Best HVAC Pros for hvac contractors San Marcos, CA. Call +1 619-843-0997. 24 Hour Calls. Guaranteed Services – Low Prices.
What We Do?
Residential HVAC Service
Are you looking for home heating or cooling support services that are focused on total home comfort remedies? The specialists at Carini Heating, Air and Plumbing sell, install, and also repair HVAC units of all makes and models. Call us today!
Commercial HVAC Service
Commercial cooling and heating maintenance and repairs are unavoidable. At Carini Heating, Air and Plumbing, we supply a comprehensive variety of heating and cooling services to meet each of your commercial HVAC installation, replacement, repair work, and maintenance demands.
Emergency HVAC Service
Emergencies may and do occur, when they do, rest comfortably that we will will be there for you! Carini Heating, Air and Plumbing is able to provide emergency assistance at any time of the day or night. Don’t hesitate to get in touch with us the moment an emergency happens!


24 Hour Service
We offer HVAC services 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year. One of our various service options ensures that your comfort needs are achieved within your time frame and that even your most worrisome heating and air conditioner issues will be solved today. Your time is precious– and our experts won’t keep you waiting!

25 YEARS EXPERIENCE
With over two decades of experience bringing our client’s total satisfaction, Carini Heating, Air and Plumbing is a top provider of HVAC services. Serving residential properties and businesses within , we perform regular servicing, repair work and also new installations modified to your needs and budget guidelines.
Testimonials
Contact Us
Carini Heating, Air and Plumbing
825 Washington St, San Diego, CA 92103, United States
Telephone
+1 619-843-0997
Hours
Open 24 hours
We also provide hvac repair services in the following cities
More About San Marcos, CA
San Marcos is a city in the North County region of San Diego County in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2010 census, the city’s population was 83,781. It is the site of California State University San Marcos. The city is bordered by Escondido to the east, Encinitas to the southwest, Carlsbad to the west, and Vista to the northwest. Lake San Marcos is an enclave, or county island, in the southwestern part of the city, within San Marcos’ sphere of influence but technically an unincorporated community.
Room pressure can be either positive or unfavorable with regard to outside the space. Positive pressure takes place when there is more air being supplied than tired, and prevails to minimize the infiltration of outdoors pollutants. Natural ventilation is an essential consider lowering the spread of air-borne diseases such as tuberculosis, the acute rhinitis, influenza and meningitis.
Natural ventilation needs little maintenance and is economical. An a/c system, or a standalone air conditioning system, offers cooling and humidity control for all or part of a structure. Air conditioned buildings typically have sealed windows, because open windows would work against the system meant to maintain continuous indoor air conditions.
The portion of return air comprised of fresh air can normally be controlled by changing the opening of this vent. Normal fresh air intake is about 10%. [] Cooling and refrigeration are provided through the elimination of heat. Heat can be gotten rid of through radiation, convection, or conduction. Refrigeration conduction media such as water, air, ice, and chemicals are described as refrigerants.

It is essential that the a/c horsepower is sufficient for the area being cooled. Underpowered cooling system will cause power wastage and ineffective use. Sufficient horsepower is needed for any a/c unit set up. The refrigeration cycle uses 4 vital components to cool. The system refrigerant starts its cycle in a gaseous state.
From there it enters a heat exchanger (in some cases called a condensing coil or condenser) where it loses energy (heat) to the outside, cools, and condenses into its liquid phase. An (also called metering device) controls the refrigerant liquid to stream at the proper rate. The liquid refrigerant is gone back to another heat exchanger where it is permitted to evaporate, thus the heat exchanger is typically called an evaporating coil or evaporator.
In the procedure, heat is taken in from inside and moved outdoors, resulting in cooling of the building. In variable environments, the system may consist of a reversing valve that changes from heating in winter to cooling in summertime. By reversing the circulation of refrigerant, the heat pump refrigeration cycle is changed from cooling to heating or vice versa.
Free cooling systems can have really high efficiencies, and are sometimes combined with seasonal thermal energy storage so that the cold of winter season can be used for summer cooling. Common storage mediums are deep aquifers or a natural underground rock mass accessed via a cluster of small-diameter, heat-exchanger-equipped boreholes.
The heat pump is added-in because the storage acts as a heat sink when the system remains in cooling (rather than charging) mode, triggering the temperature to slowly increase throughout the cooling season. Some systems consist of an “economizer mode”, which is in some cases called a “free-cooling mode”. When economizing, the control system will open (completely or partially) the outdoors air damper and close (totally or partly) the return air damper.
When the outdoors air is cooler than the demanded cool air, this will permit the demand to be fulfilled without using the mechanical supply of cooling (generally chilled water or a direct expansion “DX” system), therefore saving energy. The control system can compare the temperature of the outdoors air vs.
In both cases, the outdoors air should be less energetic than the return air for the system to get in the economizer mode. Central, “all-air” air-conditioning systems (or package systems) with a combined outside condenser/evaporator unit are frequently installed in North American homes, workplaces, and public structures, but are difficult to retrofit (set up in a building that was not created to get it) since of the bulky air ducts needed.
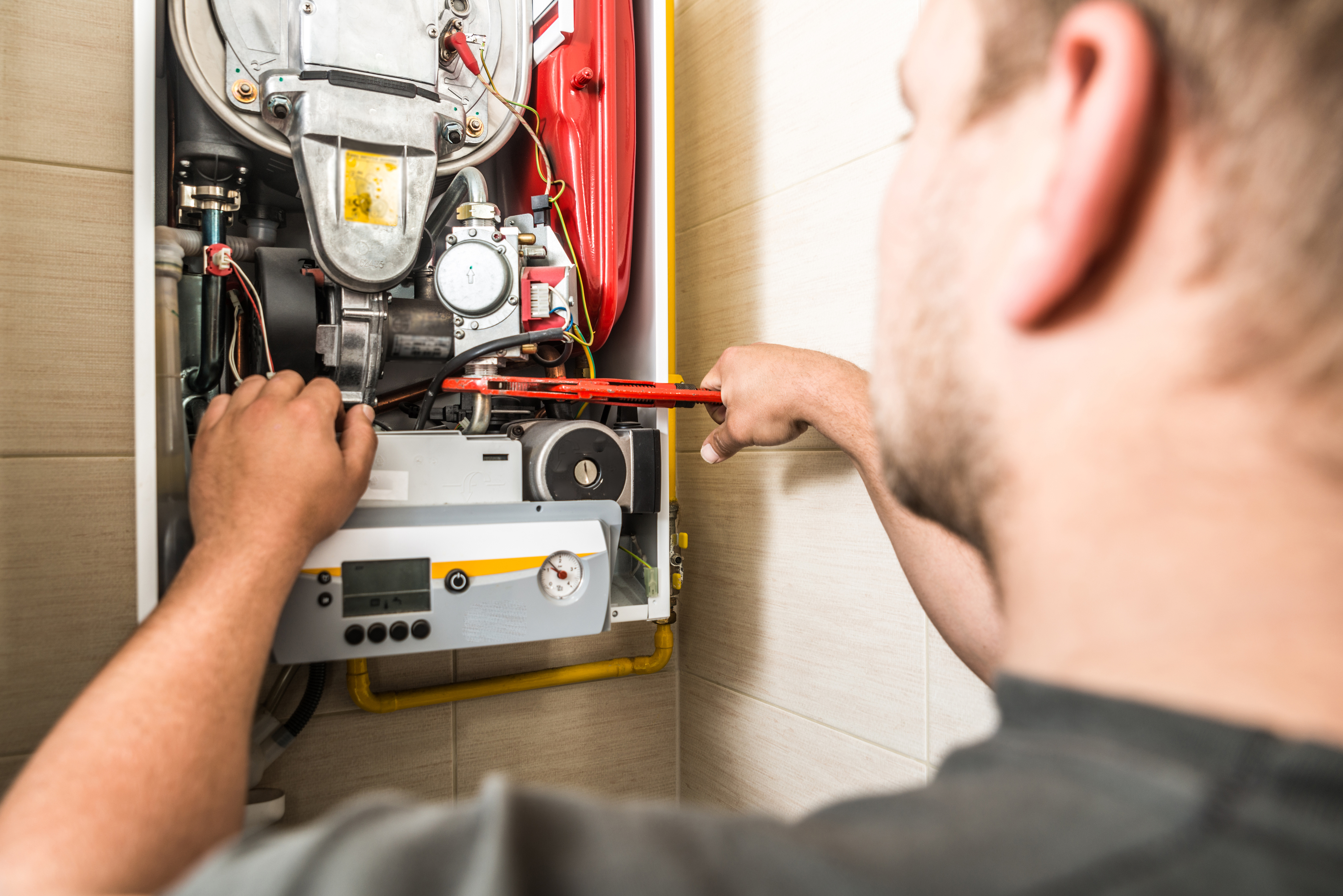

An alternative to packaged systems is making use of different indoor and outdoor coils in split systems. Split systems are chosen and widely used worldwide except in The United States and Canada. In North America, split systems are frequently seen in residential applications, but they are getting appeal in small industrial buildings.
The advantages of ductless cooling systems consist of simple setup, no ductwork, higher zonal control, flexibility of control and peaceful operation. [] In area conditioning, the duct losses can account for 30% of energy intake. Using minisplit can result in energy cost savings in space conditioning as there are no losses related to ducting.
Indoor systems with directional vents mount onto walls, suspended from ceilings, or suit the ceiling. Other indoor systems mount inside the ceiling cavity, so that brief lengths of duct deal with air from the indoor system to vents or diffusers around the rooms. Split systems are more effective and the footprint is normally smaller sized than the bundle systems.