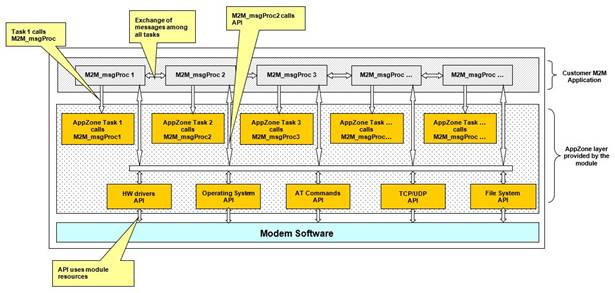
AppZone C is a software layer that provides a set of APIs to access the modem features of major operational interest. By means of AppZone C, the user M2M application runs on the module CPU; this solution does not require an external application processor.
You can develop M2M applications that can address a wide range of different applications such as remote monitoring and control, security and surveillance, telemetry, location services, billing, and fleet management. The generic user application can access the following modem resources:
•Operating System: Signals, Semaphores, Timers, Dynamic Memory Management, etc.
•HW/SW: GPIO, I2C, UART, SPI, Keypad, File-System, RTC, etc.
•GSM/GPRS: Communication services.
•Networking: BSD socket support, SSL capabilities.
Refer to documents [1]/[3]/[4] for information on module hardware resources.
Fig. 1 shows the high-level architecture of a module provided with the AppZone C software layer. Use AppZone C to develop custom M2M applications, in accordance with the AppZone layer, which provides a set of files called skeleton.

Fig. 1: Module with AppZone Software Layer
The skeleton factory default configuration includes a single M2M_procX.c template file, named M2M_proc1.c that contains the M2M_msgProc1() callback function. You can write new M2M_procX.c files, new M2M_msgProcX() callbacks, and create new AppZone Tasks. AppZone layer can support up to 32 tasks in total. In general, each AppZone Task calls its callback function, for more information refer to AppZone C APIs Reference Guide:
•AppZone Task_1 calls M2M_msgProc1 (default)
•AppZone Task_2 calls M2M_msgProc2 (created by the user)
•AppZone Task_3 calls M2M_msgProc3 (created by the user)
•AppZone Task_... calls M2M_msgProc… (created by the user)
Use the M2M_msgProcX() callback functions to develop the M2M applications. Tasks communicate with each other exchanging messages using the suitable API.
|
|
Use the C programming language to develop the M2M applications. |