Configure and Install VRA Dialog
| |
ESXi versions from 5.5 | ESXi versions before version 5.5 |
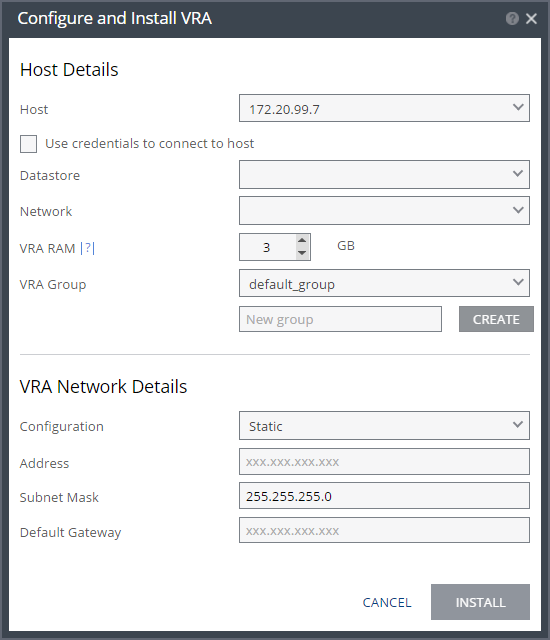
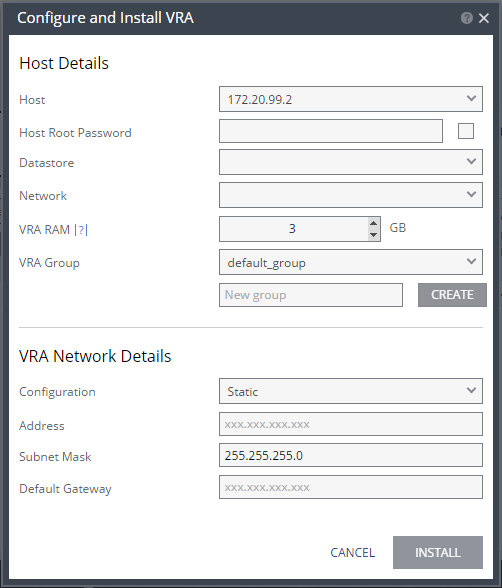
Host – The host on which the VRA is installed. The drop-down displays the hosts that do not have a VRA installed, with the selected host displayed by default.
From ESXi 5.5, by default, Zerto Virtual Manager uses a vSphere Installation Bundle, VIB, to connect to the host. When using VIB:
■ The user does not enter a password.
■ Once a day, Zerto Virtual Manager checks that the VRA and host can connect. If the connection fails, Zerto Virtual Manager re-initiates the connection automatically and logs it.
For ESX/i versions earlier than 5.5, when using a password, root access is required. Once a day, Zerto Virtual Manager checks that the password is valid. If the password was changed, an alert is issued, requesting the user enter the new password.
Use credentials to connect to host – When unchecked, the Zerto Virtual Manager uses VIB to connect to the host. This field is only relevant for ESXi 5.5 and later.
Host Root Password – When the VRA should connect to the host with a password, check Use credential to connect to host and enter the root user password used to access the host. When the box on the right side is checked, the password is displayed in plain text.This field is only relevant for ESXi 4.x and 5.x hosts. This field is disabled for ESX 4.x hosts.
Datastore – The datastore that the VRA will use for protected virtual machine data on the recovery site, including the journals. You can install more than one VRA on the same datastore.
Network – The network used to access the VRA.
VRA RAM – The amount of memory to allocate to the VRA. The amount determines the maximum buffer size for the VRA for buffering IOs written by the protected virtual machines, before the writes are sent over the network to the recovery VRA. The recovery VRA also buffers the incoming IOs until they are written to the journal. If a buffer becomes full, a Bitmap Sync is performed after space is freed up in the buffer.
Amount of VRA RAM | VRA Buffer Pool Size |
1GB | 450MB |
2GB | 1450MB |
3GB | 2300MB |
3GB | 2300MB |
4GB | 3,300MB |
5GB | 4,300MB |
6GB | 5,300MB |
7GB | 6,300MB |
8GB | 7,300MB |
9GB | 8,300MB |
10GB | 9,300MB |
11GB | 10,300MB |
12GB | 11,300MB |
13GB | 12,300MB |
14GB | 13,300MB |
15GB | 14,300MB |
16GB | 15,300MB |
The protecting VRA can use 90% of the buffer for IOs to send over the network and the recovery VRA can use 75% of the buffer. That is, for example, a protecting VRA defined with 2GB of RAM can buffer approximately 1305MB before the buffer is full and a Bitmap Sync is required.
VRA Group – Specify the VRA Group as free text to identify the group or select from a previously specified group. You group VRAs together when VRAs use different networks so they can be grouped by network, for example when the protected and recovery sites are the same site and you want to replicate to different datastores in the site. The group name is free text you use to identify the group.
The priority assigned to a VPG dictates the bandwidth used. The Zerto Virtual Manager distributes bandwidth among the VRAs based on this priority and the VPGs with higher priorities are handled before writes from VPGs with lower priorities.
To create a new group, enter the new group name over the text New group and click CREATE.
Configuration – Either have the IP address allocated via a static IP address or a DHCP server. The Static option is the recommended option.
Address – The IP address for the VRA.
Subnet Mask – The subnet mask for the network. The default value is 255.255.255.0.
Default Gateway – The default mask for the network.