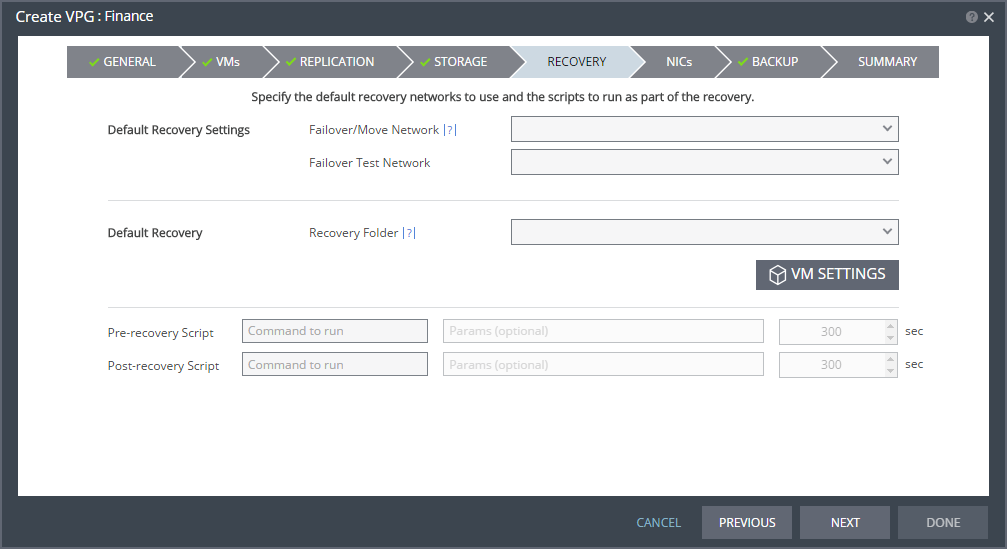
Running Scripts Before or After Recovering a VPG
Before and after executing a failover, move, or test failover, you can run executable scripts, such as Windows .bat files or PowerShell scripts. A pre-recovery script is always run at the beginning of the recovery operation. A post-recovery script is run after all the virtual machines are powered on at the recovery site.
The scripts must be saved to the machine where the remote Zerto Virtual Manager (ZVM) is installed.
Both pre-recovery and post-recovery scripts are run by the ZVM service on the ZVM machine. The account running the ZVM service is the account that will run the scripts when they are executed.
Zerto recommends duplicating scripts on the Zerto Virtual Managers for both the protected and recovery sites, so that if reverse protection is required, the scripts are available. The location of the script for reverse protection, on the machine where the Zerto Virtual Manager that manages the protected site is installed, must be to the same path as in the remote Zerto Virtual Manager machine. For example, if the scripts are saved to C:\ZertScripts on the remote Zerto Virtual Manager machine, they must be saved to C:\ZertScripts on the local Zerto Virtual Manager machine.
The scripts can include environment variables that can be included as part of the script itself, or passed to the script as parameters. When the script is passed an environment variable as a parameter, the variable is evaluated before executing the script. The following environment variables are available:
■ %ZertoVPGName%: The name of the VPG. If the name includes a space, enclose the variable in double quotes (”). For example, the VPG MyVPG uses the format %ZertoVPGName% but the VPG My VPG uses the format “%ZertoVPGName%”.
■ %ZertoOperation%: The operation being run: FailoverBeforeCommit, FailoverRollback, Test, MoveBeforeCommit, MoveRollback. Use the result returned for this variable to limit when the script runs, dependent on the operation. The scripts are run after all the virtual machines are powered on at the recovery site and the variable is set to FailoverBeforeCommit or MoveBeforeCommit. Use FailoverRollback or MoveRollback when rolling back the Failover or Move operation, to undo whatever changes a previous script has done (such as updating the DNS records).
%ZertoVCenterIP% – The IP address of the hypervisor manager, VMware vCenter Server or Microsoft SCVMM, where the VPG is recovered.
%ZertoVCenterPort% – The port used by the Zerto Virtual Manager to communicate with the hypervisor manager, VMware vCenter Server or Microsoft SCVMM.
■ %ZertoHypervisorManagerIP%: The IP address of the hypervisor manager, VMware vCenter Server or Microsoft SCVMM, where the VPG is recovered.
■ %ZertoHypervisorManagerPort%: The port used by the Zerto Virtual Manager to communicate with the hypervisor manager, VMware vCenter Server or Microsoft SCVMM.
■ %ZertoForce%: A Boolean value, Yes/No, that dictates whether to abort the recovery operation if the script fails. For example, whether to rollback a Move operation when the script fails and returns a non-zero value.
For example, if a specific VPG should not be migrated, the pre-recovery script can determine whether to continue based on the values of the %ZertoOperation% and %ZertoVPGName%.
When specifying scripts in the definition of a VPG, enter values for the Pre-recovery Script and Post-recovery Script:
Command to run: The full path of the script to run. The script must be located on the same machine as the Zerto Virtual Manager for the recovery site.
Params: The values of any parameters to pass to the script. Separate parameters with a space.
Timeout (sec): The time-out in seconds for the script to run. If the script runs before executing a failover, move, or test failover and the script fails or a timeout value is reached, an alert is generated and the failover, move, or test failover is not performed. If the script runs after executing a failover, move, or test failover and the timeout value is reached, an alert is generated. The default timeout value is specified in the Site Configuration Advanced Settings dialog.
See also: