Azure VPC Setup Guide¶
This topic describes how to set up Puddle on Azure Cloud. This topic is divided into multiple sections:
- Puddle for Azure Architecture
- Setting up Azure Resources like a resource group, vnet, etc.
- Setting up Runtime Dependencies like PostgreSQL database and Redis
- Setting up the Puddle Application
Puddle for Azure Architecture¶
The image below describes the components that work together to build and run Puddle for Azure.
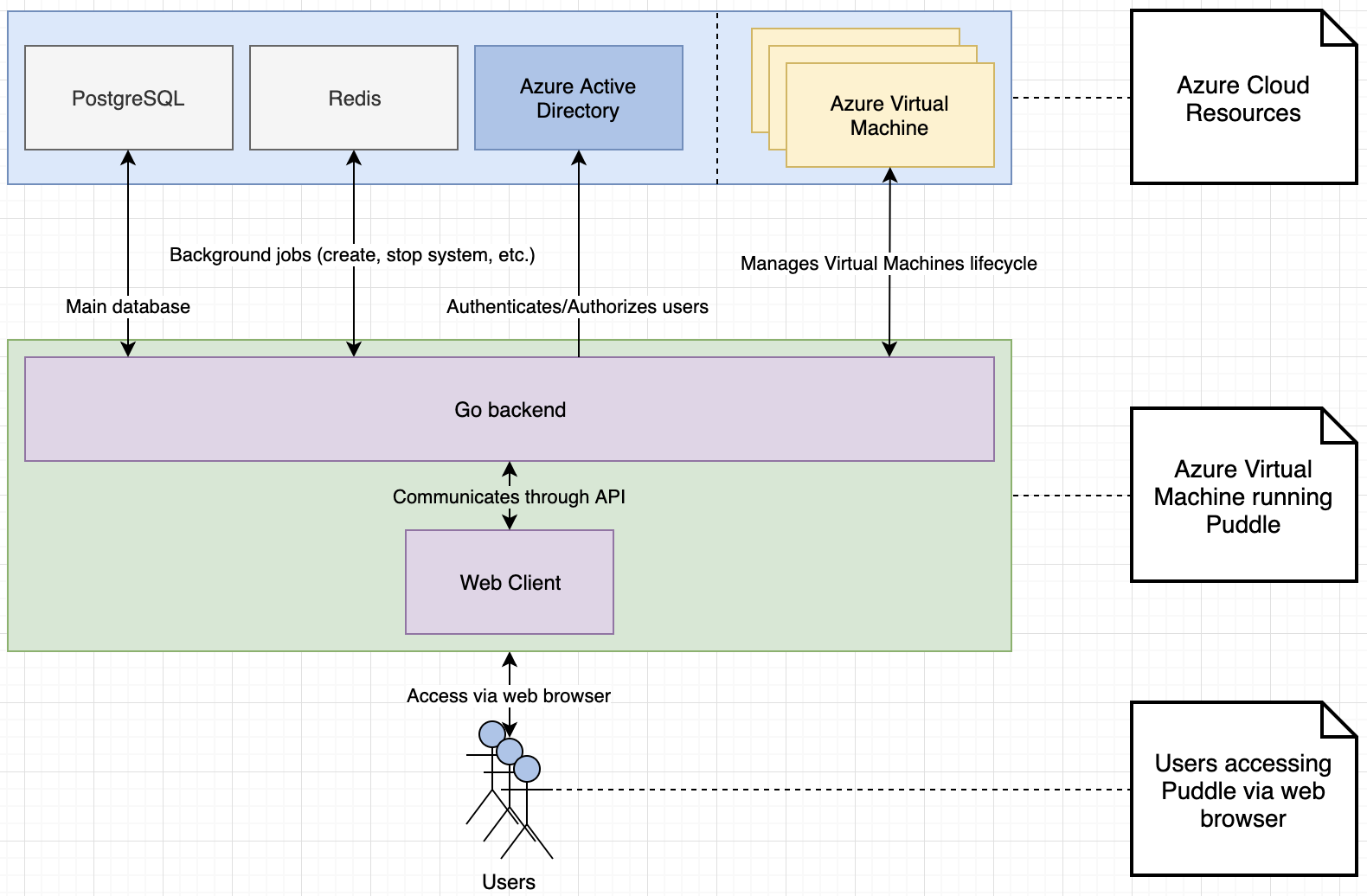
Set up Azure Resources¶
The first step is to set up Azure resources. All of these operations require a user login in at portal.azure.com.
Create a Resource Group¶
- After you are logged in to Azure, go to the Resource groups blade.
- Click Add.
- Fill in the form.
- Remember the name. We will need the name in later steps.
- Remember the location. We will need the location in later steps.
- Click Create.
Create a Network Security Group¶
- Search for Network security groups. Note: Do not use the option with (classic) suffix.
- Click Add.
- Fill in the form.
- Place the Network security group into the Resource group created in first step.
- Set the location of the Network security group to the same value that you specifed when creating the Resource group.
- Remember the name of the Network security group. We will need the name in later steps.
- Click Create.
- Select the newly created Network security group.
- Select Inbound security rules.
- Click Add.
- Set
22, 8888, 12345, 54321as the Destination port ranges.22is SSH. We need to open this port to be able to SSH into Virtual machines launched by Puddle.8888is Jupyter. We need to open this port to be able to access Jupyter.12345is the Driverless AI UI. We need to open this port to be able to access Driverless AI.54321is H2O-3. We need to open this port to be able to access H2O-3 and H2O Flow.
Create Virtual Network and Subnet¶
- Go to the Virtual networks blade.
- Click Add.
- Fill in the form.
- Place the Virtual network into the Resource group created in the first step.
- Set the location of the Virtual network to the same value that you specifed when creating the Resource group.
- Remember the name of the Virtual network. We will need the name in later steps.
- Remember the name of the Subnet. We will need the name in later steps.
Create a Virtual Machine¶
Go to the Virtual Machines blade.
Click Add.
Fill in the form.
- Place the Virtual machine into the Resource group created in the first step.
- Set the location of the Virtual machine to the same location you created in the first step.
- Use Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS as Image.
- Select Standard B2s as Size.
- Select the Authentication type that best suites your needs. Note that the SSH public key is strongly recommended.
Click Next: Disks.
Under OS disk type, select Standard SSD.
Click Next: Networking.
Under Virtual network, specify the Virtual network created in the previous step.
Under Subnet, specify the Subnet created in the previous step.
Set NIC network security group to Advanced.
Click Review + create.
Click Create.
Wait for provisioning to complete.
Go to the Virtual machines blade.
Select the newly created Virtual machine.
Click on Configure next to DNS name.
Set Static under Assignment.
Pick a DNS name. We will need this DNS name later.
Click Save.
Go back to the newly created Virtual machine.
Select Networking.
There should be two security groups available. Make sure the one not explicitly created has rules that allow inbound from ports 22, 80 and 433.
If you do not want to allow HTTP connections, then port 80 should not be allowed.
If you need to add a rule, then click on Add inbound port rule and fill in the form.
- set
22,443and possibly80under the destination port ranges.
- set
Click Add.
Create App Registration and Enterprise Application¶
- Go to Azure Active Directory blade.
- Select App Registrations.
- Click New registration.
- Fill in the form.
- In Supported account types, select Accounts in this organizational directory only (msmarketplaceh2o (Default Directory)).
- Remember the name of the app registration. We will need the name in later steps.
- This will create the Enterprise application as well.
- Click Register.
- Select Manifest.
- Set the “appRoles” key to the following value:
json "appRoles": [ { "allowedMemberTypes": [ "User" ], "description": "Users have basic set of permissions in Puddle.", "displayName": "User", "id": "77e5fac4-3f2a-497d-a70f-1c3e9ac72c83", "isEnabled": true, "lang": null, "origin": "Application", "value": "User" }, { "allowedMemberTypes": [ "User" ], "description": "Administrators have extended permissions in Puddle.", "displayName": "Administrator", "id": "d1c2ade8-98f8-45fd-aa4a-6d06b947c66f", "isEnabled": true, "lang": null, "origin": "Application", "value": "Administrator" } ]Each role definition in this manifest must have a different valid GUID for the
idkey. We will need theidof theAdministratorrole in later steps.
- Click Save.
- Select Authentication.
- Add Redirect URI with a value of
https://<Puddle Server DNS>/login-azure-callback. - Enable both Access tokens and ID Tokens.
- Click Save.
- Go to the Azure Active Directory blade.
- Select Enterprise applications.
- Select the newly created application.
- Select the Properties blade.
- Set Yes for the Enabled for users to sign-in? option.
- If you want only selected users to be able to log in, then set User assignment required? to Yes.
- Set Visible to users? to Yes.
- Click Save.
Create First Administrator¶
- Go to the Azure Active Directory blade.
- Select Enterprise applications.
- Select Users and groups.
- Click Add user.
- Select the desired user.
- Click Select.
- Assign the Administrator role.
- Click Select.
- Click Assign.
These steps can be used to add as many Administrators as required. The User role is used to revoke the Administrator access for the user.
Add Roles to Service Principal¶
- Go to the Resource groups blade.
- Select the newly created Resource group.
- Select Access control (IAM).
- Select Role assignments.
- Click Add.
- Set Owner as Role.
- Fill in the App name to Select.
- Click Save.
- Click Add.
- Set User Access Administrator as Role.
- Fill in the App name to Select.
- Click Save.
Runtime Dependencies¶
After the basic setup of Azure resources is completed, the next step is to set up runtime dependencies for Puddle.
PostgreSQL Database¶
Run the following steps to provision the PostgreSQL database.
- Search for Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers.
- Click Add.
- Fill in the form.
Place the PostgreSQL database into the Resource group created in the first step.
Set the location of the PostgreSQL database to the location that you specified in the first step.
Remember the Server admin login name and Password. We will need them in later steps.
Set the version to 9.6.
Click on Pricing tier.
- Select Basic.
- Set vCore to 2 vCores.
- Set storage to 50GB.
- Click Create to begin provisioning.
Provisioning of the PostgreSQL database will take a few minutes, but we can continue with other steps.
Redis¶
Run the following steps to provision Redis.
- Search for Azure Cache for Redis.
- Click Add.
- Fill in the form.
- Place the Redis into the Resource group created in first step.
- Set the location of the Redis to the same location that you specified in the first step.
- Set Pricing tier to Standard C1.
- Click Create
Provisioning of the Redis will take a few minutes, but we can continue with other steps.
Puddle Application¶
For this part, we will need to create a Virtual machine where the Puddle application will run. Then we will configure nginx and create a configuration file for Puddle. After those are complete, we can start Puddle.
Additional PostgreSQL Configuration¶
- Search for Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers.
- Select the newly created database.
- Select Connection security.
- Click Add client IP.
- Use the Public IP of the Virtual machine as the Start IP and End IP.
- Click Save.
Review the Resource Group¶
The newly created Resource group should now contain these items (some of them are created implicitly):
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL server
- Azure Cache for Redis
- Virtual machine
- Disk
- Network interface
- Public IP address
- Network security group
- Storage account
- Network security group
Install Ansible¶
Puddle requires ansible. Use the following to install ansible:
Ubuntu
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
sudo apt-add-repository --yes --update ppa:ansible/ansible
sudo apt install -y wget unzip redis-tools postgresql-client ansible
wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/puddle-release.h2o.ai/1.5.0/x86_64-ubuntu18/puddle_1.5.0_amd64.deb
sudo apt install -y puddle_1.5.0_amd64.deb
RHEL
sudo bash
yum install epel-release
yum install ansible
yum install postgres10
yum install redis
Create the License File¶
- ssh into the Virtual Machine.
- Create a file
/opt/h2oai/puddle/license.sigcontaining the license. Different path might be used, but this is the default.
Configuring Puddle¶
Now we will need to fill in the config.yaml file, which is located at /etc/puddle/config.yaml. The config.yaml should contain the following:
redis:
connection:
protocol: tcp
address:
password:
tls: true
db:
connection:
drivername: postgres
host:
port: 5432
user:
dbname: puddle
sslmode: require
password:
tls:
certFile:
keyFile:
connection:
port: 8081
license:
file: /opt/h2oai/puddle/license.sig
ssh:
publicKey: /opt/h2oai/puddle/ssh/id_rsa.pub
privateKey: /opt/h2oai/puddle/ssh/id_rsa
auth:
token:
secret:
activeDirectory:
enabled: false
server:
port: 389
baseDN:
security: tls
objectGUIDAttr: objectGUID
displayNameAttr: displayName
administratorsGroup: Puddle-Administrators
usersGroup: Puddle-Users
implicitGrant: false
azureAD:
enabled: false
useAADLoginExtension: true
awsCognito:
enabled: false
userPoolId:
userPoolWebClientId:
domain:
redirectSignIn:
redirectSignOut:
adminsGroup: Puddle-Administrators
usersGroup: Puddle-Users
implicitGrant: false
ldap:
enabled: false
host:
port: 389
skipTLS: false
useSSL: true
insecureSkipVerify: false
serverName:
baseDN:
bindDN:
bindPassword:
bindAllowAnonymousLogin: false
authenticationFilter: "(uid=%s)"
authorizationFlow: userAttribute
authorizationFilter: "(memberOf=%s)"
authorizationSearchValueAttribute: dn
uidAttributeName: uid
uidNumberAttributeName: uidnumber
emailAttributeName: email
implicitGrant: false
adminsGroup: Puddle-Administrators
usersGroup: Puddle-Users
oidc:
enabled: false
issuer:
clientId:
clientSecret:
redirectUrl: /oicd/authorization-code/callback
logoutUrl:
scopes:
- openid
- profile
- email
implicitGrant: false
adminRole: Puddle-Administrators
userRole: Puddle-Users
tokenRefreshInterval: 15min
packer:
path: /opt/h2oai/puddle/deps/packer
usePublicIP: true
buildTimeoutHours: 1
imageNameFormat: '%s'
nvidiaDriversURL:
cudaURL:
cudnnURL:
cudnnDevURL:
terraformURL:
driverlessAIURLPrefix:
h2o3URLPrefix:
terraform:
path: /opt/h2oai/puddle/deps/terraform
usePublicIP: true
pluginDir: /opt/h2oai/puddle/deps/terraform_plugins/
reverseProxy:
enabled: true
port: 443
caCertificate: /opt/h2oai/puddle/certs/ca/cert.pem
caPrivateKey: /opt/h2oai/puddle/certs/ca/key.pem
clientCertificate: /opt/h2oai/puddle/certs/client/cert.pem
clientPrivateKey: /opt/h2oai/puddle/certs/client/key.pem
backend:
baseURL:
connections:
usePublicIP: true
webclient:
usePublicIP: true
userSshAccessEnabled: true
providers:
azure:
enabled: false
authority:
location:
rg:
vnetrg:
vnet:
sg:
subnet:
enterpriseApplicationObjectId:
adminRoleId:
publicIpEnabled: true
packerInstanceType:
sshUsername: puddle
sourceSharedImageGallery:
subscriptionId:
rg:
name:
imageName:
imageVersion:
sourceImageRG:
sourceImageName:
sourceImagePublisher: Canonical
sourceImageOffer: UbuntuServer
sourceImageSku: 16.04-LTS
imageTags:
customDataScriptPath:
preflightScriptPath:
packerCustomDataScriptPath:
packerPreflightScriptPath:
packerPostflightScriptPath:
storageDiskLun: 0
storageDiskFileSystem: ext4
storageDiskDevice: /dev/sdc
aws:
enabled: false
owner:
vpcId:
sgIds:
subnetId:
iamInstanceProfile:
publicIpEnabled: true
packerInstanceType:
encryptEBSVolume: true
ebsKMSKeyArn:
metadataEndpointIAMRole: http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/info
suppressIAMRoleCheck: false
sshUsername: ubuntu
sourceAMIOwner: '099720109477'
sourceAMINameFilter: ubuntu/images/*ubuntu-xenial-16.04-amd64-server-*
packerRunTags:
amiTags:
userDataScriptPath:
preflightScriptPath:
packerUserDataScriptPath:
packerPreflightScriptPath:
packerPostflightScriptPath:
storageEBSDeviceName: /dev/sdf
storageDiskFileSystem: ext4
storageDiskDevice: /dev/nvme1n1
storageDiskDeviceGpu: /dev/xvdf
gcp:
enabled: false
project:
zone:
network: default
subnetwork: ""
publicIpEnabled: true
encryptVolume: true
volumeKmsKeyId: ""
volumeKmsKeyRingName:
volumeKmsKeyRingLocation:
serviceAccountEmail: ""
sshUsername: puddle
storageDiskFileSystem: ext4
startupScriptPath: ""
preflightScriptPath: ""
imageLabels:
packerServiceAccountEmail: ""
packerSourceImageProject: ubuntu-os-cloud
packerSourceImageFamily: ubuntu-1604-lts
packerInstanceType: n1-highmem-8
packerAcceleratorType: nvidia-tesla-v100
packerAcceleratorCount: 1
packerStartupScriptPath: ""
packerPreflightScriptPath: ""
packerPostflightScriptPath: ""
packerRunLabels:
products:
dai:
configTomlTemplatePath: "/opt/h2oai/puddle/configs/dai/config.toml"
license:
authType: local
openid:
baseURL:
configurationURL:
introspectionURL:
authURLSuffix: "/auth"
tokenURLSuffix: "/token"
userinfoURLSuffix: "/userinfo"
endSessionURLSuffix: "/logout"
clientId:
clientSecret:
scope:
- openid
- profile
- email
usernameFieldName: name
userinfoAuthKey: sub
h2o3:
authEnabled: true
q:
license:
appStoreURL: https://appstore.h2o.ai/store
logs:
dir: /opt/h2oai/puddle/logs
maxSize: 1000
maxBackups: 15
maxAge: 60
compress: true
level: trace
mailing:
enabled: true
server:
username:
password:
fromAddress: puddle@h2o.ai
fromName: Puddle
recipients:
offsetHours: 24
idleTimeout:
options:
30min: 30
1h: 60
2h: 120
3h: 180
4h: 240
Never: -1
- ssh into the Virtual machine.
- Fill in the fields in the config.yaml.
Values for
redis.connection.*can be found in following way:
- Microsoft Azure:
- Search for Azure Cache for Redis.
- Select the newly created Redis instance.
- Select Access keys.
- Amazon AWS:
- Go to ElastiCache Dashboard.
- Select Redis.
- Select the cluster used by Puddle.
- Select Description tab.
- Google GCP:
- Go to Memorystore > Redis
- Select the instance used by Puddle.
- See Connection properties
Values for
db.connection.*can be found in following way:
- Microsoft Azure:
- Search for Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers.
- Select the newly created PostgreSQL instance.
- Select Connection strings.
- Use the password that was provided when creating the PostgreSQL database.
- Amazon AWS:
- Go to Amazon RDS.
- Select Databases.
- Select the database used by Puddle.
- Google GCP:
- Go to SQL
- Select the instance used by Puddle.
- See Connect to this instance
tls.certFileshould point to the PEM encoded certificate file if you want to use HTTPS. If you don’t want to use HTTPS, leave this property empty. If you set this property, thentls.keyFilemust be set as well.
tls.keyFileshould point to the PEM encoded private key file if you want to use HTTPS. The private key must be not encrypted by password. If you don’t want to use HTTPS, leave this property empty. If you set this property, thentls.certFilemust be set as well.
connection.portshould be the port where Puddle backend should be running. Defaults to 80 or 443 based on TLS config.
license.fileshould be a path to the file containing the license (created in previous step).
ssh.publicKeyshould be the path to ssh public key (for example /opt/h2oai/puddle/ssh/id_rsa.pub), which will be used by Puddle to talk to the Systems. If this ssh key is changed, Puddle won’t be able to talk to the Systems created with old key, and these will have to be destroyed.
ssh.privateKeyshould be the path to ssh private key (for example /opt/h2oai/puddle/ssh/id_rsa), which will be used by Puddle to talk to the Systems. If this ssh key is changed, Puddle won’t be able to talk to the Systems created with old key, and these will have to be destroyed.
auth.token.secretshould be a random string. It is used to encrypt the tokens between the backend and frontend. For example the following could be used to generate the secret:tr -cd '[:alnum:]' < /dev/urandom | fold -w32 | head -n1
auth.activeDirectory.enabledshould be true/false and is false by default. If true then authentication using ActiveDirectory is enabled.
auth.activeDirectory.servershould be the hostname of the ActiveDirectory server, for example puddle-ad.h2o.ai.
auth.activeDirectory.portshould be the port where ActiveDirectory is accessible, defaults to 389.
auth.activeDirectory.baseDNshould be the BaseDN used for search.
auth.activeDirectory.securityshould be the security level used in communication with AD server. Could be none, start_tls, tls, defaults to tls.
auth.activeDirectory.objectGUIDAttrshould be the name of the attribute used as ID of the user, defaults to objectGUID.
auth.activeDirectory.displayNameAttrshould be the name of the attribute used to determine groups where user is member, defaults to memberOf.
auth.activeDirectory.administratorsGroupshould be the name of the Administrators group. Users in this group are assigned Administrator role in Puddle, users in Administrators group and Users group are considered Administrators.
auth.activeDirectory.usersGroupshould be the name of the Users group. Users in this group are assigned User role in Puddle, users in Administrators group and Users group are considered Administrators.
auth.activeDirectory.implicitGrantshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then users are allowed access to Puddle (using user role) even if they are not members of Administrators nor Users group. If false, then users must be members of at least one group to be allowed access to Puddle.
auth.azureAD.enabledshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then authentication using Azure Active Directory is enabled. Also, if true, you have to setprovider.azure.authority,provider.azure.enterpriseApplicationObjectId, andprovider.azure.adminRoleId(provider.azure.enabledcan be remain false); you also have to setAZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID,AZURE_TENANT_ID, andAZURE_CLIENT_ID(see below).
auth.azureAD.useAADLoginExtensionshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then ssh access to provisioned Virtual machines will use the Azure AD for authentication. Check https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/linux/login-using-aad for more information. Cannot be enabled, if using proxy for egress.
auth.awsCognito.enabledshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then authentication using AWS Cognito is enabled.
auth.awsCognito.userPoolIdshould be the Pool Id, for example us-east-1_SlxxxxML1.
auth.awsCognito.userPoolWebClientIdshould be the App client id. The App client id can be found in following way:
- Go to the AWS Cognito User Pool used by Puddle.
- Select the App client settings.
- Use the value under ID.
auth.awsCognito.domainshould be the domain of the AWS Cognito User Pool, for example https://puddle.auth.<REGION>.amazoncognito.com. The domain can be found in following way:
- Go to the AWS Cognito User Pool used by Puddle.
- Select the Domain name.
auth.awsCognito.redirectSignInshould be https://<SERVER_ADDRESS>/aws-cognito-callback, please replace <SERVER_ADDRESS> with hostname where Puddle is running.
auth.awsCognito.redirectSignOutshould be https://<SERVER_ADDRESS>/logout, please replace <SERVER_ADDRESS> with hostname where Puddle is running.
auth.awsCognito.adminsGroupshould be the name of a group in AWS Cognito User Pool. If users are members of this group, they are assigned Administrator role in Puddle.
auth.awsCognito.usersGroupshould be the name of a group in AWS Cognito User Pool. If users are members of this group, they are assigned User role in Puddle.
auth.awsCognito.implicitGrantshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then users are allowed access to Puddle (using user role) even if they are not members of Administrators nor Users group. If false, then users must be members of at least one group to be allowed access to Puddle.
auth.ldap.enabledshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then authentication using LDAP is enabled.
auth.ldap.hostshould be the LDAP server hostname.
auth.ldap.portshould be the port where LDAP is accessible, defaults to 389.
auth.ldap.skipTLSshould be true/false and is false by default. If true then do not use TLS.
auth.ldap.useSSLshould be true/false and is true by default. If true, then use SSL.
auth.ldap.insecureSkipVerifyshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then skip the server’s certificate verification.
auth.ldap.serverNameshould be the server name from server’s certificate. Defaults to auth.ldap.host.
auth.ldap.baseDNshould be the BaseDN where authentication search will start.
auth.ldap.bindDNshould be the BindDN used by Puddle to query LDAP.
auth.ldap.bindPasswordshould be the password of the user used by Puddle to query LDAP.
auth.ldap.bindAllowAnonymousLoginshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then bind won’t be executed before getting user’s groups.
auth.ldap.authenticationFiltershould be the filter used when authenticating user. Defaults to"(uid=%s)".
auth.ldap.authorizationFlowshould be userAttribute | groupAttribute. Defaults to userAttribute. Based on the value, either attribute of group (for example member) of attribute of user (for example memberOf) will be used in authorization.
auth.ldap.authorizationFiltershould be the filter used when querying user’s groups. Defaults to"(memberOf=%s)".
auth.ldap.authorizationSearchValueAttributeshould be name of the attribute used during authorization. Defaults todn.
auth.ldap.uidAttributeNameshould be the name of the uid attribute. Defaults to uid. Value of uid attribute cannot be empty. Values of uid and uid number create unique identifier of the user.
auth.ldap.uidNumberAttributeNameshould be the name of the uid number attribute. Defaults to uidnumber. Value of uid number attribute cannot be empty. Values of uid and uid number create unique identifier of the user.
auth.ldap.emailAttributeNameshould be the name of the email attribute. Defaults to email. Value of email attribute might be empty.
auth.ldap.implicitGrantshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then users are allowed access to Puddle (using user role) even if they are not members of Administrators nor Users group. If false, then users must be members of at least one group to be allowed access to Puddle.
auth.ldap.adminsGroupshould be the name of the Administrators group. Users in this group are assigned Administrator role in Puddle, users in Administrators group and Users group are considered Administrators.
auth.ldap.usersGroupshould be the name of the Users group. Users in this group are assigned User role in Puddle, users in Administrators group and Users group are considered Administrators.
auth.ldap.cloudResourcesTagsMappingshould be a mapping from LDAP attributes to tags of provisioned cloud resources. The values of the specified LDAP tags are used as values for the specified cloud tags. User cannot change these and they are applied to every system a user launches.
auth.oidc.enabledshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then authentication using OpenID Connect is enabled.
auth.oidc.issuershould be the issuer of the tokens.
auth.oidc.clientIdshould be the clientId used by Puddle.
auth.oidc.clientSecretoptional clientSecret used by Puddle.
auth.oidc.redirectUrlshould be the redirect URL, defaults to /oicd/authorization-code/callback.
auth.oidc.logoutUrlshould be the URL used to sign out users. end_session_endpoint value from the /.well-known/openid-configuration should be used.
auth.oidc.scopesshould be the list of required scopes, defaults to openid, profile, email
auth.oidc.implicitGrantshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then users are allowed access to Puddle (using user role) even if they are not members of Administrators nor Users group. If false, then users must be members of at least one group to be allowed access to Puddle.
auth.oidc.adminRoleshould be the name of the Administrators role. Users with this role are assigned Administrator role in Puddle, users with Administrator role and User role are considered Administrators.
auth.oidc.userRoleshould be the name of the Users role. Users with this role are assigned User role in Puddle, users with Administrator role and User role are considered Administrators.
auth.oidc.tokenRefreshIntervalshould be the interval how often the OAuth2 tokens should be refreshed. Defaults to 15m.
packer.pathshould point to the packer binary. Defaults to/opt/h2oai/puddle/deps/packer.
packer.usePublicIPshould be true/false and is true by default. If true then packer will create VMs with public IP addresses, otherwise private IP will be used.
packer.buildTimeoutHoursshould be the number of hours after which the packer build times out. Default is 1 hour.
packer.imageNameFormatoptional format string used to compute the name of the images. The format string has to contain exactly one %s placeholder. The %s will be substituted by <PRODUCT>-<VERSION>-<TIMESTAMP>. For example if the format string is cust-%s-image and Puddle is building Driverless AI image of version 1.8.0, then the name of the resulting image will be cust-dai-1.8.0-<TIMESTAMP>-image.
packer.nvidiaDriversURLif some custom URL for downloading NVIDIA drivers is required, for example because of internet access restrictions, set it here. Make sure to use version 440.59. Defaults to http://us.download.nvidia.com/XFree86/Linux-x86_64/440.59/NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-440.59.run. For local files use file:///absolute-path/to/required.file.
packer.cudaURLif custom URL for downloading NVIDIA CUDA 10.0 is required, for example because of internet access restrictions, set it here. Make sure to use version 10.0 runfile(local). Defaults to https://developer.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/10.0/Prod/local_installers/cuda_10.0.130_410.48_linux. For local files use file:///absolute-path/to/required.file.
packer.cudnnURLif custom URL for downloading CUDnn is required, for example because of internet access restrictions, set it here. Make sure to use version 7.6.0.64. Defaults to https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/machine-learning/repos/ubuntu1604/x86_64/libcudnn7_7.6.0.64-1+cuda10.0_amd64.deb. For local files use file:///absolute-path/to/required.file.
packer.cudnnDevURLif custom URL for downloading CUDnn-dev is required, for example because of internet access restrictions, set it here. Make sure to use version 7.6.0.64. Defaults to https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/machine-learning/repos/ubuntu1604/x86_64/libcudnn7-dev_7.6.0.64-1+cuda10.0_amd64.deb. For local files use file:///absolute-path/to/required.file.
packer.terraformURLif custom URL for downloading Terraform is required, for example because of internet access restrictions, set it here. Make sure to use version 0.11.14. Defaults to https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/0.11.14/terraform_0.11.14_linux_amd64.zip. For local files use file:///absolute-path/to/required.file.
packer.driverlessAIURLPrefixif custom URL for downloading Driverless AI is required, for example because of internet access restrictions, set it here. For local directory containing Driverless AI installers use file:///absolute-path/to/dir/.
packer.h2o3URLPrefixif custom URL for downloading H2O-3 is required, for example because of internet access restrictions, set it here. For local directory containing H2O-3 installers use file:///absolute-path/to/dir/.
packer.qURLPrefixif custom URL for downloading Q is required, for example because of internet access restrictions, set it here. For local directory containing Q installers use file:///absolute-path/to/dir/. The absolute path to Q installer must have the following structure: file:///absolute-path/to/dir/v<Q_VERSION>/q.tar.gz.
terraform.pathshould point to the terraform binary. Defaults to/opt/h2oai/puddle/deps/terraform.
terraform.usePublicIPshould be true/false and is true by default. If true then terraform will use public IP to communicate with the provisioned Virtual machines, otherwise private IP will be used.
terraform.pluginDiroptional path where Terraform plugins are stored. If set, Terraform will not try to download plugins during initialization.
reverseProxy.enabledshould be true/false and is false by default. If true then reverse proxy is used.
reverseProxy.portshould be port where reverse proxy is running, defaults to 1234.
reverseProxy.caCertificateshould be path to the CA certificate used to issue HTTPS certificates for systems provisioned by Puddle. Must be a PEM encoded certificate with no password protection.
reverseProxy.caPrivateKeyshould be path to the CA private key. Must be a PEM encoded private key with no password protection.
reverseProxy.clientCertificateshould be path to the certificate used when doing forward auth (relevant for H2O-3 systems). Must be a PEM encoded certificate with no password protection.
reverseProxy.clientPrivateKeyshould be path to the private key used when doing forward auth (relevant for H2O-3 systems). Must be a PEM encoded private key with no password protection.
backend.baseURLshould be the URL where Puddle is running, for example https://puddle.h2o.ai.
backend.connections.usePublicIpshould be true/false and is true by default. If true then backend will use public IP to communicate with the provisioned Virtual machines, otherwise private IP will be used.
webclient.usePublicIpshould be true/false and is true by default. If true then public IP is shown in UI, otherwise private IP is displayed.
webclient.outOfCUsUserMsgshould be a message displayed to users when they try to create or start a system, but there are not enough Compute Units available.
webclient.userSshAccessEnabledshould be true/false and is true by default. If true then users are able to download SSH keys of the provisioned VMs.
providers.azure.enabledshould be true/false and is false by default. If true then Microsoft Azure is enabled as provider in Puddle. All variables underproviders.azuremust be set if enabled.
providers.azure.authorityshould be set tohttps://login.microsoftonline.com/<Azure ActiveDirectory Name>.onmicrosoft.com. The Azure Active Directory name can be found in following way:
- Go to Azure Active Directory blade.
- Select Overview.
providers.azure.locationshould be set to the same value that was specified for the Resource group, for exampleeastus.
providers.azure.rgshould be set to the name of the newly created Resource group.
providers.azure.vnetrgshould be set to the name of the Resource group where VNET and Subnet are present.
providers.azure.vnetshould be set to the id of the newly created Virtual network.
providers.azure.sgshould be set to the id of the newly created Network security group.
providers.azure.subnetshould be set to the id of the newly created Subnet.
providers.azure.enterpriseApplicationObjectIdshould be the Object ID of the Enterprise Application. The Enterprose Application Object ID can be found in following way:
- Go to the Azure Active Directory blade.
- Select Enterprise Applications.
- Select the newly created Enterprise Application.
- Use the Object ID.
providers.azure.adminRoleIdshould be set to the ID of the newly created Administator Role in the Application Registration Manifest. The Administator Role ID can be found in following way:
- Go to the Azure Active Directory blade.
- Select App registrations (preview).
- Select the newly created App registration.
- Select Manifest.
- Search for Administator role under appRoles and use the ID of this role.
providers.azure.publicIpEnabledshould be true/false and is true by default. Public IP is created if and only if this is set to true. Must be set to true if at least one of packer, terraform, backend or webclient uses public IP.
providers.azure.packerInstanceTypeshould be the instance type used by Packer to build images. Defaults to Standard_NC6.
providers.azure.sshUsernameshould be the username used when doing SSH/SCP from backend. Defaults to puddle.
providers.azure.sourceSharedImageGallery.subscriptionIdID of the subscription where the Shared Image Gallery with image used as source is present. Leave empty or remove if other image source should be used.
providers.azure.sourceSharedImageGallery.rgname of the resource group where the Shared Image Gallery with image used as source is present. Leave empty or remove if other image source should be used.
providers.azure.sourceSharedImageGallery.namename of the Shared Image Gallery with image used as source is present. Leave empty or remove if other source should be used.
providers.azure.sourceSharedImageGallery.imageNamename of the Image from Shared Image Gallery to use as source. Leave empty or remove if other source should be used.
providers.azure.sourceSharedImageGallery.imageVersionversion of the Image from Shared Image Gallery to use as source. Leave empty or remove if other source should be used.
providers.azure.sourceImageRGname of the resource group containing the private image used as the source for newly built Puddle images. Leave empty or remove if other source should be used.
providers.azure.sourceImageNamename of the private image which should be used as the source for newly built Puddle images. Leave empty or remove if other source should be used.
providers.azure.sourceImagePublisherignored if other source image is set as well (for example private image, or image from Shared Image Gallery). Should be the name of the publisher of the image used as source for newly built Puddle images. Defaults to Canonical. Leave empty or remove if other source should be used.
providers.azure.sourceImageOfferignored if other source image is set as well (for example private image, or image from Shared Image Gallery). Should be the name of the offering of the publisher used as source for newly build Puddle images. Defaults to UbuntuServer. Leave empty or remove if other source should be used.
providers.azure.sourceImageSkuignored if other source image is set as well (for example private image, or image from Shared Image Gallery). Should be the image sku used as source for newly built Puddle images. Defaults to 16.04-LTS. Leave empty or remove if other source should be used.
providers.azure.imageTagsmap of tags used for all Packer resources and produced Image.
providers.azure.customDataScriptPathoptional path to script with custom data to supply to the machine when provisioning new system. This can be used as a cloud-init script.
providers.azure.preflightScriptPathoptional path to script which will be executed during System provisioning by Puddle. This is not a cloud-init script, but a shell script which is executed after cloud init is finished.
providers.azure.packerCustomDataScriptPathoptional path to script with custom data to supply to the machine when building new image. This can be used as a cloud-init script.
providers.azure.packerPreflightScriptPathoptional path to script which will be executed at the beginning of image build process. This is not a cloud-init script, but a shell script which is executed after cloud init is finished.
providers.azure.packerRebootAfterPreflightshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then the Packer VM is rebooted after executing preflight script (even if there no script configured).
providers.azure.packerPostflightScriptPathoptional path to script which will be executed at the end of image build process. This is not a cloud-init script, but a shell script which is executed after cloud init is finished.
providers.azure.packerRebootAfterPostflightshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then the Packer VM is rebooted after executing postflight script (even if there no script configured).
providers.azure.storageDiskLunshould be the LUN of the storage data disk, defaults to 0.
providers.azure.storageDiskFileSystemshould be the filesystem used with storage data disk, default to ext4.
providers.azure.storageDiskDeviceshould be the path to the device used as a storage data disk, defaults to /dev/sdc.
providers.aws.enabledshould be true/false and is false by default. If true then Amazon AWS is enabled as provider in Puddle. All variables underproviders.awsmust be set if enabled.
providers.aws.ownershould be the owner of the newly created resources.
providers.aws.vpcIdshould be the ID of the VPC where Virtual machines will be launched.
providers.aws.sgIdsshould be the list of IDs of the Security Groups applied to provisioned Virtual machines.
providers.aws.subnetIdshould be the ID of the Subnet where Virtual machines will be placed.
providers.aws.iamInstanceProfileshould be the name of the IAM Instance Profile assigned to the Virtual machines.
providers.aws.publicIpEnabledshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then no public IP will be assigned. Must be set to true if at least one of packer, terraform, backend or webclient uses public IP.
providers.aws.packerInstanceTypeshould be the instance type used by packer to build images, defaults to p3.2xlarge.
providers.aws.encryptEBSVolumeshould be true/false and is false by default. If true then EBS Volumes are encrypted using KMS Key. The KMS Key is unique for every system.
providers.aws.ebsKMSKeyArn`should be the arn of KMS key used to encrypt all VMs. If this is empty then a new KMS is created for every VM.
providers.aws.metadataEndpointIAMRoleshould be URL which is used to check assigned IAM role. Defaults to http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/info.
providers.aws.suppressIAMRoleCheckshould be true/false and is false by default. If true then Puddle does not try to obtain assigned IAM role from AWS Metadata endpoint.
providers.aws.sourceAMIOwnerowner of the AMI used as source for newly built Puddle AMIs. Defaults to 099720109477 (Canonical).
providers.aws.sourceAMINameFiltername of the image, with wildcards, which should be used as source for newly built Puddle images. Defaults to ubuntu/images/ubuntu-xenial-16.04-amd64-server-.
providers.aws.packerRunTagsmap of tags used for Packer EC2 instance and Volume. These tags are not applied to produced AMI.
providers.aws.amiTagsmap of tags used for AMIs built by Puddle.
providers.aws.userDataScriptPathoptional path to script with custom user data script which should be used when launching new systems.
providers.aws.preflightScriptPathoptional path to script which will be executed during System provisioning by Puddle. This is not a cloud-init script, but a shell script which is executed after cloud init is finished.
providers.aws.packerUserDataScriptPathoptional path to script with custom user data script which should be used when building new images.
providers.aws.packerPreflightScriptPathoptional path to script which will be executed at the beginning of image build process. This is not a cloud-init script, but a shell script which is executed after cloud init is finished.
providers.aws.packerRebootAfterPreflightshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then the Packer VM is rebooted after executing preflight script (even if there no script configured).
providers.aws.packerPostflightScriptPathoptional path to script which will be executed at the end of image build process. This is not a cloud-init script, but a shell script which is executed after cloud init is finished.
providers.aws.packerRebootAfterPostflightshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then the Packer VM is rebooted after executing postflight script (even if there no script configured).
providers.aws.storageEBSDeviceNameshould be the device name used when attaching EBS Volume, defaults to /dev/sdf
providers.aws.storageDiskFileSystemshould be the filesystem used with storage data disk, default to ext4.
providers.aws.storageDiskDeviceshould be the path to the device used as a storage data disk, defaults to /dev/nvme1n1.
providers.gcp.enabledshould be true/false and is false by default. If true then Google GCP is enabled as provider in Puddle. At least the variablesproviders.gcp.projectandproviders.gcp.zonemust be set if enabled.
providers.gcp.projectshould be id of the project that will host the newly created resources.
providers.gcp.zoneshould be the GCE Zone that will host the newly created resources.
providers.gcp.networkshould be the name of the network that will host the newly created VMs, defaults to “default”. Optional ifproviders.gcp.subnetworkis set (needs to point to the subnet’s network).
providers.gcp.subnetworkshould the name of the subnetwork that will host the newly created VMs, required for custom subnetmode networks, has to be in a region that includesproviders.gcp.zone, has to be inproviders.gcp.networkif specified (incl. the default), defaults to empty.
providers.gcp.publicIpEnabledshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then no public IP will be assigned to Puddle-managed VMs. Must be set to true if at least one of packer, terraform, backend or webclient uses public IP.
providers.gcp.encryptVolumeshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, all systems’ VM volumes will be encrypted. If true, eitherproviders.gcp.volumeKmsKeyIdorproviders.gcp.volumeKmsKeyRingNameandproviders.gcp.volumeKmsKeyRingLocationhave to be set.
providers.gcp.volumeKmsKeyIdshould be the full resource name of the key used to encrypt all VMs, for example projects/XXX/locations/XXX/keyRings/XXX/cryptoKeys/XXX. If empty andproviders.gcp.encryptVolumeis true then a new KMS is created for every system, defaults to empty.
providers.gcp.volumeKmsKeyRingNameshould be the name of the KMS key ring in which unique volume KMS keys will be created. Ignored ifproviders.gcp.volumeKmsKeyIdis set.
providers.gcp.volumeKmsKeyRingLocationshould be the location of the KMS key ring in which unique volume KMS keys will be created. Ignored ifproviders.gcp.volumeKmsKeyIdis set.
providers.gcp.serviceAccountEmailshould be the service account used for Puddle system VMs, uses the default GCE service account if empty, defaults to empty.
providers.gcp.sshUsernameshould be the username for SSH/SCP, defaults to “puddle”.
providers.gcp.storageDiskFileSystemshould be the file system name used for storage disks (must be compatible withmkfson the image), defaults to “ext4”.
providers.gcp.startupScriptPathoptional path to script used as input for startup script (cloud init).
providers.gcp.preflightScriptPathoptional path to script which will be executed during System provisioning by Puddle. This is not a cloud-init script, but a shell script which is executed after cloud init is finished.
providers.gcp.imageLabelsshould be map of labels to be applied to the images built by Puddle, see https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/labeling-resources for value restrictions.
providers.gcp.packerServiceAccountEmailshould be the service account used for Puddle Packer VMs, uses the default GCE service account if empty, defaults to empty.
providers.gcp.packerSourceImageProjectshould be the project that hosts the image family to be used as source for newly built Puddle images, defaults to “ubuntu-os-cloud”.
providers.gcp.packerSourceImageFamilyshould be the image family that should be used as source for newly built Puddle images, defaults to “ubuntu-1604-lts”.
providers.gcp.packerInstanceTypeshould be the machine type used by Packer to build images, defaults to “n1-highmem-8”.
providers.gcp.packerAcceleratorTypeshould be the type of accelerators to be attached to the VM used by Packer to build images, defaults to “nvidia-tesla-v100”. Needs to be available inproviders.gcp.zone.
providers.gcp.packerAcceleratorCountshould be the number of accelerators to be attached to the VM used by Packer to build images, must be >= 0, defaults to 1.
providers.gcp.packerStartupScriptPathoptional path to script used as input for startup script (cloud init) in packer VMs.
providers.gcp.packerPreflightScriptPathoptional path to script which will be executed at the beginning of image build process. This is not a cloud-init script, but a shell script which is executed after cloud init is finished.
providers.gcp.packerRebootAfterPreflightshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then the Packer VM is rebooted after executing preflight script (even if there no script configured).
providers.gcp.packerPostflightScriptPathoptional path to script which will be executed at the end of image build process. This is not a cloud-init script, but a shell script which is executed after cloud init is finished.
providers.gcp.packerRebootAfterPostflightshould be true/false and is false by default. If true, then the Packer VM is rebooted after executing postflight script (even if there no script configured).
providers.gcp.packerRunLabelsshould be map of tags used for Packer VMs and Volumes, these tags are not applied to the resulting image, see https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/labeling-resources for value restrictions.
products.dai.configTomlTemplatePathshould be the path to custom config.toml file, which will be used as default configuration for all new Driverless AI Systems. If not set, the default file is used.
products.dai.licenseshould be the path to DriverlessAI license file. If set, then this license will be automatically installed on all provisioned systems.
products.dai.authTypeshould be local/openid and defaults to local. Local auth uses the htpasswd file injected by Puddle. OpenID auth uses the OpenID Connect. If openid is set, then all of the products.dai.openid.* values are required.
products.dai.openid.baseURLshould be the base url of all the OpenID endpoints. For example if the authorization endpoint is https://example.com/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/auth then the baseURL should be https://example.com/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect.
products.dai.openid.configurationURLshould be the absolute url of configuration endpoint, for example https://example.com/auth/realms/master/.well-known/openid-configuration
products.dai.openid.introspectionURLshould be the absolute url of introspection endpoint, for example https://example.com/auth/realms/master/protocol/openid-connect/token/introspect
products.dai.openid.authURLSuffixshould be the URL suffix for the authorization endpoint. It can be obtained from the configuration URL response.
products.dai.openid.tokenURLSuffixshould be the URL suffix for the token endpoint. It can be obtained from the configuration URL response.
products.dai.openid.userinfoURLSuffixshould be the URL suffix for the userinfo endpoint. It can be obtained from the configuration URL response.
products.dai.openid.endSessionURLSuffixshould be the URL suffix for the logout endpoint. It can be obtained from the configuration URL response.
products.dai.openid.clientIdshould be the client id used by Driverless AI to query the identity provider.
products.dai.openid.clientSecretshould be the client secret used by Driverless AI to query the identity provider.
products.dai.openid.scopeshould be array of required scopes. Usually [openid, profile, email] is sufficient.
products.dai.openid.usernameFieldNameshould be the name of the field in the ID token. Value of this field is then used as username.
products.dai.openid.userinfoAuthKeyshould be the name of the field in Access Token. Value of this field is then used to authorize the user access. Please note, that the value of this field must match the sub from ID token. In most cases this should be sub.
products.h2o3.authEnabledshould be true/false and is false by default. If true the H2O-3 has Basic Auth enabled. Use of reverse proxy is recommended in this case to enable one-click login to H2O-3.
products.q.licenseshould be the path to Q license file. If set, then this license will be automatically installed on all provisioned systems.
products.q.appStoreURLshould be the URL where Q AppStore is running. Defaults to https://appstore.h2o.ai/store
logs.dirshould be set to a directory where logs should be placed.
logs.maxSizeshould be the max size of log file, in MB, defaults to 1000.
logs.maxBackupsshould be the number of old files retained, defaults to 15.
logs.maxAgeshould be the max age of retained files, in days, defaults to 60. Older files are always deleted.
logs.compressshould be true/false and is true by default. If true then the files will be compressed when rotating.
logs.levellog level to use, should be trace/debug/info/warning/error/fatal and is trace by default.
mailing.enabledshould be true/false. If true then mailing is enabled. All fields undermailingare mandatory if this is set to true.
mailing.servershould be the hostname and port of the SMTP server, for example smtp.example.com:587.
mailing.usernameshould be the client username.
mailing.passwordshould be the client password.
mailing.fromAddressshould be the email address used as FROM, for example in case of an address ‘<Puddle> puddle@h2o.ai’ this field should be set to puddle@h2o.ai.
mailing.fromNameshould be the name used as FROM, defaults to Puddle, for example in case of an address ‘<Puddle> puddle@h2o.ai’ this field should be set to Puddle.
mailing.recipientsshould be the space-separated list of recipients.
mailing.offsetHoursshould be a number of hours between repeated email notifications, defaults to 24, does not apply to FAILED system notifications.
idleTimeout.optionsshould be a mapping from labels to values (in minutes) of possible idle timeout options. Use -1 as value for option to never time out.
Configuring Environment Variables¶
The next step is to to fill in the variables in EnvironmentFile file, which is located at /etc/puddle/EnvironmentFile. The EnvironmentFile should contain the following:
# Should point to dir with config.yaml
PUDDLE_config_dir='/etc/puddle/'
# AzureRM Provider should skip registering the Resource Providers
ARM_SKIP_PROVIDER_REGISTRATION=true
# Azure related environment variables, please fill-in all values if you use Azure as provider
# AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID='YOUR-SUBSCRIPTION-ID'
# AZURE_TENANT_ID='YOUR-TENANT-ID'
# AZURE_CLIENT_ID='YOUR-CLIENT-ID'
# AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET='YOUR-CLIENT-SECRET'
# AWS related environment variables, please fill-in all values if you use AWS as provider
# AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='YOUR-AWS-ACCESS-KEY-ID'
# AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY='YOUR-AWS-SECRET-ACCESS-KEY'
# AWS_REGION='AWS-REGION'
# General variables, delete those which are not necessary
# http_proxy=http://10.0.0.100:3128
# https_proxy=http://10.0.0.100:3128
# no_proxy=localhost,127.0.0.1
PUDDLE_config_dirdirectory where the config.yaml file is present.ARM_SKIP_PROVIDER_REGISTRATION- AzureRM Provider should skip registering the Resource Providers. This should be left as true.AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_IDis the ID of the subscription that should be used. This value can be found in following way:- Search for Subscriptions.
- Use the SUBSCRIPTION ID of the subscription you want to use.
AZURE_TENANT_IDis ID of tenant that should be used. This value can be found in following way:- Select Azure Active Directory blade.
- Select App registrations (preview).
- Select the newly created App registration.
- Use Directory (tenant) ID.
AZURE_CLIENT_IDis the Application ID that should be used. This value can be found in following way:- Select Azure Active Directory blade.
- Select App registrations (preview).
- Select the newly created App registration.
- Use Application (client) ID.
AZURE_CLIENT_SECRETclient secret that should be used. This value can be found in following way:- Select the Azure Active Directory blade.
- Select App registrations (preview).
- Select the newly created App registration.
- Select Certificates & Secrets.
- Click New client secret.
- Fill in the form and click Add.
- The secret value should be visible. Copy it because after refreshing the page, this value is gone and cannot be restored.
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS Access Key Id used by Puddle to access the AWS services.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYAWS Secret Access Key used by Puddle to access the AWS services.AWS_REGIONAWS Region used by Puddle to access the AWS services.http_proxyis the URL of proxy server to be used (if required), for example http://10.0.0.3:3128.https_proxyis the URL of proxy server to be used (if required), for example http://10.0.0.3:3128.no_proxyis the comma-separated list of hosts that should be excluded from proxying, for example localhost,127.0.0.1.
Note that you don’t need to enter credentials on GCP by default, since Puddle uses application default credentials (i.e., the VM service account).
Running Puddle¶
After all of the previous steps are successfully completed, we can now start Puddle. Execute the following command to start the server and web UI:
systemctl start puddle
Puddle is accessible on port 443 if HTTPS is enabled, or on port 80 if HTTP is being used.
First Steps¶
At first, you will have to perform some initialization steps:
- Log in to Puddle as the Administrator.
- Go to Administration > Check Updates.
- Either use the update plan from the default URL location, or specify a custom update plan file.
- Click Submit.
- Review the plan and click Apply.
- Go to Administration > Images.
- Build all the images you want to use. Please be aware this can take up to 1 hour.
Once the images are built, your Puddle instance is ready.
Stats Board (Optional)¶
The stats board is an optional component. It’s distributed as Python wheel, and it requires Python 3.6. It’s recommended (although not necessary) to run the board inside a virtual environment.
Use the following to install the required dependencies:
apt install gcc libpq-dev python3.6-dev python-virtualenv
yum install epel-release
yum install gcc postgresql-devel python36-devel python-virtualenv
Use the following to create the virtualenv:
mkdir -p /opt/h2oai/puddle/envs
cd /opt/h2oai/puddle/envs
virtualenv -p python3.6 puddle-stats-env
Please make sure that the virtualenv uses the same name and is available at the same path as in this provided snippet. Otherwise the systemd script used to manage Stats Board will not work.
Use the following to install the stats board. Please note that this command will install dependencies as well:
source /opt/h2oai/puddle/envs/puddle-stats-env/bin/activate
pip install puddle_stats_board-<VERSION>-py3-none-any.whl
Use the following to run the stats board:
systemctl start puddle-dashboard
The stats board is running on port 8050 and is accessible from Puddle UI at http://<PUDDLE_SERVER_ADDRESS>/board. There is a link in the Administration menu as well.