Top HVAC Experts for heat pump prices Capitol Heights, MD. Dial +1 888-829-8510. 24 Hour Calls. Guaranteed Services – Low Prices.
What We Do?
Residential
HVAC Service
Are you searching for residential heating and cooling services that are focused on total home comfort remedies? The experts at Magnolia Plumbing, Heating & Cooling sell, install, and also repair HVAC systems of all makes and models. Call us today!
Commercial
HVAC Service
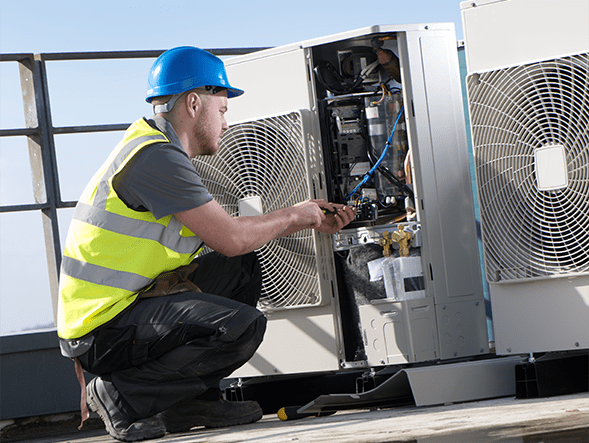
Commercial heating and cooling maintenance and repairs are unavoidable. At Magnolia Plumbing, Heating & Cooling, we provide a comprehensive array of heating as well as cooling solutions to meet every one of your commercial HVAC installation, replacement, repair work, and routine maintenance demands.
Emergency
HVAC Service
Emergencies can and do occur, when they do, rest assured that our experts will be there for you! Magnolia Plumbing, Heating & Cooling can easily provide emergency services at any moment of the day or night. Don’t hesitate to call us the minute an emergency occurs!


24 Hour Service
We offer HVAC services 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year. Among our countless service options ensures that your comfort needs are fulfilled within your timespan and that even your most worrisome heating and air conditioner troubles will be fixed today. Your time is precious– and our team will never keep you waiting!

25 YEARS EXPERIENCE
With over two decades of experience bringing our customer’s total satisfaction, Magnolia Plumbing, Heating & Cooling is a premier provider of HVAC services. Serving homes and businesses in , we perform regular maintenance, repairs as well as new installations modified to your needs and budget requirements.
Testimonials
Contact Us
Magnolia Plumbing, Heating & Cooling
600 Gallatin St NE, Washington, DC 20017, United States
Telephone
+1 888-829-8510
Hours
Open 24 hours
We also provide hvac repair services in the following cities
- ac maintenance Bethesda, MD
- furnace prices District Heights, MD
- furnace prices Falls Church, VA
- central air conditioning unit Temple Hills, MD
- new air conditioner Glen Echo, MD
- ac maintenance Mclean, VA
- ac maintenance Annandale, VA
- heat pump prices Temple Hills, MD
- home ac Mount Rainier, MD
- air conditioner maintenance Mclean, VA
- hvac maintenance Washington , DC
- furnace prices Glen Echo, MD
- ac technician Bethesda, MD
- heating and cooling companies Bethesda, MD
- ac system Chevy Chase, MD
- ac technician Hyattsville, MD
- new air conditioner Hyattsville, MD
- furnace prices Brentwood, MD
- ac system Washington , DC
- heating and cooling companies Mclean, VA
More About Capitol Heights, MD
Capitol Heights is a town in Prince George’s County, Maryland, United States, located on the border of both the Northeast & Southeast quadrants of Washington. The town of Capitol Heights is officially bounded between Southern Avenue NE/SE to the north, Yost Place, and Eastern Avenue NE to the east, the Watts Branch Stream, Brooke Road, and Capitol Heights Boulevard to the south, and Marlboro Pike to the west. The zip code of Capitol Heights is 20743.
Capitol Heights is located at 38°52′55″N 76°54′52″W / 38.88194°N 76.91444°W / 38.88194; -76.91444 (38.881862, -76.914474).[5] East Capitol Street (MD 214), which is a major street in Capitol Heights, evenly divides the Northeast and Southeast quadrants of Washington after leaving Capitol Heights and entering Washington.
Room pressure can be either favorable or negative with respect to outside the space. Positive pressure takes place when there is more air being provided than tired, and prevails to reduce the seepage of outside contaminants. Natural ventilation is an essential aspect in lowering the spread of airborne diseases such as tuberculosis, the cold, influenza and meningitis.
Natural ventilation needs little upkeep and is low-cost. A cooling system, or a standalone a/c unit, provides cooling and humidity control for all or part of a structure. Air conditioned buildings often have sealed windows, due to the fact that open windows would work versus the system intended to preserve constant indoor air conditions.
The percentage of return air comprised of fresh air can normally be controlled by changing the opening of this vent. Typical fresh air consumption is about 10%. [] Cooling and refrigeration are offered through the elimination of heat. Heat can be removed through radiation, convection, or conduction. Refrigeration conduction media such as water, air, ice, and chemicals are described as refrigerants.

It is imperative that the cooling horse power is adequate for the location being cooled. Underpowered air conditioning system will result in power waste and inefficient usage. Appropriate horse power is needed for any air conditioning system set up. The refrigeration cycle uses four important components to cool. The system refrigerant starts its cycle in a gaseous state.
From there it goes into a heat exchanger (sometimes called a condensing coil or condenser) where it loses energy (heat) to the outdoors, cools, and condenses into its liquid phase. An (likewise called metering device) controls the refrigerant liquid to stream at the appropriate rate. The liquid refrigerant is returned to another heat exchanger where it is allowed to vaporize, hence the heat exchanger is often called an evaporating coil or evaporator.
In the procedure, heat is absorbed from indoors and transferred outdoors, leading to cooling of the building. In variable climates, the system might include a reversing valve that changes from heating in winter to cooling in summer season. By reversing the flow of refrigerant, the heat pump refrigeration cycle is altered from cooling to heating or vice versa.
Free cooling systems can have very high efficiencies, and are sometimes integrated with seasonal thermal energy storage so that the cold of winter season can be used for summertime air conditioning. Common storage mediums are deep aquifers or a natural underground rock mass accessed by means of a cluster of small-diameter, heat-exchanger-equipped boreholes.
The heat pump is added-in since the storage serves as a heat sink when the system remains in cooling (rather than charging) mode, causing the temperature to gradually increase throughout the cooling season. Some systems consist of an “economizer mode”, which is often called a “free-cooling mode”. When saving money, the control system will open (totally or partially) the outdoors air damper and close (totally or partly) the return air damper.
When the outdoors air is cooler than the required cool air, this will allow the demand to be fulfilled without using the mechanical supply of cooling (typically cooled water or a direct expansion “DX” system), thus saving energy. The control system can compare the temperature level of the outside air vs.
In both cases, the outside air needs to be less energetic than the return air for the system to get in the economizer mode. Central, “all-air” air-conditioning systems (or package systems) with a combined outside condenser/evaporator unit are typically set up in North American houses, offices, and public buildings, but are difficult to retrofit (set up in a structure that was not created to get it) due to the fact that of the bulky duct required.
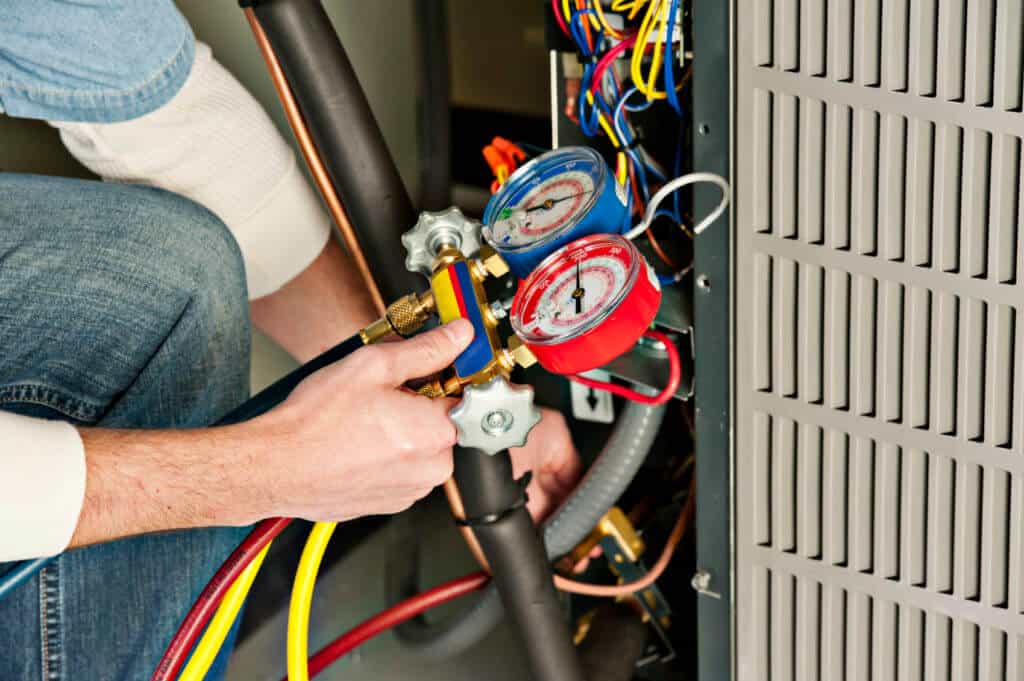

An option to packaged systems is the usage of different indoor and outside coils in split systems. Split systems are chosen and commonly utilized worldwide other than in North America. In North America, divided systems are usually seen in property applications, however they are acquiring appeal in small industrial buildings.
The advantages of ductless cooling systems include simple installation, no ductwork, greater zonal control, flexibility of control and peaceful operation. [] In area conditioning, the duct losses can represent 30% of energy usage. The use of minisplit can lead to energy savings in area conditioning as there are no losses connected with ducting.
Indoor systems with directional vents install onto walls, suspended from ceilings, or fit into the ceiling. Other indoor units mount inside the ceiling cavity, so that brief lengths of duct manage air from the indoor system to vents or diffusers around the rooms. Split systems are more efficient and the footprint is typically smaller sized than the package systems.