Adding a Checkpoint to a VPG to Identify a Key Point
In addition to the automatically generated checkpoints, you can add checkpoints manually to ensure application consistency and to identify events that might influence recovery, such as a planned switch-over to a secondary generator. You can recover the machines in a VPG to any checkpoint in the journal, to one added automatically or to one added manually. Thus, recovery is done to a point-in-time when the data integrity of the protected virtual machines is ensured.
Note:
■ Adding a checkpoint manually does not guarantee transaction consistency.
■ Changes to a VPG that result in re-synchronization of the VPG results in all checkpoints being removed. Adding checkpoints to the journal is resumed after synchronization completes. A forced synchronization of the VPG only removes checkpoints if the journal fills up during the synchronization.
To add a checkpoint to a VPG:
1. In the Zerto User Interface select ACTIONS > ADD CHECKPOINT.
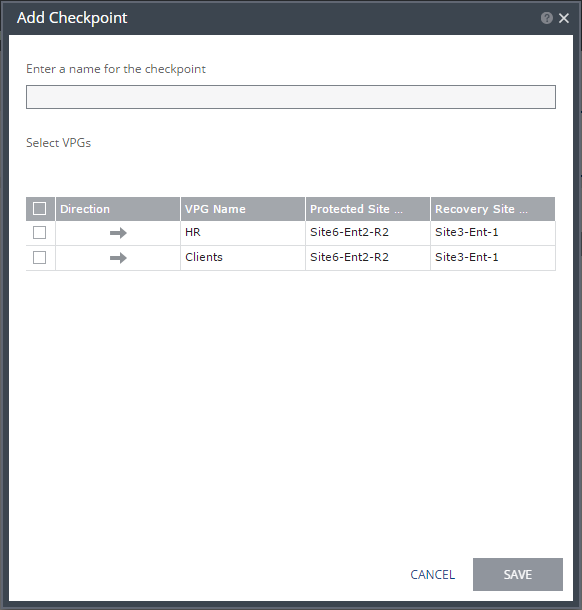
The Add Checkpoint dialog is displayed.
A list of VPGs is displayed with the requested VPG selected. You can select more VPGs to add the same checkpoint to, for example, when something is happening at your site that affects multiple VPGs.
Note: Crash-consistency is per VPG and not across VPGs, even if a checkpoint was added to multiple VPGs.
2. Enter a name for the checkpoint.
3. Click SAVE.
When testing a failover, as described in
“Testing Recovery”, on page 331, or actually performing a failover, as described in
“Managing Failover”, on page 355, you can choose the checkpoint as the point to recover to.