Replication From Protected Site vCloud Director to a Recovery Site vCloud Director
When both sites have vCloud Director installed, you can protect:
■ Virtual machines in the underlying vCenter Server.
When the vCD site is set up within Zerto Cloud Manager, as described in Zerto Cloud Manager Administration Guide, virtual machines in the underlying vCenter Server cannot be specified.
The protected machines are protected as a vCD vApp in the recovery site vCD. Both the VM-level and vCD vApp-level metadata is also replicated to the recovery site.
To create a VPG from and to vCloud Director:
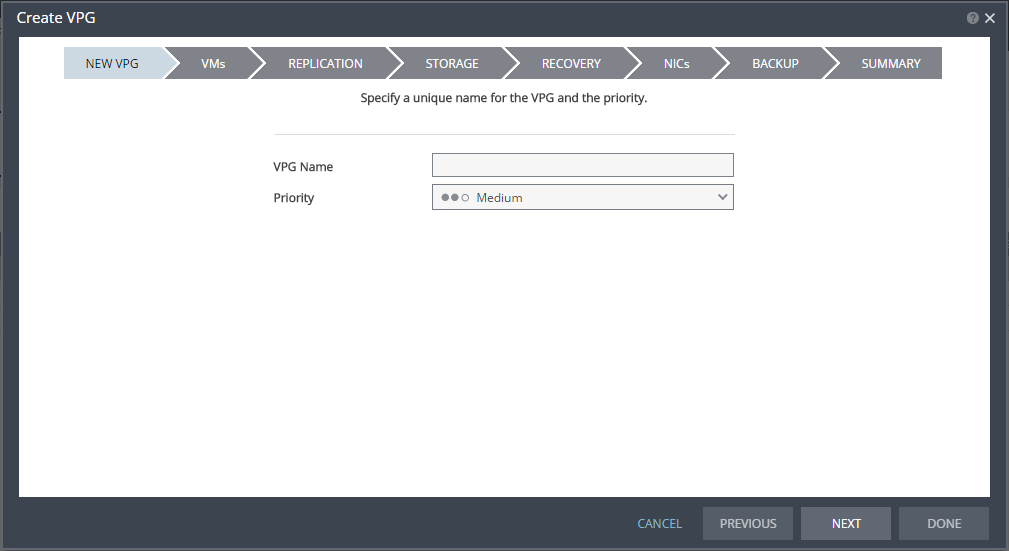
1. In the Zerto User Interface, select ACTIONS > CREATE VPG.
The NEW VPG step of the Create VPG wizard is displayed.
2. Specify the name of the VPG and the priority of the VPG.
VPG Name – The VPG name must be unique. The name cannot be more than 80 characters.
Priority – Determine the priority for transferring data from the protected site to the recovery site when there is limited bandwidth and more than one VPG is defined on the protected site. When there are updates to virtual machines protected in VPGs with different priorities, first the updates from the VPG with the highest priority are passed over the WAN. Medium priority VPGs will only be able to use whatever bandwidth is left after the high priority VPGs have used it. This is also true between medium and low priorities. Note that updates to the protected virtual machines are always sent across the WAN before synchronization data, such as during a bitmap or delta sync. During a synchronization, only after updates to the virtual machines are sent over the WAN, based on the VPG priority, is synchronization data from the VPG sent, and the synchronization data from the VPG with the highest priority is passed over the WAN before data from medium and low priority VPGs.
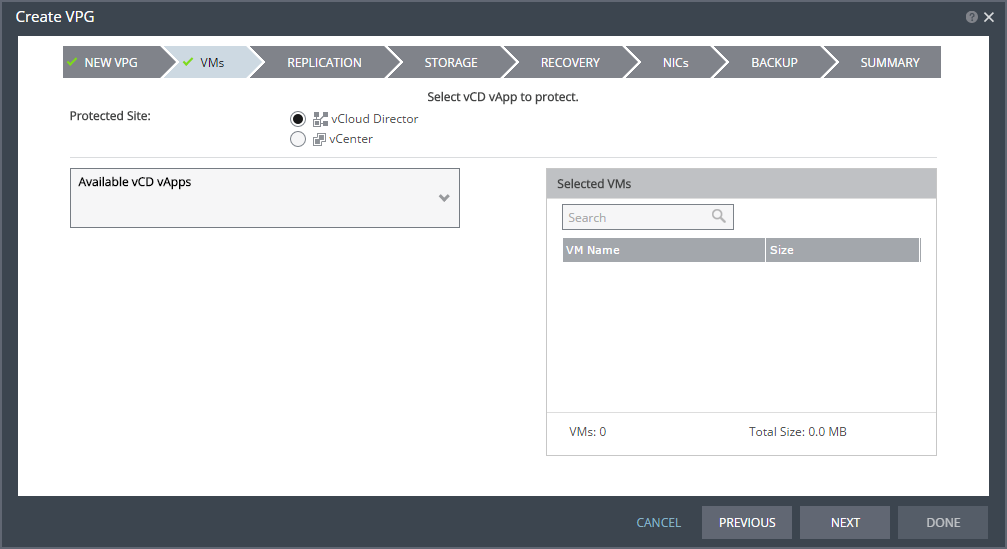
3. Click NEXT.
The VMs step is displayed.
You can select virtual machines to protect either from the underlying vCenter Server or as a vCD vApp.
4. Select the vCD vApp to protect in this VPG. The protected vCD vApp is recovered as a vCD vApp.
Zerto Virtual Replication uses the SCSI protocol. Only virtual machines with disks that support this protocol can be specified.
Note: Define the required boot order for vCD vApps in the vCloud Director console.
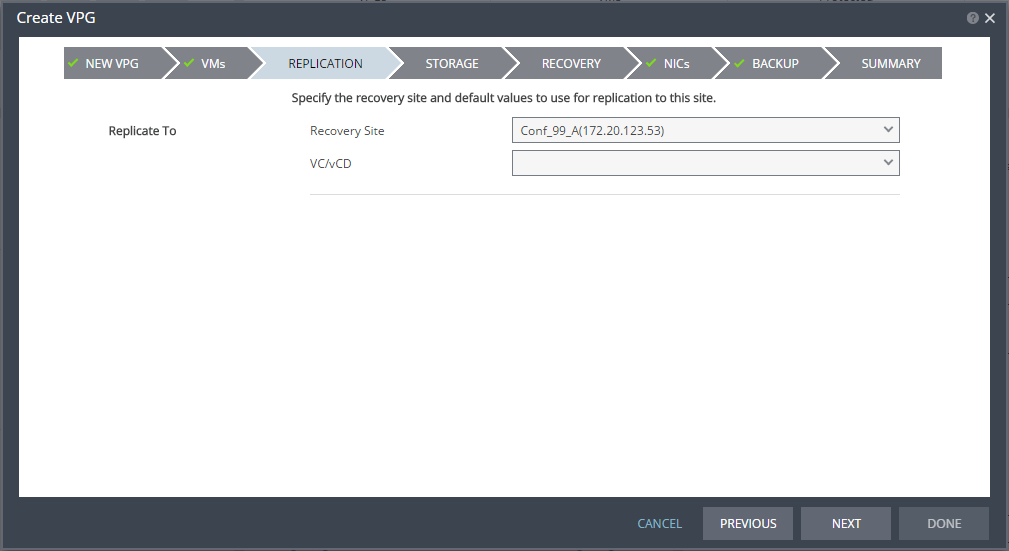
5. Click NEXT.
The REPLICATION step is displayed.
Note: If there are multiple sites paired with the protected site, the VC/vCD field is not displayed until the site with vCD is selected.
6. Choose the recovery site and whether recovery will be to VC or vCD.
The REPLICATION step is re-displayed, with additional fields that are relevant for VC or vCD. If you chose vCD, this screen is displayed.
If
VC is selected, the procedure is the same as described in
Protecting Virtual Machines to a Recovery Site vCenter Server.
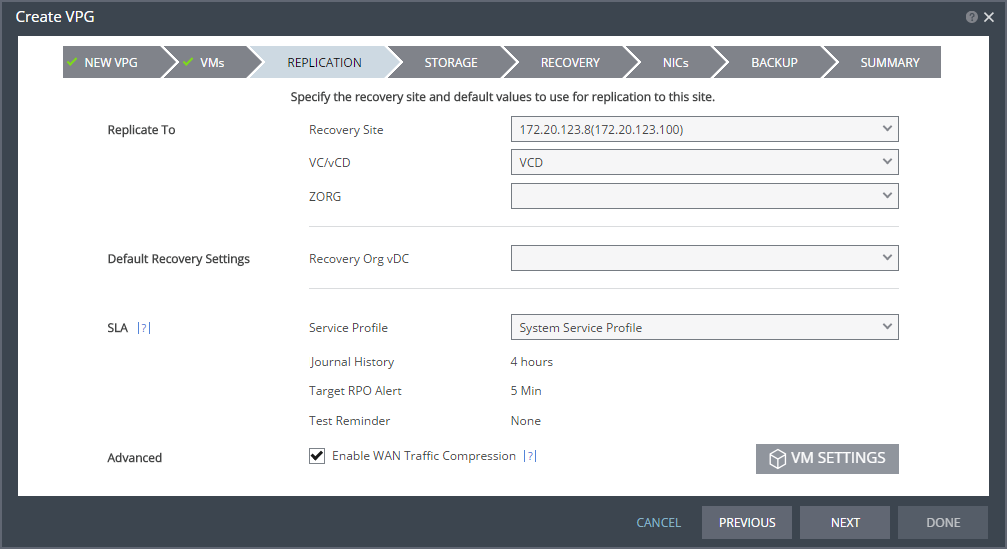
If the site is defined in Zerto Cloud Manager, you specify the name the cloud service provider uses to identify you as a Zerto Organization, ZORG. For details about Zerto Cloud Manager, refer to Zerto Cloud Manager Administration Guide.
If vCD is selected, specify the Recovery Org vDC to use in the recovery site.
7. When the Zerto Cloud Manager is used select the service profile.
Service Profile – The name of the service profile to use which determines the VPG SLA settings for the group, which apply to every virtual machine in the group. To change the VPG SLA settings, select the Custom Service Profile.
8. If the VPG SLA settings are editable, when the Zerto Cloud Manager is not used or when a Custom service profile is available, specify these settings for the group, which apply to every virtual machine in the group.
Journal History – The time that all write commands are saved in the journal. The longer the information is saved in the journal, the more space is required for each journal in the VPG. You can select the number of hours from 1 to 24 or the number of days from 2 to 14.
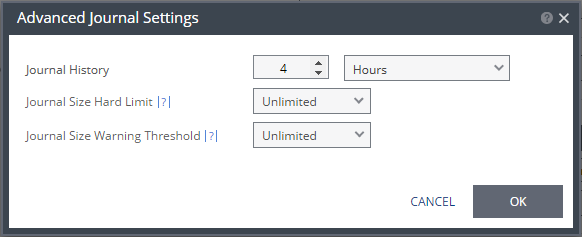
For additional journal-related fields, click ADVANCED.
The Advanced Journal Settings dialog is displayed.
Journal Size Hard Limit – The maximum size that the journal can grow, either as a percentage or a fixed amount. The minimum journal size, set by Zerto Virtual Replication, is 8GB. The journal is always thin-provisioned.
Unlimited – The size of the journal is unlimited and it can grow to the size of the recovery datastore.
Size (GB) – The maximum journal size in GB.
Percentage – The percentage of the virtual machine volume size the journal can grow to.
Journal Size Warning Threshold – The size of the journal that triggers a warning that the journal is nearing its hard limit.
Unlimited – The size of the journal is unlimited and it can grow to the size of the recovery datastore.
Size (GB) – The size in GB that will generate a warning.
Percentage – The percentage of the virtual machine volume size that will generate a warning.
Both the value of Size and Percentage must be less than the configured hard limit so that the warning will be generated when needed. In addition to the warning threshold, Zerto Virtual Replication will issue a message when the free space available for the journal is almost full.
Target RPO Alert – The maximum desired time between each automatic checkpoint write to the journal before an alert is issued. To increase the value, move the slider right; to decrease the value, move the slider left.
Test Reminder – The time recommended between testing the integrity of the VPG. A warning is issued if a test is not done within this time frame.
9. Optionally, change the Advanced value.
Enable WAN Traffic Compression – Whether or not data is compressed before being transferred to the recovery site. Compressing the data is more efficient but results in a small performance degradation. Enable WAN traffic compression if network considerations are more critical than CPU usage considerations. When WAN compression is enabled, the compressed data is written in compressed format to the recovery site journal. Even if WAN compression is selected, Zerto Virtual Replication decreases the level of compression if it takes too many resources. The VRA automatically adjusts the compression level according to CPU usage, including totally disabling it if needed. Zerto recommends enabling WAN compression. Zerto Virtual Replication can also work with third-party WAN optimization and acceleration technologies, such as those supplied by Riverbed Technologies and Silver Peak. When third-party WAN optimization is implemented, Zerto recommends disabling VPG WAN compression.
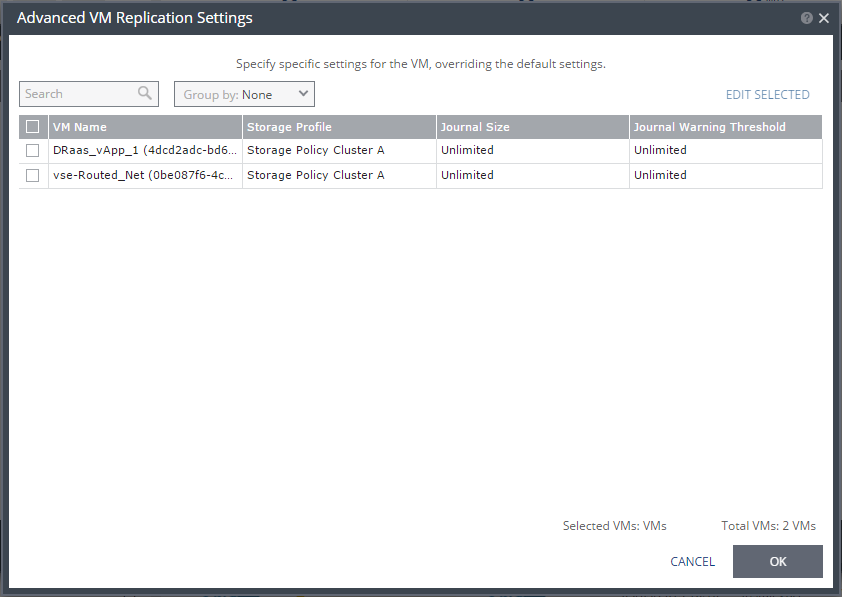
10. If you want to change the replication settings per virtual machine, click VM SETTINGS.
The Advanced VM Replication Settings dialog is displayed.
In this dialog, you can edit the values of one or more of the virtual machines in the VPG.
11. If you want to edit information in one field, click the field and update the information. If you want to edit information for several virtual machines at the same time, select the virtual machines and click EDIT SELECTED.
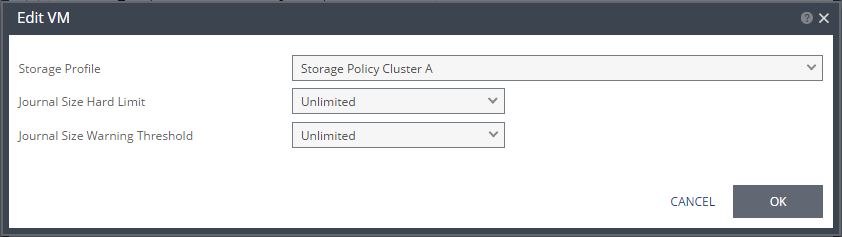
The Edit VM dialog is displayed.
Storage Profile – Storage profiles enable mapping virtual machines to storage levels according to predefined service levels, storage availability, performance requirements or cost. You can define and label storage tiers and then specify the tier to use as a storage profile, for each virtual machine in the VPG. The default storage profile is the default for the Recovery Org vDC.
Zerto will place all the volumes of each virtual machine in a datastore, according to the following considerations:
■ The datastore is part of the selected storage profile.
■ The datastore is configured as recovery datastore target in the Configure PVDC dialog.
■ The datastore has enough space to contain all of the virtual machine volumes.
If Zerto Virtual Replication cannot find a storage profile that can be used as target storage, the value is set to Zerto_Any. In this case, any of the datastores configured in the Configure Provider vDCs dialog can be selected as recovery datastores, provided they are exposed to the relevant recovery hosts. Upon recovery, Zerto Virtual Replication chooses a storage profile available to the Org vDC, for the recovered vApp, that contains all of the datastores on which recovery volumes of the VPG reside. If there is no such storage profile, the recovery operation cannot start. The storage profile can be set to Zerto_Any for a number of reasons, such as adding a virtual machine to the VPG which does not have a storage profile that can be used as the target.
Journal Size Hard Limit – The maximum size that the journal can grow, either as a percentage or a fixed amount. The minimum journal size, set by Zerto Virtual Replication, is 8GB. The journal is always thin-provisioned.
Unlimited – The size of the journal is unlimited and it can grow to the size of the recovery datastore.
Size (GB) – The maximum journal size in GB.
Percentage – The percentage of the virtual machine volume size the journal can grow to.
Journal Size Warning Threshold – The size of the journal that triggers a warning that the journal is nearing its hard limit.
Unlimited – The size of the journal is unlimited and it can grow to the size of the recovery datastore.
Size (GB) – The size in GB that will generate a warning.
Percentage – The percentage of the virtual machine volume size that will generate a warning.
Both the value of Size and Percentage must be less than the configured hard limit so that the warning will be generated when needed. In addition to the warning threshold, Zerto Virtual Replication will issue a message when the free space available for the journal is almost full.
12. Click OK.
13. In the Advanced VM Replication Settings dialog, click OK.
14. Click NEXT.
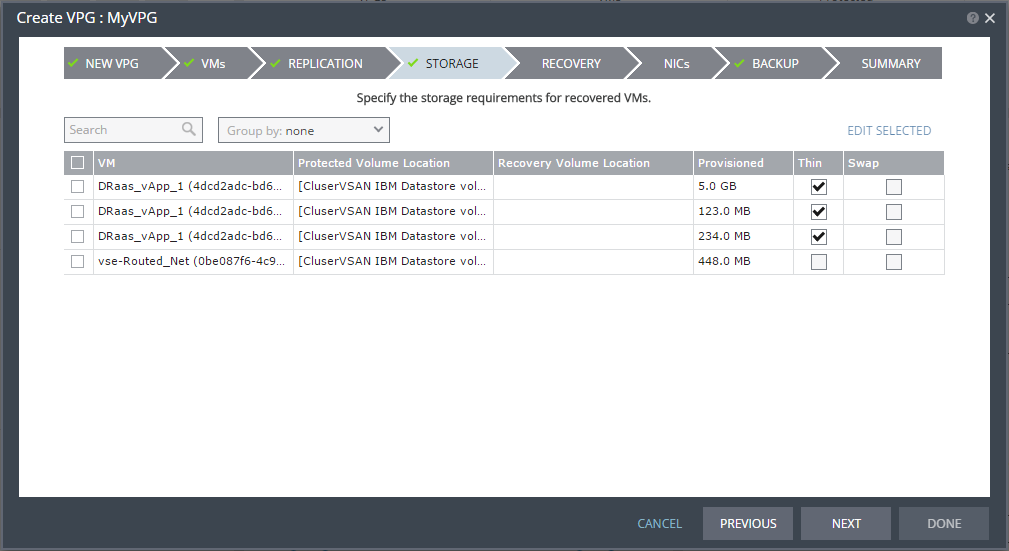
The STORAGE step is displayed. By default the storage used for the virtual machine definition is also used for the virtual machine data. For each virtual machine in the VPG, Zerto Virtual Replication displays its storage-related information.
Note: Steps that do not require input are marked with a check mark. You can jump directly to a step that has been marked with a check mark to edit the values for that step. Every step must be marked with a check mark before you can click DONE to create the VPG.
Thin – If the recovery volumes are thin-provisioned or not.
Swap – If the virtual machine to be replicated includes a swap disk as part of its configuration, mark the recovery disk for this disk as a swap disk. In this case, data is not replicated to the swap disk after initial synchronization.
15. If you want to edit storage information for one of the virtual machines, select the machine and click EDIT SELECTED.
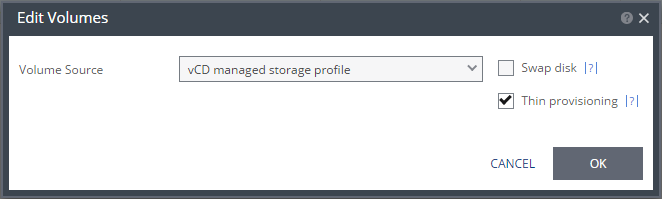
The Edit Volumes dialog is displayed.
16. Specify the volume source for recovery from one of the options.
vCD managed storage profile – The datastore is allocated based on the available free space. You can specify whether the recovery volume is thin-provisioned or not. If the Org vDC only supports thin-provisioned volumes, you cannot change the setting.
Preseeded volume – A virtual disk (the VMDK flat file and descriptor) in the recovery site that has been prepared with a copy of the protected data. Zerto recommends using this option particularly for large disks so that the initial synchronization is much faster since a Delta Sync is used to synchronize any changes written to the recovery site after the creation of the preseeded disk. When not using a preseeded disk the initial synchronization phase has to copy the whole disk over the WAN. Browse to the preseed folder configured for the customer and the disk name, of the preseeded disk. In order to use a preseeded VMDK, do the following:
■ Create a folder in vCD to use for the preseeded disks in the datastore you want to use for the customer.
■ Specify this datastore as a provider datastore for preseeded disks in the Configure Provider vDCs dialog, from the Advanced Settings dialog, as described in Zerto Cloud Manager Administration Guide.
■ In the Zerto Cloud Manager specify the Preseed Folder Name for the ZORG, in the Manage ZORG tab.
Zerto Virtual Replication searches for the preseeded folder in the available datastores in the Org vDCs specified in the vCD Cloud Resources for the ZORG in the Zerto Cloud Manager and takes ownership of the preseeded disk, moving it from its source folder to the folder used by the VRA. Note that if the virtual machine has more than one preseeded disk, these disks must reside on the same datastore. If the preseeded disk is greater than 1TB on NFS storage, the VPG creation might fail. This is a known VMware problem when the NFS client does not wait for sufficient time for the NFS storage array to initialize the virtual disk after the RPC parameter of the NFS client times out. The timeout default value is 10 seconds. Refer
to the VMware documentation, http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=1027919, which describes the configuration option to tune the RPC timeout parameter using the
esxcfg-advcfg -s <Timeout> /NFS/SetAttrRPCTimeout command.
If the VPG is being defined for a Zerto Organization, ZORG, the location of the preseeded disk must be defined in the Zerto Cloud Manager. For details, refer to Zerto Cloud Manager Administration Guide.
Zerto Virtual Replication supports the SCSI protocol. Only disks that support this protocol can be specified. Virtual machine RDMs in a vCenter Server are replicated as VMDKs in a vCD environment.
17. Specify the other volume options.
Swap disk – If the virtual machine to be replicated includes a swap disk as part of its configuration, mark the recovery disk for this disk as a swap disk. In this case, data is not replicated to the swap disk after initial synchronization.
Thin provisioning – If the recovery volumes are thin-provisioned or not.
18. Click OK.
19. Click NEXT.
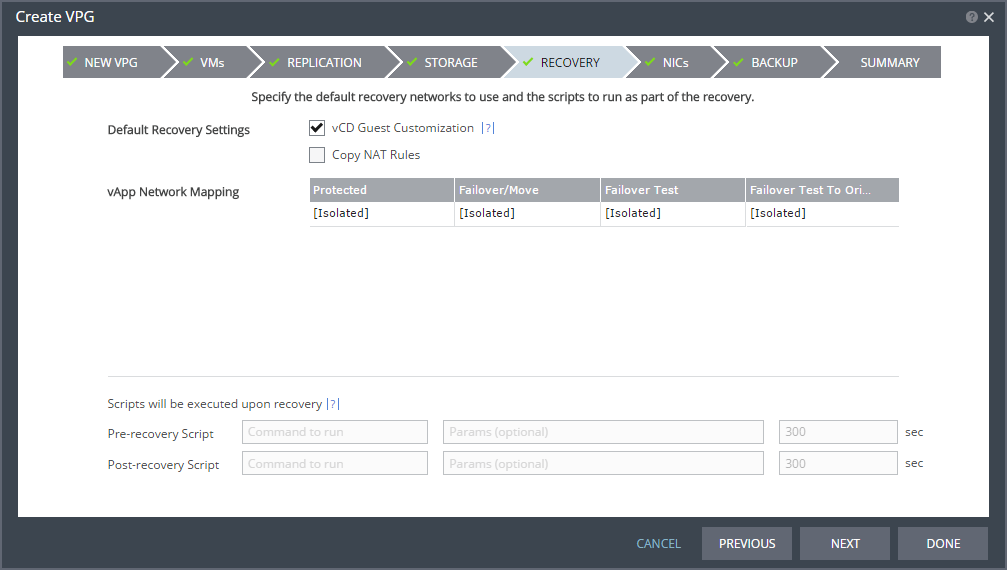
The RECOVERY step is displayed. Recovery details include the scripts that should be run either at the start or end of a recovery operation.
20. Select the default recovery settings.
vCD Guest Customization – When checked, VMware Guest OS Customization is enabled for the virtual machine in vCloud Director. Enabling guest customization means that the computer name and network settings configured for this virtual machine are applied to its Guest OS when the virtual machine is powered on. vCD Guest Customization must be checked to enable re-IPing the recovered virtual machines.
Copy NAT Rules– When checked, NAT rules on source vApp networks are copied to the recovery vApp during recovery. The automatic setting is applied as automatic and the manual setting is applied as manual using the IPs on the source.
vApp Network Mapping – The networks to use for failover and move operations, for failover test operations, and for test failover operations after a failover or move when reverse protection is configured. The list of current Org Networks is displayed and you can specify what network to use in each of the situations. <Isolated> means that the network is an internal only vApp network.
21. Enter the name of the script to run in the Command to run text box. You can then enter details about the script.
Pre-recovery Script – The information about a script that should run at the beginning of the recovery process.
Post-recovery Script – The information about a script that should run at the end of the recovery process.
For both types of scripts, enter the following information:
Text Box | Description |
Command to run | The full path of the script. The script must be located on the same machine as the Zerto Virtual Manager for the recovery site. |
Params | The parameters to pass to the script. Separate parameters with a space. |
Timeout | The time-out, in seconds, for the script to run. If the script runs before executing a failover, move, or test failover, and the script fails or the timeout value is reached, an alert is generated and the failover, move, or test failover is not performed. If the script runs after executing a failover, move, or test failover, and the timeout value is reached, an alert is generated. The default time-out value is specified in Performance and Throttling tab in the Site Settings dialog. |
22. Click NEXT.
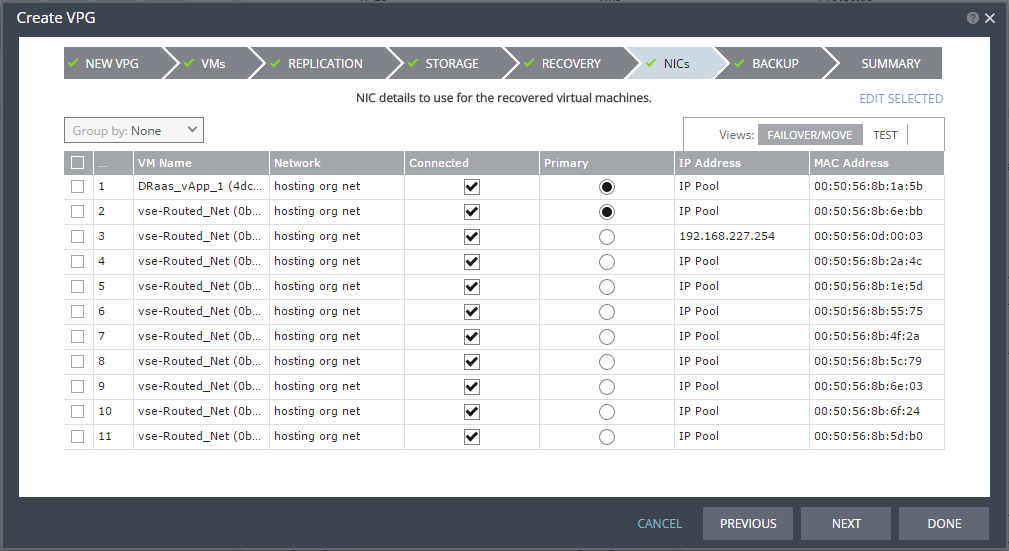
The NICs step is displayed. In this step, you can specify the NIC details to use for the recovered virtual machines after a failover, a test failover, or migration.
23. If you want to edit information in one field, click the field and update the information. If you want to edit information for several virtual machines at the same time, select the virtual machines and click
EDIT SELECTED. Otherwise, go to step
26.
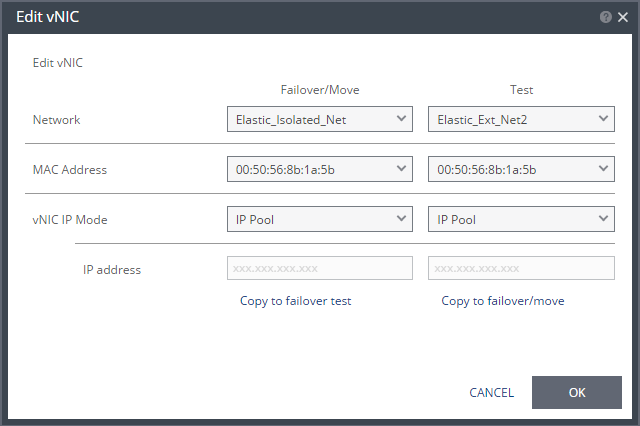
The Edit VNIC dialog is displayed.
24. Specify the network details to use for the recovered virtual machines after a failover or move operation, in the Failover/Move column, and for the recovered virtual machines when testing replication, in the Test column.
In each column, specify the following:
Network: The network to use for this virtual machine.
MAC Address – Whether the Media Access Control address (MAC address) used on the protected site should be replicated on the recovery site. The default is to use the same MAC address on both sites.
vNIC IP Mode – Which IP mode to use. Specify the IP address if you choose static IP pool.
Refer to the
Zerto Virtual Replication Interoperability Matrix for the list of operating systems for which Zerto supports Re-IPing.
During a failover, move, or test failover, if the recovered virtual machine is assigned a different IP than the original IP, after the virtual machine has started it is automatically rebooted so that it starts up with the correct IP. If the same network is used for both production and test failovers, Zerto recommends changing the IP address for the virtual machines started for the test, so that there is no IP clash between the test machines and the production machines.
Copy to failover test – Copies the settings in the Failover/Move column to the Test column.
Copy to failover/move – Copies the settings in the Test column to the Failover/Move column.
25. Click OK.
26. Click NEXT.
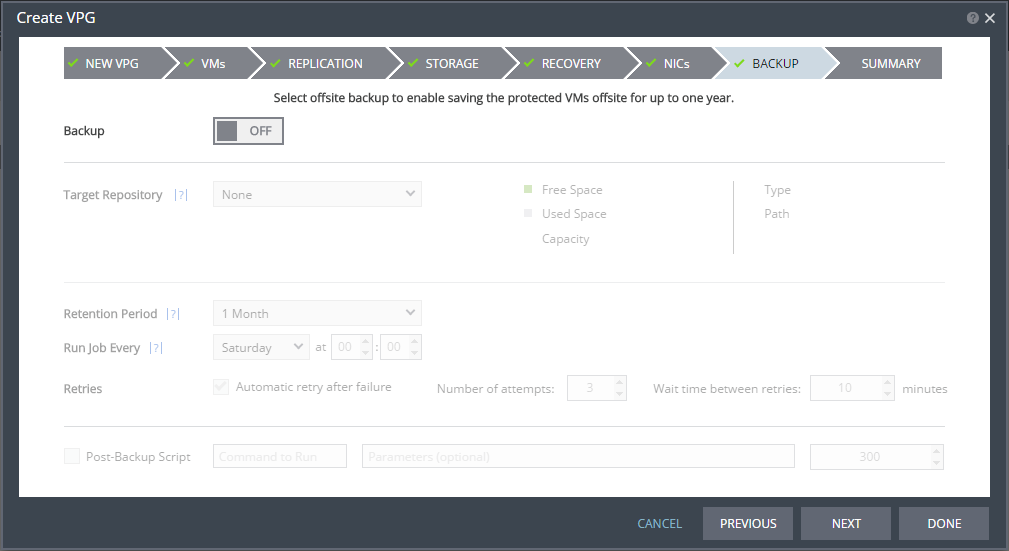
The BACKUP step is displayed. Backup properties govern the VPG backup, including the repository where the backups are saved. Backup extends the ability to recover virtual machines in a VPG going back one year.
27. By default, backup is off. If you do not want to change this value, go to step
28. Otherwise, toggle OFF to ON and enter the following information:
Target Repository – The name of the repository where the offsite backups are written. Repositories are configured via the
SETUP tab as described in
Setting Up Offsite Backups.
Retention Period – The length of time to keep offsite backups, up to a maximum of one year. For details of how this affects the number of backups saved, see
Offsite Backups.
Run Job Every – The day and time to start the backup.
Retries – Whether to rerun the backup job automatically if the job fails. If you select this option, you must also define the number of retries that will be attempted and the time to wait after a job fails before running the backup job again.
Post-Backup Script – The information about a script that should run at the end of the recovery process. Enter the following information:
Text Box | Description |
Command to run | The full path of the script. The script must be located on the same machine as the Zerto Virtual Manager for the recovery site. |
Parameters | The values of parameters to pass to the script. Separate parameters with a space. |
Timeout | The time-out, in seconds, for the script to run. If the timeout value is reached, an alert is generated. The default time-out value is specified in the Performance and Throttling tab of the Site Settings dialog. |
28. Click NEXT.
The SUMMARY step is displayed. It shows the VPG configuration that you defined in previous steps.
29. Click DONE.
The VPG is created.