vCD to Azure
You can protect a vCD vApp to Microsoft Azure.
When creating a VPG from vCloud Director to Azure the data is stored in a storage account and all replicated data from protected virtual machines to Azure is encrypted in the storage account. All recovery operations bring up the recovered machines in resource groups in Azure.
■ Azure ZCA can be installed only on Windows Server 2012 R2 and higher.
■ Only virtual machines that are supported by Azure can be protected by Zerto Virtual Replication. All Windows operating systems are supported.
Note: Microsoft does not support operating systems that are past the
End of Support date, without a
Custom Support Agreement (CSA). For more information about Microsoft operating systems support for Microsoft Azure, refer to
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/2721672.
■ To replicate between Azure and your site, you must have a virtual machine in Azure with a Zerto Cloud Appliance installed on it. This ZCA must be paired with your site.
■ For Linux distribution, refer to Azure documentation:
Requirements for Replication From Azure
■ For Virtual Machines to be protected from Azure, the VM volumes must reside in the Standard storage account defined during ZCA installation.
A Standard storage account is created or selected upon ZCA installation.
■ Type: Standard storage
■ Recovery and journal volumes reside on this Zerto Storage Account
■ Azure VMs with all disks on this Zerto Storage Account can be protected by Zerto.
■ Blob Storage is not supported.
■ Managed Disks are not supported.
■ VMs which are not deployed via the Azure Resource Manager cannot be protected from Azure.
Requirements for Replication To Azure
■ Protected volumes are recovered in Azure as VHD disks in a page blob. Virtual machines with disks that are less than 1GB are recovered with disks of 1GB.
Note: For some instance sizes, the Azure virtual machine is created with a Local SSD disk which is a temporary disk. This disk is in addition to the disks associated with each protected virtual machine.
■ The following limitations apply when protecting to Azure
■ Virtual machines with UEFI Firmware cannot be protected.
■ You cannot protect machines that have a disk larger than 4 TB.
■ The protected virtual machines needs to have at least one NIC.
■ Reserve at least 2 CPUs and 4GB RAM for the machine using a subnet accessible by other Zerto Virtual Replication sites.
■ The supported number of data disks and NICS per virtual machine is dependent on the selected instance size. For example, instance size D3_v2 allows up to eight data disks per virtual machine.
Requirements for Replication within Azure
■ Azure ZCA on both Azure sites need to be version 6.0 and higher.
■ The following limitations apply when protecting within Azure:
■ Self replication is not supported.
Additional Azure Considerations
For additional considerations, see
Azure subscription and service limits, quotas and constraints:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-subscription-service-limits.For example from the link, see the following default values:
■ There can be multiple Zerto Cloud Appliances per Azure subscription and region.
■ 20 cores per subscription
■ 200 Storage accounts per subscription
■ 20 VMs per region per subscription
■ 20 VMs per series (Dv2, F, etc.) cores per subscription per Region
Additionally, see the following example for maximum values:
■ A Standard storage account has a maximum total request rate of 20,000 IOPS. The total IOPS across all of your virtual machine disks in a Standard storage account should not exceed this limit.
VM Tier | Basic Tier VM | Standard Tier VM |
Disk size | 4 TB | 4 TB |
Max 8 KB IOPS per persistent disk | 300 | 500 |
Max number of disks performing max IOPS | 66 | 50 |
Azure Limitations Which Affect Installation and Recoverability
Below are the default Azure limitations which affect installation and recovery.
Default Azure limitations which Affect Installation
■ Storage Limitations:
■ Number of storage accounts: 200 per subscription (note: max is 250)
Default Azure Limitations which Affect Recovery
Virtual Machines Limitations | VMs per subscription per region: | 20 (max: 10K) |
VM total cores per subscription per region: | 20 |
Instance sizes: | Limited per region. Many of them are 20 cores per region per subscription |
Resource groups per subscription: | 800 |
Networking | Network interfaces per region: | 350 |
NICs per instance: | Depends on instance size: |
Private IP Addresses per VNET per subscription per region: | 4096 |
Cloning of IP addresses during recovery operations: | Due to an Azure limitation, failing over Linux VMs with static IP is not supported. |
Storage | Storage account total size limitation: | 500 TB (# of entities (blobs, containers etc) within a storage account: unlimited) |
Max size of a page blob (vhd): | 4 TB |
Min size of a page blob (vhd): | 20 MB |
Max number of data disks: | Depends on instance size |
To create a VPG from vCloud Director to Azure:
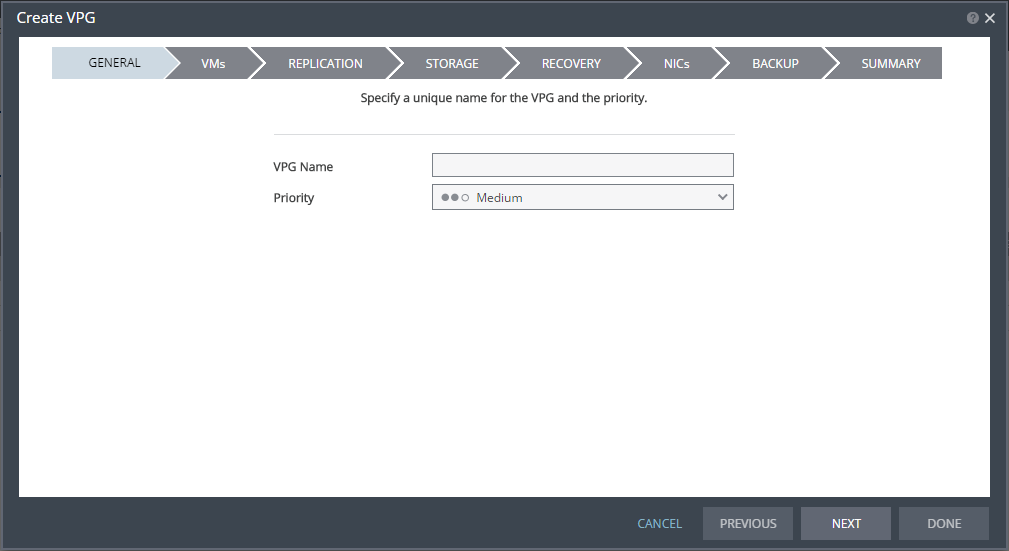
1. In the Zerto User Interface, select ACTIONS > CREATE VPG.
The GENERAL step of the Create VPG wizard is displayed.
2. Specify the name of the VPG and the priority of the VPG.
■ VPG Name: The VPG name must be unique. The name cannot be more than 80 characters.
■ Priority: Determine the priority for transferring data from the protected site to the recovery site when there is limited bandwidth and more than one VPG is defined on the protected site.
■ High Priority: When there are updates to virtual machines protected in VPGs with different priorities, updates from the VPG with the highest priority are passed over the WAN first.
■ Medium Priority: Medium priority VPGs will only be able to use whatever bandwidth is left after the high priority VPGs have used it.
■ Low Priority: Low priority VPGs will use whatever bandwidth is left after the medium priority VPGs have use it.
Updates to the protected virtual machines are always sent across the WAN before synchronization data, such as during a bitmap or delta sync.
During synchronization, data from the VPG with the highest priority is passed over the WAN before data from medium and low priority VPGs.
3. Click NEXT.
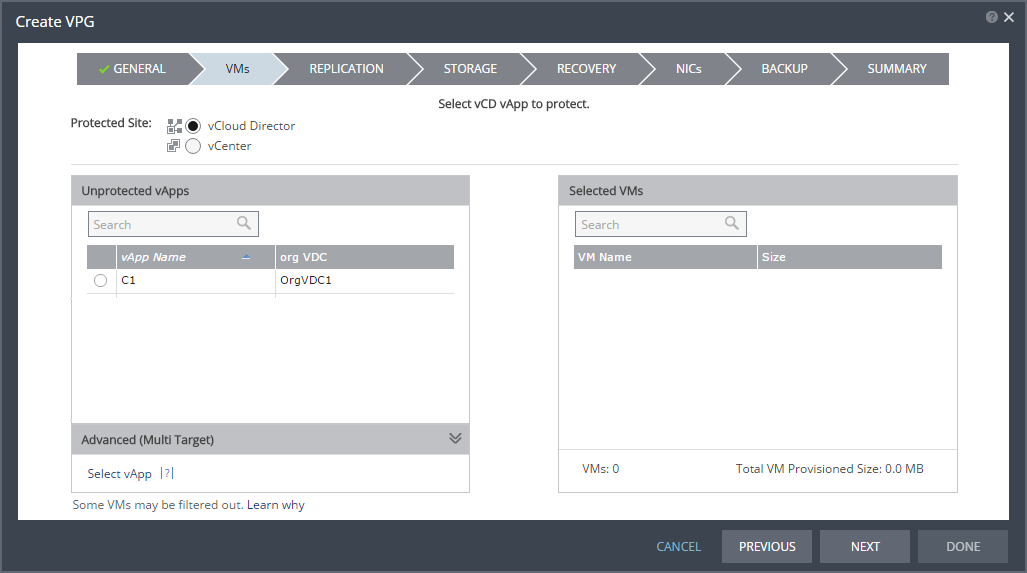
The VMs step is displayed.
You can select virtual machines to protect from the underlying vCenter Server or as a vCD vApp.
4. Select the vCD vApp to protect in this VPG.
■ When using the Search field, you can use the wildcards; * or ?.
■ Only vCD vApps that are unprotected are displayed in the list. A VPG can include:
■ Only one vApp.
■ vApps that are not yet protected.
■ vApps that are already protected.
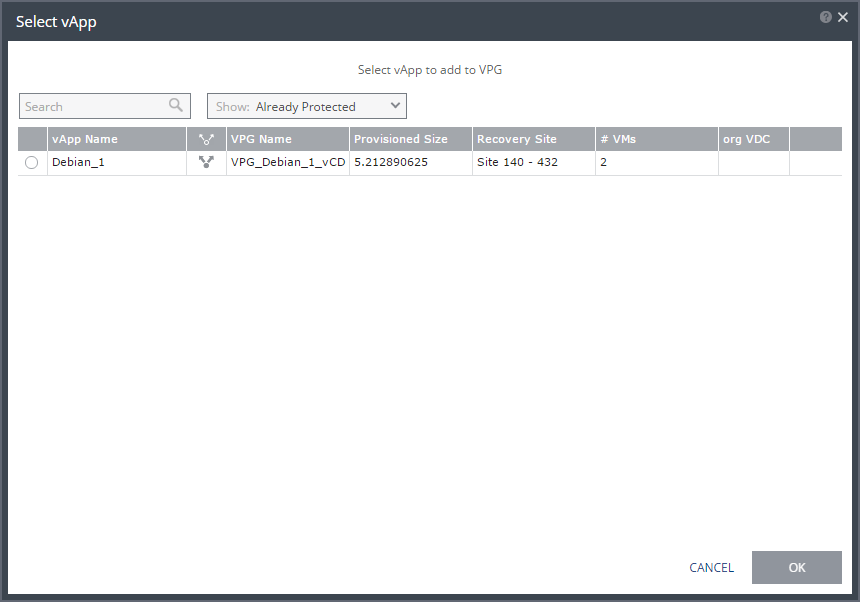
5. To view protected vApps, in the Advanced (One-to-Many) section, click Select vApp.
The Select vApp window is displayed.
Note: With the One-to-Many feature, a VPG containing a single vApp can be recovered to a maximum of three different sites and cannot be recovered to the same site more than once.
vApps protected in the maximum number of VPGs are not displayed in the Select VMs window.
Protecting vApps in several VPGs is enabled only if both the protected and recovery sites, and the VRAs installed on these sites, are of version 5.0 and higher.
Note: Define the required boot order for vCD vApps in the vCloud Director console.
6. Click NEXT.
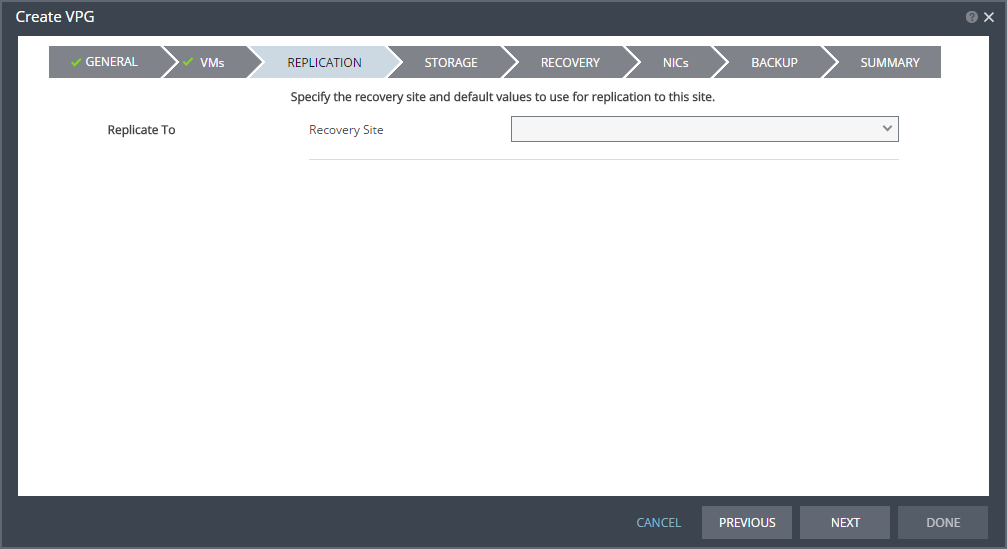
The REPLICATION step is displayed.
Note: If the protected site is paired with only one recovery site, the recovery step is displayed with the Recovery Site field automatically filled in and defaults set, as shown below.
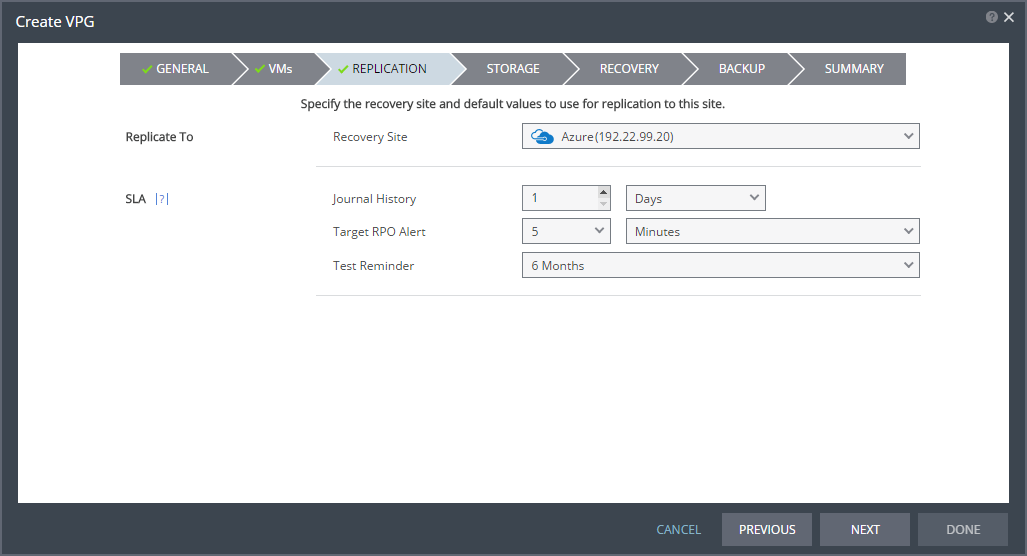
7. Specify the Recovery Site. This is the site to which you want to recover the virtual machines. After specifying the recovery site, other fields are displayed.
Note: Steps that do not require input are marked with a check mark. You can jump directly to a step that has been marked with a check mark to edit the values for that step. Every step must be marked with a check mark before you can click DONE to create the VPG.
You cannot select a recovery site if any of the virtual machines you selected are already in VPGs that recover to that site.
8. ZORG: If the site is defined in Zerto Cloud Manager, select the name used by the cloud service provider (CSP) to identify you as a Zerto Organization (ZORG). For details about Zerto Cloud Manager, see Zerto Cloud Manager Administration Guide.
9. When the Zerto Cloud Manager is used, select the service profile.
■ Service Profile – The name of the service profile to use which determines the VPG SLA settings for the group, which apply to every virtual machine in the group. To change the VPG SLA settings, select the Custom Service Profile.
10. If the VPG SLA settings are editable, when the Zerto Cloud Manager is not used or when a Custom service profile is available, specify these settings for the group, which apply to every virtual machine in the group.
■ Journal History: The time that all write commands are saved in the journal.
The longer the information is saved in the journal, the more space is required for each journal in the VPG.
Select the number of hours from 1 to 24 or the number of days from 2 to 30.
11. Target RPO Alert: The maximum desired time between each automatic checkpoint write to the journal before an alert is issued.
12. Test Reminder: The amount of time in months recommended between each test, where you test the integrity of the VPG. A warning is issued if a test is not performed within this time frame.
Click NEXT.
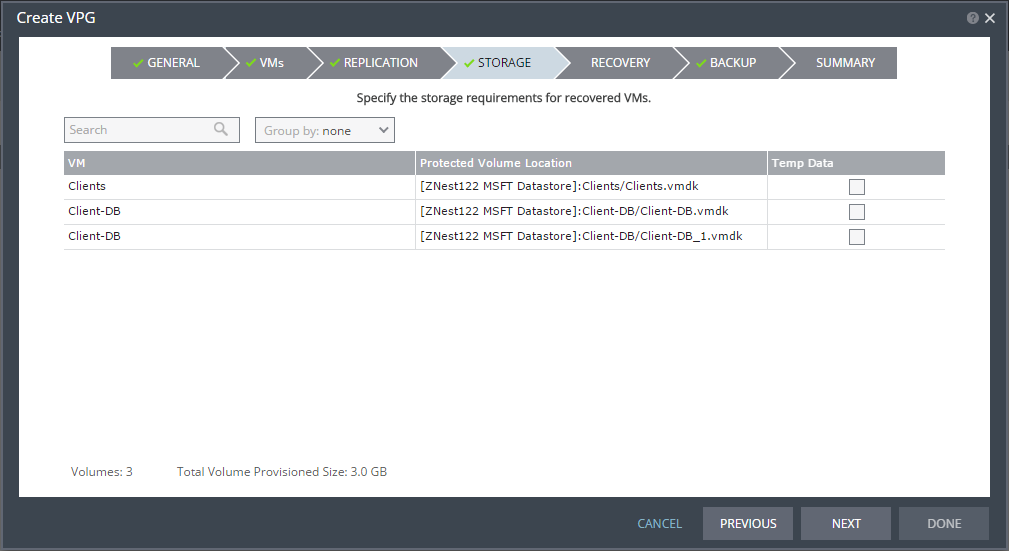
The STORAGE step is displayed.
By default the storage used for the virtual machine definition is also used for the virtual machine data.
For each virtual machine in the VPG, Zerto Virtual Replication displays its storage-related information.
13. Specify whether the protected volume is a temp data disk.
Temp Data: If the virtual machine to be replicated includes a temp data disk as part of its configuration, mark the recovery disk for this disk as a temp data disk. In this case, data is not replicated to the temp data disk after initial synchronization.
14. Click NEXT.
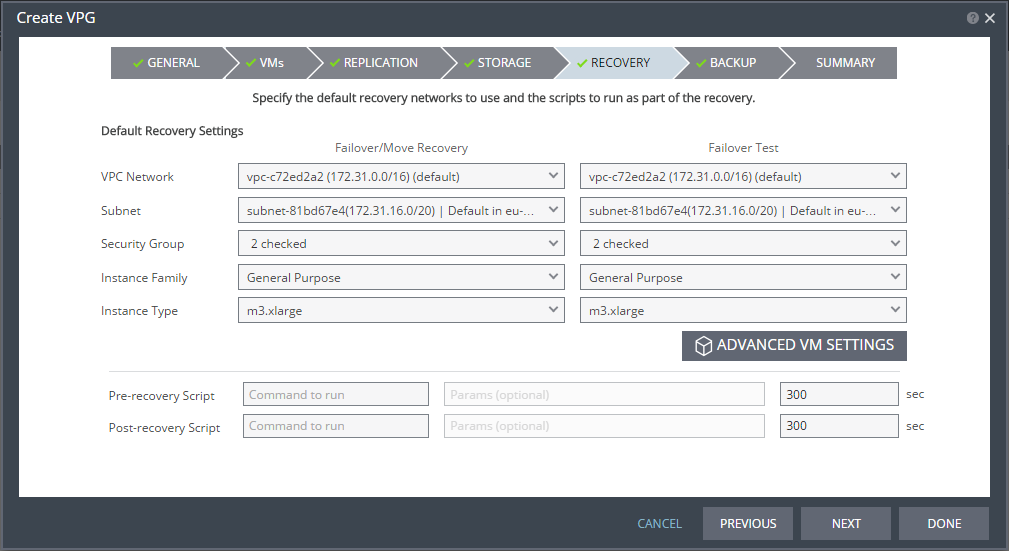
The RECOVERY step is displayed. Recovery details include the networks, network security group, instance family, and instance size to use for failover, move, and testing failover, and whether scripts should run as part of the recovery process.
Note: Steps that do not require input are marked with a check mark. You can jump directly to a step that has been marked with a check mark to edit the values for that step. Every step must be marked with a check mark before you can click DONE to create the VPG.
15. Select recovery settings for failover/move and failover testing.
■ VNet: The virtual network dedicated to your Azure subscription.
■ Subnet: The subnet or the VNet network.
■ Network Security Group: The Azure network security to be associated with the virtual machines in this VPG. You can associate one network security group with the virtual machines. The NIC will be associated with the network security group defined at the virtual machine level.
■ Virtual Machine Series: The virtual machine series from which to select the size. Azure virtual machine series are optimized for different types of applications. The default is set to Dv2-series.You can choose the virtual machine series appropriate for the application being protected in the VPG.
■ Virtual Machine Size: The virtual machine size, within the virtual machine series, to assign to recovered virtual machines. Different sizes within a virtual machine series vary, for example in a number of cores, RAM, and local storage size. The default is set to Standard_D1_v2.You can choose the virtual machine size appropriate for the application being protected in the VPG. The price per virtual machine is related to the virtual machine configuration.
16. For additional settings, click ADVANCED VM SETTINGS.
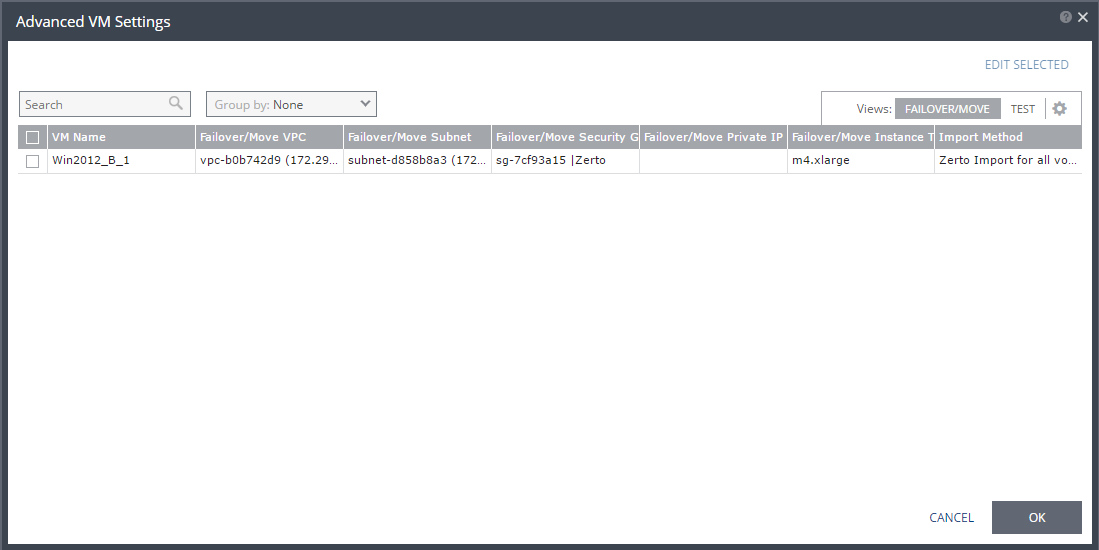
The Advanced VM Settings window is displayed, which shows the recovery network settings for FAILOVER/MOVE for virtual machines in the VPG. You can see the recovery network settings for failover tests by clicking TEST.
17. To edit information in one field, click the field and update the information.
18. To edit information for several virtual machines at the same time, select the virtual machines and click EDIT SELECTED.
The Edit VM Network window is displayed.
19. Update the values for VNet, subnet, security group, instance family, instance size, and private IP as necessary.
Note: Only private IPs specified for Windows machines are assigned during a recovery operation. For Linux machines, the IP is assigned from the specified subnet range.
Clearing the values in the Private IP field results in an IP being automatically assigned from the subnet range during a recovery operation.
Refer to the
Zerto Virtual Replication Interoperability Matrix for the list of operating systems for which Zerto supports re-IP.
20. Click OK twice to return to the main page of the RECOVERY step.
21. Click NEXT.
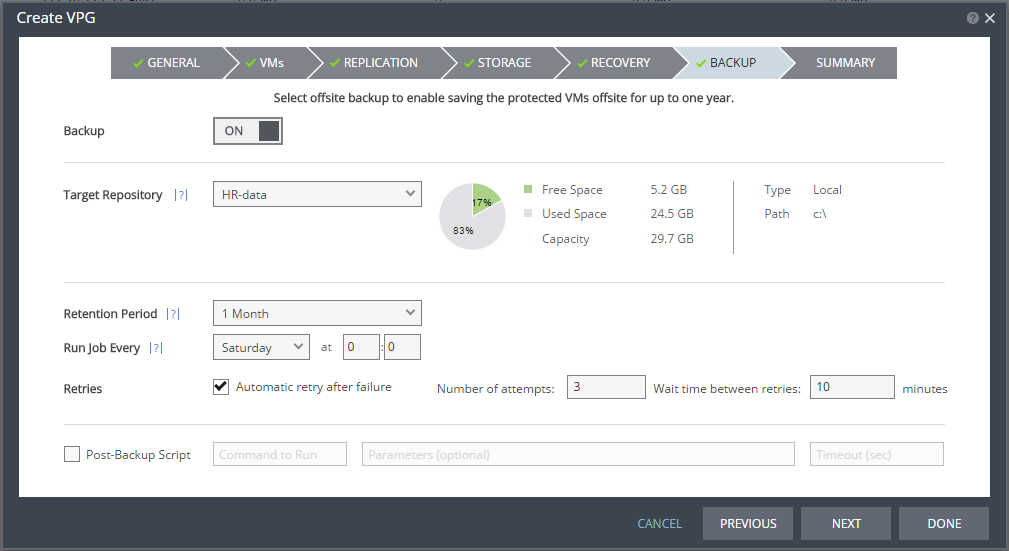
The BACKUP step is displayed. Backup properties govern the VPG backup, including the repository where the backups are saved. Backup extends the ability to recover virtual machines in a VPG for up to one year.
22. By default, backup is OFF. To keep this value, go to step
45.
23. Otherwise, toggle OFF to ON and enter the following information:
■ Retention Period – The length of time to keep offsite backups, up to a maximum of one year. For details of how this affects the number of backups saved, see
“Offsite Backups”, on page 44.
■ Run Job Every – The day and time to start the backup.
■ Retries – Whether to rerun the backup job automatically if the job fails. If you select this option, you must also define the number of retries that will be attempted and the time to wait after a job fails before running the backup job again.
■ Post-Backup Script – The information about a script that should run at the end of the recovery process. Enter the following information:
Text Box | Description |
Command to run | The full path of the script. The script must be located on the same machine as the Zerto Virtual Manager for the recovery site. |
Parameters | The values of parameters to pass to the script. Separate parameters with a space. |
Timeout | The time-out, in seconds, for the script to run. If the timeout value is reached, an alert is generated. The default time-out value is specified in the Performance and Throttling tab of the Site Settings window. |
Note: You cannot restore a backup in AWS.
24. Click NEXT.
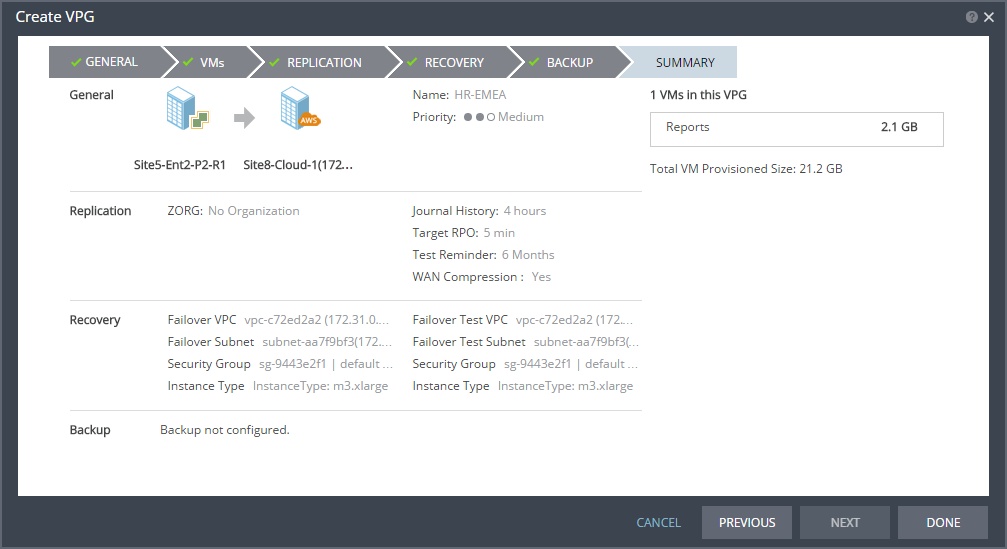
The SUMMARY step is displayed. It shows the VPG configuration that you defined in the previous steps.
25. Click DONE. The VPG is created.
For details of what happens after creating the VPG, see
“What Happens After the VPG is Defined”, on page 42.