Performing a Custom Installation
You can install Zerto specifying the ports that will be used by Zerto and full contact details.
(vSphere only) In addition, when performing a custom install, you can provide information to connect to VMware vCloud Director,
Before you Begin:
To perform a custom install of Zerto:
1. Run the Zerto Installer for VMware or Hyper-V.
■ If the required version of Microsoft .NET Framework is not installed, you are prompted to install the required version of .NET Framework, which is included as part of the Zerto installation package.
After .NET is installed, the machine automatically restarts and the Zerto installation begins.
2. Follow the wizard until the Installation Type window appears, then select the option, Custom Installation.
3. Click Next.
The Choose Stand-alone Or Clustered Installation window appears.
4. Select Stand-alone Installation, then click Next.
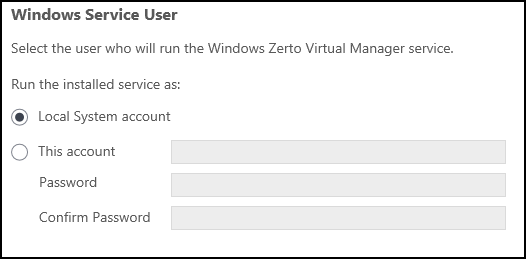
5. Click NEXT. The Windows Service User window appears.
6. Select either Local System account or This account:
■ Local System account: Use the Local System account to run the Zerto Virtual Manager service, which is installed as part of Zerto. The Local System account has unrestricted access to local resources.
■ This account: Use a specific account as the user account to run the Zerto Virtual Manager service, which is installed as part of Zerto. The account must have unrestricted access to local resources.
■ Password: The password to use to run the service under the specified account.
■ Confirm Password: Confirmation of the password.
7. Click NEXT.
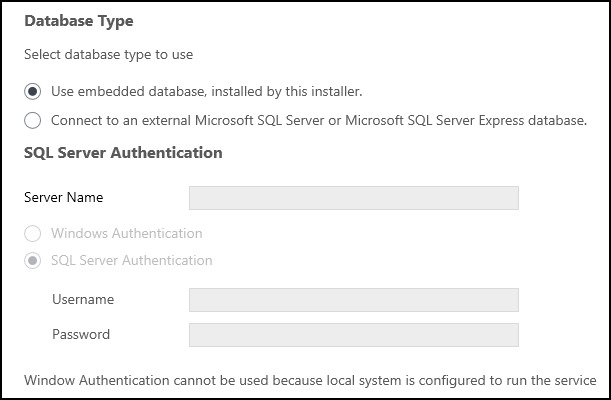
The Database Type window appears.
■ Information required by Zerto is stored by default in a database embedded in the Zerto Virtual Manager. This information includes details of the site where the Zerto Virtual Manager is installed, details of the Virtual Replication Appliances and the volumes they use, and points-in-time recorded for recovery purposes.
■ By default an embedded SQL-based database is installed, but you can use an externally managed database, for example, Microsoft SQL Server.
■ Protection and recovery can only be performed when the database is running.
■ If you use an external database and it is down for any reason, protection stops.
8. To use the
embedded database, leave the
default which is installed with this installation, then continue with
11.
9. To use an external database, select the option, Connect to an external Microsoft SQL Server or Microsoft SQL Server Express database.
10. If you selected an external database, the SQL Server Authentication area is enabled. Enter the following authentication details to enable access to the SQL Server database:
a) Server Name: The domain name and server instance to connect to, with the format: <server_name>\<instance_name> or <Server_IP>\<instance_name>
b) You must specify an authentication method. Select one of the following:
■ Windows Authentication
- or -
■ SQL Server Authentication
c) If you selected
Windows Authentication: This option is enabled only if a specific service user account was specified in Windows Service User, in
5. In this case, the service account name and password are used.
d) If you selected SQL Server Authentication, the Test Authentication button is also displayed.
After you define the following, click Test Authentication:
■ Username: The user name for the SQL Server database.
■ Password: A valid password for the given user name.
The installer checks whether it can connect to the specified database with the specified username and password.
You can only continue when the authentication is successful.
11. Click NEXT. The vCenter or SCVMM Server Connectivity window appears.
12. Enter connection settings that the Zerto Virtual Manager uses to communicate with the vCenter or SCVMM Server:
■ IP/Host name: The IP address or host name of the machine where the SCVMM runs.
■ (Hyper-V only) Domain: The domain for a user with administrator level privileges to the vCenter Server or SCVMM.
■ Username: The user name for a user with administrator level privileges to the vCenter Server or SCVMM. The name can be entered using either of the following formats:
■ username
■ (vSphere only) domain/username
■ Password: A valid password for the given user name.
13. Click NEXT.
■ For further steps on vCloud Direct (vCD) Connectivity, continue to
14.
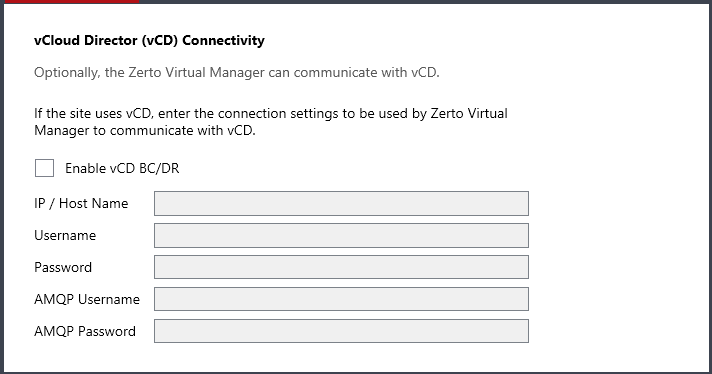
14. The vCloud Director Connectivity window is displayed.
15. When using vCloud Director and you have installed an AMQP server, click the Enable vCD BC/DR checkbox and enter the VMware vCloud Director access details:
■ IP / Host name: The IP address or host name of the machine where vCD runs. When connecting to vCD with multiple cells, enter the virtual IP for the network load balancing used by the cells.
■ Username: The user name for an administrator to vCD.
■ Password: A valid password for the given user name.
■ AMQP Username: The user name for the AMQP server.
■ AMQP Password: A valid password for the given AMQP user name.
If the vCD connection settings are not specified, for example, when you do not have an AMQP server installed, they can be set in the Advanced Settings dialog in the Site Configuration panel, in the Zerto User Interface after installation, as described in the Zerto Cloud Manager Administration Guide.
TIP:
Zerto provides an AMQP installation kit if you do not have one installed for vCD.
■ Run ZertoAMQPInstallWizard.exe as described in the Zerto Cloud Manager Administration Guide, and enter the following credentials:
■ Username: The AMQP user account Zerto will use. RabbitMQ prior to version 3.3 installs with a default administrator user: guest. In RabbitMQ version 3.3 and higher, specify a user with administrator privileges.
■ Password: The password for the user. RabbitMQ prior to version 3.3 installs with a default password of guest.
■ Click NEXT.
16. The Zerto Virtual Manager Site Details window appears, where you define general information about the site.
17. Enter the site details:
Site Name: | A name to identify the site. This name is displayed in the Zerto User Interface. This field is mandatory. |
Location: | (Optional) Information such as the address, or name of the site to identify it. |
Contact Information: | (Optional) The name of the person to contact if a need arises. |
Contact Email: | (Optional) The email address to contact if a need arises. |
Contact Phone: | (Optional) The phone number to contact if a need arises. |
18. Click NEXT.
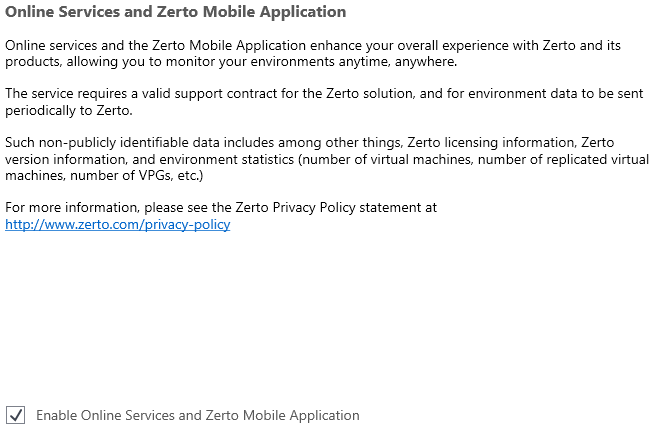
The Online Services and Zerto Mobile Application window appears.
The Online Services and Zerto Mobile Application are enabled by default.
■ You can disable these services by deselecting Enable Online Services and Zerto Mobile Application.
19. Click NEXT.
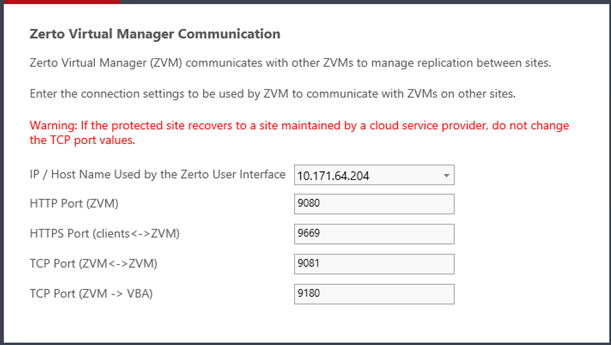
The Zerto Virtual Manager Communication window appears.
In this window you define the connection settings (ports) which are used by Zerto Virtual Manager to communicate with Zerto Virtual Managers on other sites.
Port Description Parameter | Default Port Number | Communication Direction | Between... | Comments |
IP/Host Name Used by the Zerto User Interface | NA | | Zerto User Interface - and - Zerto Virtual Manager | IP to access the Zerto Virtual Manager from the Zerto User Interface. If the machine has more than one NIC, select the appropriate IP from the list. Otherwise, the IP that is displayed is the only option. |
HTTP Port (ZVM) | 9080 | Inbound | Zerto Virtual Manager - and - Zerto internal APIs, and Cmdlets | |
HTTP Port (clients<->ZVM) | 9669 | Inbound | Zerto User Interface - and - Zerto Virtual Manager | |
TCP Port (ZVM<->ZVM) | 9081 | Inbound and outbound | Zerto Virtual Manager - and - Zerto Virtual Manager | ■ When both the protected and recovery sites belong to the same enterprise: ■ If you change this value, when pairing sites, use the TCP port value specified here. Pairing the sites is described in “Pairing Sites”, on page 52. ■ When an enterprise uses a cloud service provider to supply disaster recovery services: ■ Do not change this value |
TCP Port (ZVM->VBA) | 9180 | Inbound and outbound | Zerto Virtual Manager - and - Virtual Backup Appliance (VBA) | |
20. Click NEXT.
The installation performs checks to verify that the installation can proceed successfully.
21. If you intend managing your disaster recovery
from this machine, you can select to open the Zerto Virtual Manager (ZVM) Interface at the end of the installation, logging in with the user name and password for the vCenter Server or SCVMM connected to the Zerto Virtual Manager. In this user interface you set up Zerto, as described in
“Initial Configuration”, on page 48.
22. You must exclude the following folders from antivirus scanning:
Zerto Virtual Replication |
%ProgramData%\Zerto\Data\zvm_db.mdf |
C:\Program Files\Zerto\Zerto Virtual Replication\Zerto.Zvm.Service.exe |
C:\Program Files\Zerto\Zerto Virtual Replication\Zerto.Vba.VbaService.exe |
C:\Program Files\Zerto\Zerto Virtual Replication\Zerto Online Services Connector\Zerto.Online.Services.Connector.exe |
C:\Program Files\Zerto\Zerto Virtual Replication\Embedded DB Manager Service\Zerto.LocalDbInstanceManagerService.exe |
Failure to do so may lead to the Zerto Virtual Replication folder being incorrectly identified as a threat and in some circumstances corrupt the Zerto Virtual Replication folder.
23. Add the machine to the relevant host boot configuration, so that on starting up the host, this machine, running the Zerto Virtual Manager, is also powered on automatically.
24. Install Zerto on peer sites.
■ The installation creates the Zerto Virtual Manager and Virtual Backup Appliance as services, and the installation package to enable installing Virtual Replication Appliances on hosts.
■ Zerto creates folders, such as C:\ZertoAgent, which must not be removed.
Note: If the vSphere Client console was open during the installation, close it and reopen it to ensure you have the Zerto Virtual Manager user interface loaded.