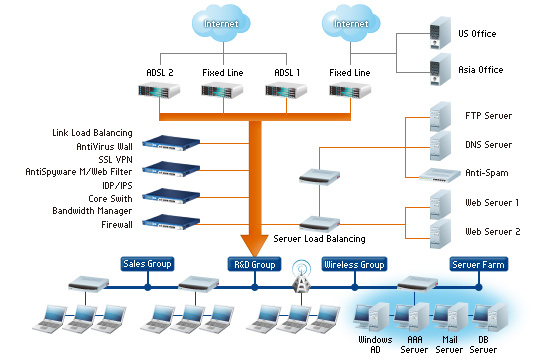
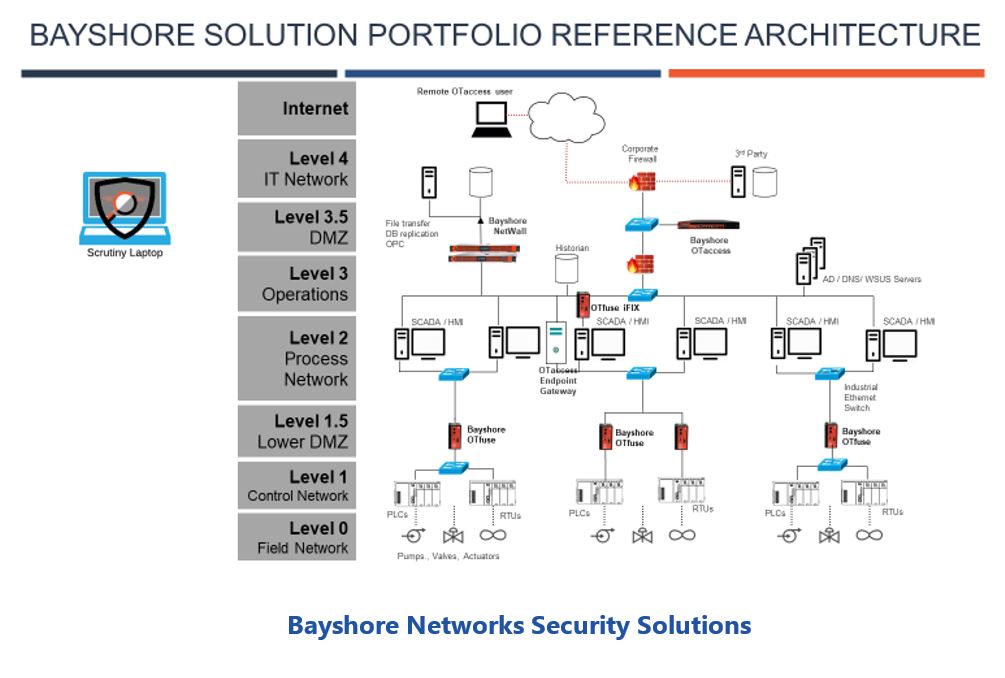
Have you ever tried to access your router settings but were prompted to enter a login password? A router login password is a unique security feature that restricts unauthorized access to your router settings. This password is needed to configure or troubleshoot the router, change its security settings, and much more. Knowing how to set, change and reset this password is essential for every router user.
To start with, the router login password is different from your Wi-Fi network password which allows devices to connect to your wireless network. By default, routers come with a generic password that's easy to guess, making your network vulnerable to hacking attacks. The first step to secure your router settings is to change this password.
To set a router login password, access your router settings by typing its IP address in a web browser. Then, locate the password settings and create a strong password that consists of a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using personal information like your birthdate or name to minimize the risk of a breach. Keep this password in a secure place.
Now, what if you lose or forget the router login password? Don't worry, there's always a way to reset it. Usually, routers have a reset button that's located at the back or bottom of the device. Press and hold this button for about 10 seconds to restore the router to its default settings. Note that this process will also erase all custom settings, so you'll need to reconfigure the router from scratch.
In conclusion, a router login password is a crucial security feature that protects your network from unauthorized access. Setting a strong and unique password and resetting it when needed will make your router and network less vulnerable to hacking attempts.
Wireless transmission analysis
Wireless transmission analysis is a field of study that aims to understand the intricacies of wireless networks and how they operate. The analysis of wireless transmission involves the study of various parameters that impact the quality and efficiency of wireless networks, such as signal strength, interference, noise, and other environmental factors.
Wireless transmission analysis is an essential component of wireless communications engineering. The goal of wireless transmission analysis is to optimize and improve the performance of wireless networks by identifying potential issues and developing solutions to address them.
There are several tools and techniques available to perform wireless transmission analysis. One such technique is the use of signal analyzers, which can measure the signal strength and other important parameters of wireless networks. Other tools such as spectrum analyzers and network analyzers are also commonly used to analyze wireless transmissions.
Wireless transmission analysis is particularly important in the development of new wireless technologies. Understanding the behavior of wireless networks and the factors that affect their performance is crucial to the development of new wireless products and services. By analyzing wireless transmissions, engineers can identify potential issues and work to optimize the performance of wireless networks.
In conclusion, wireless transmission analysis is a critical field of study that plays a vital role in the development and optimization of wireless networks. The analysis of wireless transmissions is a complex and challenging task that requires an in-depth understanding of radio frequency technology, network protocols, and the various factors that impact the performance of wireless networks. Through careful analysis and optimization, the performance of wireless networks can be greatly improved, leading to better user experiences and more efficient wireless communication.
Wireless transmission analysis is an essential component of wireless communications engineering. The goal of wireless transmission analysis is to optimize and improve the performance of wireless networks by identifying potential issues and developing solutions to address them.
There are several tools and techniques available to perform wireless transmission analysis. One such technique is the use of signal analyzers, which can measure the signal strength and other important parameters of wireless networks. Other tools such as spectrum analyzers and network analyzers are also commonly used to analyze wireless transmissions.
Wireless transmission analysis is particularly important in the development of new wireless technologies. Understanding the behavior of wireless networks and the factors that affect their performance is crucial to the development of new wireless products and services. By analyzing wireless transmissions, engineers can identify potential issues and work to optimize the performance of wireless networks.
In conclusion, wireless transmission analysis is a critical field of study that plays a vital role in the development and optimization of wireless networks. The analysis of wireless transmissions is a complex and challenging task that requires an in-depth understanding of radio frequency technology, network protocols, and the various factors that impact the performance of wireless networks. Through careful analysis and optimization, the performance of wireless networks can be greatly improved, leading to better user experiences and more efficient wireless communication.