What Happens After the VPG is Defined
The following topics appear in this section:
| • | Recovery |
| • | File and Folder Recovery |
After defining a VPG, the VPG is created. For the creation to be successful, the storage used for the recovery must have either 30GB free space or 15% of the size free. This requirement ensures that during protection the VRA, which manages the virtual machine journal and data, cannot completely fill the storage, which would result in the VRA freezing and stopping to protect all virtual machines using that VRA.
The synchronization process can take some time, depending on the size of the virtual machines, the amount of data in its volumes, and the bandwidth between the sites. During this synchronization, you cannot perform any replication task, such as adding a checkpoint.
During this synchronization, you cannot perform any replication task, such as adding a checkpoint.
For synchronization to work, the protected virtual machines must be powered on. The VRA requires an active IO stack to access the virtual machine data to be synchronized across the sites. If the virtual machine is not powered on, there is no IO stack to use to access the protected data to replicate to the target recovery disks and an alert is issued.
Once synchronized,
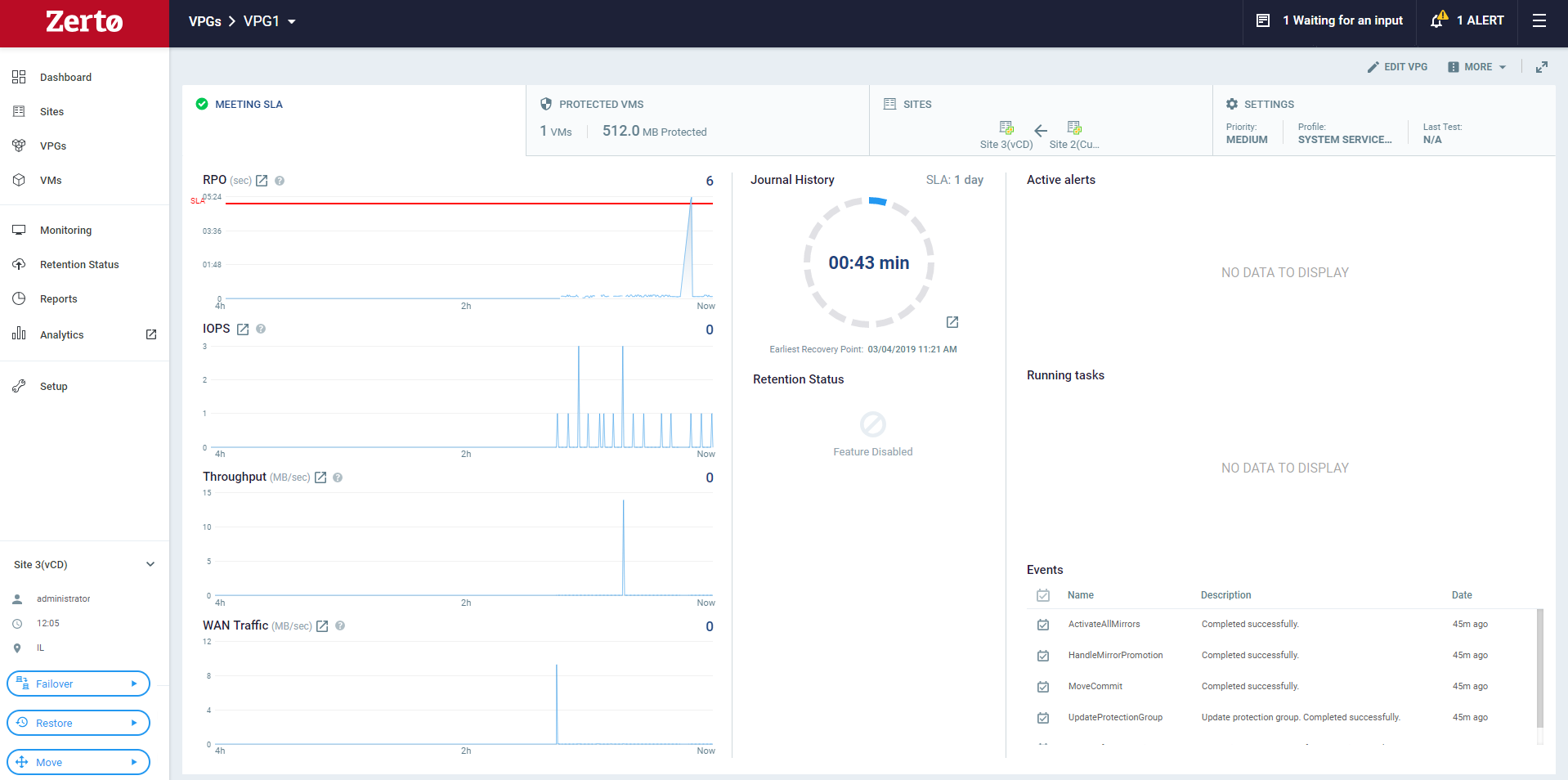
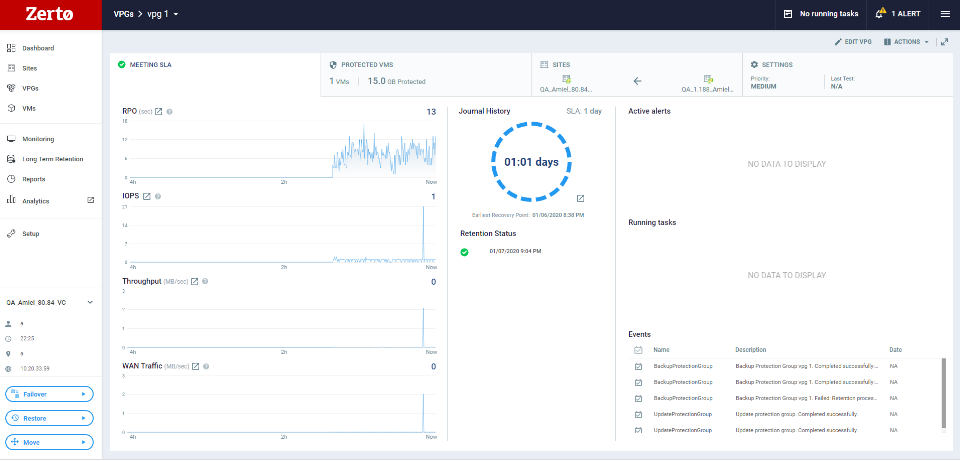
For details of the screen, see
See also:
| • | Configuring Virtual Protection Groups |
| • | Virtual Machines That Cannot Be Replicated |
| • | The Role of the Journal During Protection |