Testing VPGs
You can test the protection of the virtual machines in a VPG using the Start-FailoverTest and Stop-FailoverTest cmdlets.
To start a failover test on a VPG:
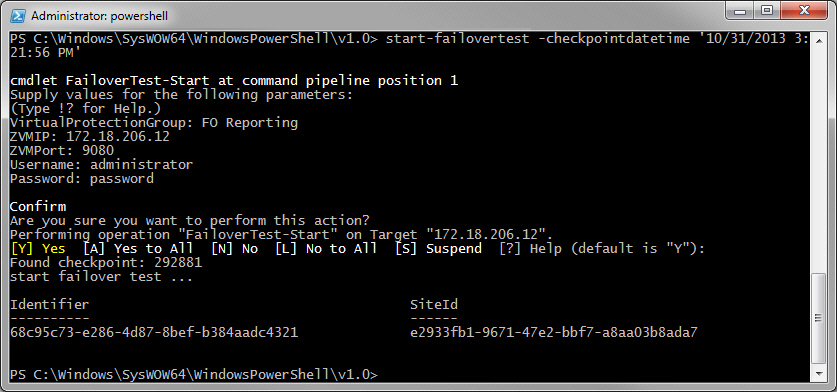
1. Run the Start-FailoverTest cmdlet from the PowerShell prompt, specifying one of CheckpointDateTime, CheckpointID in the command line.
PS C:\Users\Administrators> Start-FailoverTest -CheckpointDateTime ’10/31/2013 3:21:56 PM’ |
2. You are prompted for the VPG to test. The VPG name is case-sensitive.
3. You are prompted for the IP address of one of the Zerto Virtual Manager sites, either where the virtual machines in the VPG are protected or recovered, for the HTTP port used for inbound communication with that Zerto Virtual Manager and a valid username and password, defined in the
users.txt file for the Zerto Virtual Manager where the cmdlet is run, as described in
Defining Credentials to Run Zerto Virtual Replication Cmdlets.
The Start-FailoverTest cmdlet completes, returning the command task identifier and site identifier.
The actual failover test takes time to start up and you can see the progress in the Zerto User Interface.
To stop a failover test:
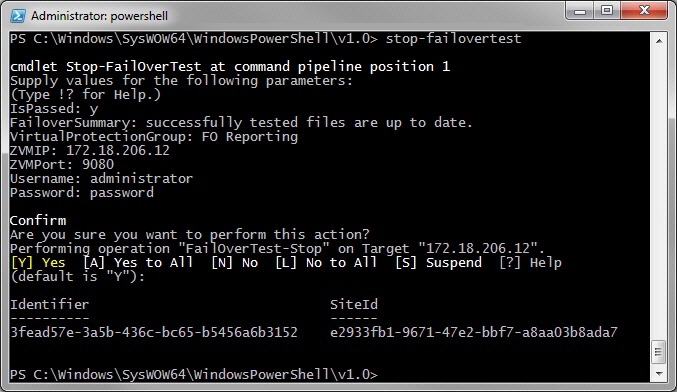
1. Run the Stop-FailoverTest cmdlet from the PowerShell prompt.
PS C:\Windows\SysWOW64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0> Stop-FailoverTest |
2. You are prompted whether the test was successful and then for free text summarizing the test.
3. You are prompted for the VPG to stop testing. The VPG name is case-sensitive.
4. You are prompted for the IP address of one of the Zerto Virtual Manager sites, either where the virtual machines in the VPG are protected or recovered, for the HTTP port used for inbound communication with that Zerto Virtual Manager and a valid username and password, defined in the
users.txt file for the Zerto Virtual Manager where the cmdlet is run, as described in
Defining Credentials to Run Zerto Virtual Replication Cmdlets.
The Stop-FailoverTest cmdlet completes, returning the command task identifier and site identifier.