Top Rated HVAC Pros for amana hvac La Jolla, CA. Phone +1 619-843-0997. 24 Hour Calls. Guaranteed Services – Low Prices.
What We Do?
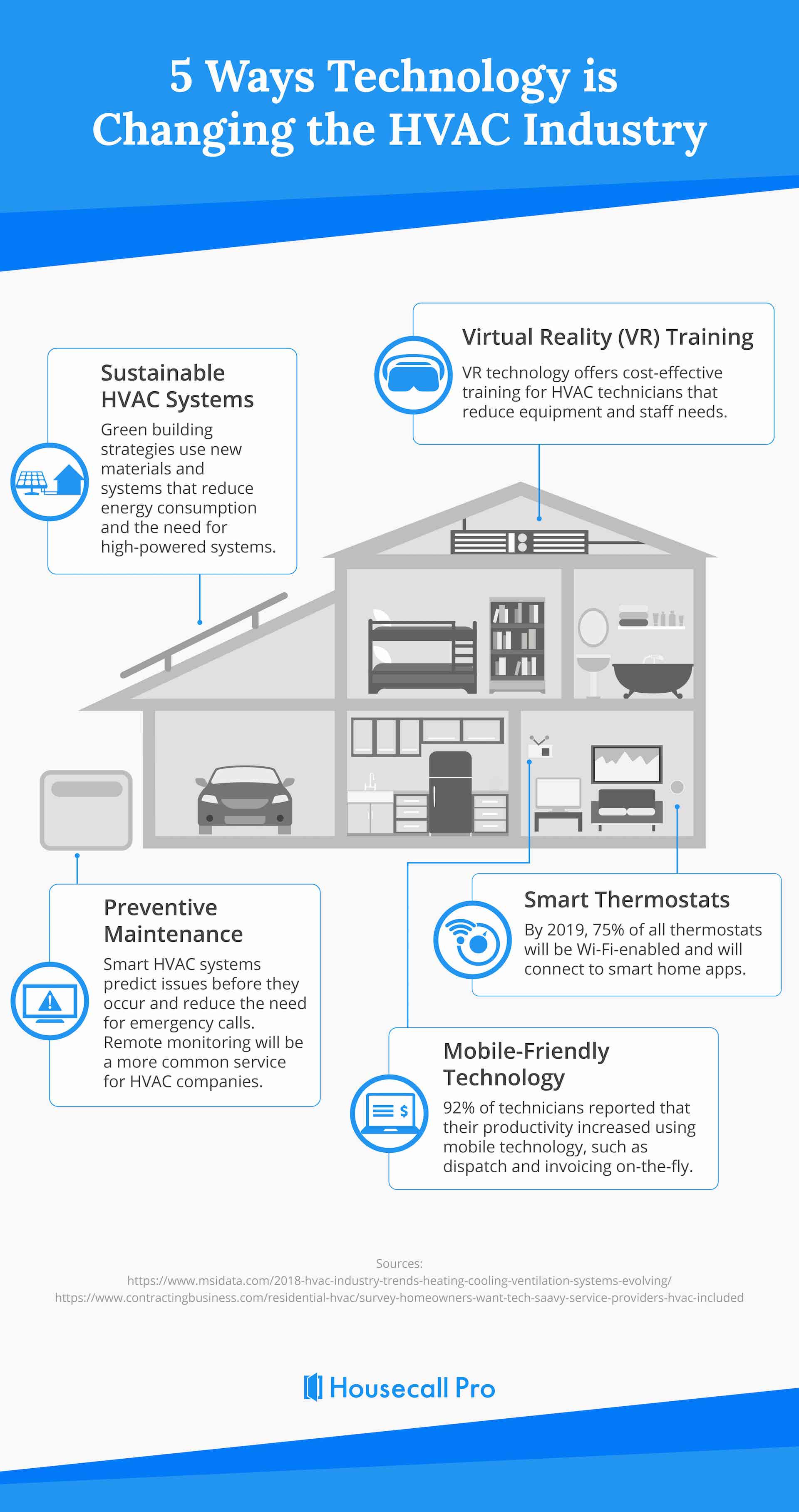
Residential HVAC Service
Are you searching for home heating or cooling support services that are focused on complete home comfort remedies? The experts at Carini Heating, Air and Plumbing sell, install, as well as repair HVAC units of all makes and models. Reach out to us today!
Commercial HVAC Service
Commercial cooling and heating repairs are unavoidable. At Carini Heating, Air and Plumbing, we supply a comprehensive array of heating and cooling solutions to meet every one of your commercial HVAC installation, replacement, repair, and servicing needs.
Emergency HVAC Service
Emergencies will and do develop, and when they do, rest assured that our experts will be there for you! Carini Heating, Air and Plumbing can provide emergency services at any moment of the day or night. Don’t hesitate to contact us the moment an emergency occurs!


24 Hour Service
We deliver HVAC services 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year. One of our countless service options promises that your comfort needs are met within your timespan and also even your most worrisome heating or air conditioner troubles will be solved today. Your time is valuable– and our experts will not keep you waiting!

25 YEARS EXPERIENCE
With over two decades of experience bringing our client’s complete satisfaction, Carini Heating, Air and Plumbing is a premier provider of HVAC services. Serving residential properties and businesses in , we complete routine maintenance, repair work and new installations modified to your needs and budget guidelines.
Testimonials
Contact Us
Carini Heating, Air and Plumbing
825 Washington St, San Diego, CA 92103, United States
Telephone
+1 619-843-0997
Hours
Open 24 hours
We also provide hvac repair services in the following cities
- hvac air purifier La Mesa, CA
- hvac contractors near me Bonita, CA
- hvac contractors near me Del Mar, CA
- hutchinson hvac Del Mar, CA
- hvac compressor El Cajon, CA
- goodman hvac Solana Beach, CA
- high velocity hvac San Marcos, CA
- heil hvac Coronado, CA
- horizon hvac Rancho Santa Fe, CA
- goodman hvac La Jolla, CA
- hvac condensate pump Escondido, CA
- hvac condensate pump El Cajon, CA
- hvac duct cleaning La Jolla, CA
- hvac compressor Escondido, CA
- hutchinson hvac San Diego, CA
- home hvac system Rancho Santa Fe, CA
- bard hvac Bonita, CA
- high velocity hvac Del Mar, CA
- hvac condensate pump San Diego, CA
- commercial hvac La Mesa, CA
More About La Jolla, CA
La Jolla (/lə ˈhɔɪə/ lə HOY-ə, American Spanish: [la ˈxoʝa]) is a hilly, seaside community within the city of San Diego, California, occupying 7 miles (11 km) of curving coastline along the Pacific Ocean within the northern city limits. The population reported in the 2010 census was 46,781.[1][a]
La Jolla is surrounded on three sides by ocean bluffs and beaches[3] and is located 12 miles (19 km) north of Downtown San Diego and 45 miles (72 km) south of Orange County.[4][5] The climate is mild, with an average daily temperature of 70.5 °F (21.4 °C).[6][7]
Space pressure can be either favorable or unfavorable with regard to outside the space. Favorable pressure happens when there is more air being provided than tired, and prevails to decrease the seepage of outdoors contaminants. Natural ventilation is an essential consider reducing the spread of air-borne illnesses such as tuberculosis, the cold, influenza and meningitis.
Natural ventilation needs little upkeep and is economical. An air conditioning system, or a standalone air conditioner, provides cooling and humidity control for all or part of a structure. Air conditioned structures frequently have sealed windows, because open windows would work against the system intended to preserve consistent indoor air conditions.
The percentage of return air comprised of fresh air can usually be manipulated by changing the opening of this vent. Normal fresh air consumption is about 10%. [] A/c and refrigeration are offered through the removal of heat. Heat can be gotten rid of through radiation, convection, or conduction. Refrigeration conduction media such as water, air, ice, and chemicals are described as refrigerants.
It is imperative that the cooling horse power suffices for the area being cooled. Underpowered cooling system will lead to power wastage and inefficient usage. Adequate horse power is required for any air conditioning system installed. The refrigeration cycle utilizes four necessary aspects to cool. The system refrigerant begins its cycle in a gaseous state.
From there it enters a heat exchanger (often called a condensing coil or condenser) where it loses energy (heat) to the outside, cools, and condenses into its liquid stage. An (also called metering device) manages the refrigerant liquid to flow at the proper rate. The liquid refrigerant is returned to another heat exchanger where it is permitted to evaporate, hence the heat exchanger is typically called an evaporating coil or evaporator.
In the process, heat is absorbed from inside and moved outdoors, resulting in cooling of the structure. In variable climates, the system may consist of a reversing valve that changes from heating in winter season to cooling in summer. By reversing the flow of refrigerant, the heat pump refrigeration cycle is altered from cooling to heating or vice versa.
Free cooling systems can have extremely high efficiencies, and are in some cases integrated with seasonal thermal energy storage so that the cold of winter can be used for summer a/c. Typical storage mediums are deep aquifers or a natural underground rock mass accessed through a cluster of small-diameter, heat-exchanger-equipped boreholes.
The heatpump is added-in since the storage functions as a heat sink when the system is in cooling (instead of charging) mode, causing the temperature to slowly increase during the cooling season. Some systems include an “economizer mode”, which is often called a “free-cooling mode”. When economizing, the control system will open (totally or partially) the outside air damper and close (totally or partly) the return air damper.
When the outside air is cooler than the demanded cool air, this will enable the demand to be fulfilled without utilizing the mechanical supply of cooling (normally chilled water or a direct growth “DX” unit), hence saving energy. The control system can compare the temperature level of the outdoors air vs.
In both cases, the outside air needs to be less energetic than the return air for the system to get in the economizer mode. Central, “all-air” air-conditioning systems (or bundle systems) with a combined outdoor condenser/evaporator system are typically set up in North American residences, offices, and public structures, however are tough to retrofit (set up in a building that was not created to get it) due to the fact that of the large air ducts required.

An alternative to packaged systems is making use of separate indoor and outdoor coils in split systems. Split systems are preferred and widely used worldwide except in North America. In North America, divided systems are usually seen in residential applications, but they are getting popularity in small commercial buildings.
The advantages of ductless air conditioning systems consist of simple setup, no ductwork, greater zonal control, flexibility of control and peaceful operation. [] In space conditioning, the duct losses can represent 30% of energy consumption. Making use of minisplit can lead to energy cost savings in area conditioning as there are no losses connected with ducting.
Indoor systems with directional vents mount onto walls, suspended from ceilings, or fit into the ceiling. Other indoor units mount inside the ceiling cavity, so that brief lengths of duct manage air from the indoor system to vents or diffusers around the spaces. Split systems are more effective and the footprint is typically smaller sized than the package systems.
