Top Heating & Cooling Pros for commercial hvac service Petersburg, VA. Phone +1 804-409-9159. 24 Hour Calls. Guaranteed Services – Low Prices.
What We Do?
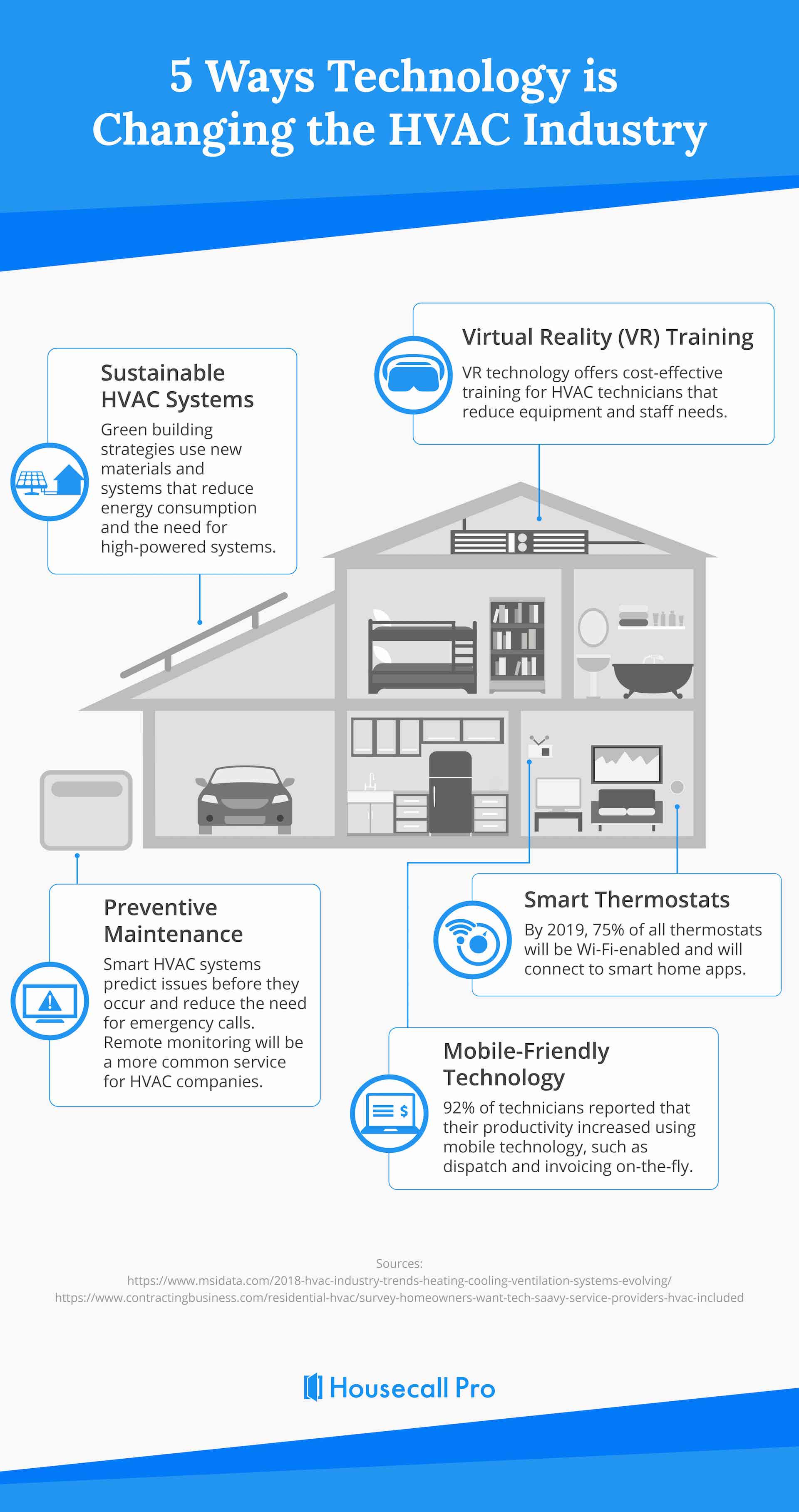
Residential
HVAC Service
Are you searching for home heating and cooling services that are centered on total home comfort remedies? The professionals at River City Heating & Air sell, install, as well as fix HVAC systems of all makes and models. Call us today!
Commercial
HVAC Service
Commercial heating and cooling maintenance and repairs are unavoidable. At River City Heating & Air, we supply a comprehensive range of heating and cooling solutions to meet every one of your commercial HVAC installation, replacement, repair work, and routine maintenance needs.
Emergency
HVAC Service
Emergencies will and do develop, and when they do, rest assured that our team will be there for you! River City Heating & Air is able to deliver emergency support at any moment of the day or night. Don’t hesitate to contact us the minute an emergency happens!


24 Hour Service
We deliver HVAC services 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year. Among our countless service options promises that your comfort needs are achieved within your timespan and also even your trickiest heating or air conditioner troubles will be solved today. Your time is precious– and our company will never keep you waiting!

25 YEARS EXPERIENCE
With over two decades of experience bringing our client’s total satisfaction, River City Heating & Air is a top provider of HVAC services. Serving residential properties and businesses within , we perform routine maintenance, repair work and new installations customized to your needs and budget requirements.
Testimonials
Contact Us
River City Heating & Air
6404 Mallory Dr, Richmond, VA 23226, United States
Telephone
+1 804-409-9159
Hours
Mon-Fri, 8am – 5pm
We also provide hvac repair services in the following cities
- commercial hvac rooftop units West Point, VA
- 24 hour emergency hvac Ashland, VA
- emergency hvac near me Williamsburg, VA
- emergency hvac repair Louisa, VA
- emergency hvac near Prince George, VA
- commercial hvac rooftop units Amelia Court House, VA
- commercial hvac service near me Chester, VA
- commercial hvac preventive maintenance Glen Allen, VA
- carrier finity hvac emergency switch Tappahannock, VA
- hvac emergency service Amelia Court House, VA
- commercial hvac repair Tappahannock, VA
- commercial hvac service technician Amelia Court House, VA
- hvac emergency Fort Lee, VA
- emergency hvac Sandston, VA
- hvac companies emergency Petersburg, VA
- emergency hvac repair Richmond, VA
- commercial hvac repair Mechanicsville, VA
- emergency hvac near Ashland, VA
- commercial hvac services Louisa, VA
- emergency service call hvac Colonial Heights, VA
More About Petersburg, VA
Petersburg is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. As of the 2010 census, the population was 32,420.[5] The Bureau of Economic Analysis combines Petersburg (along with the city of Colonial Heights) with Dinwiddie County for statistical purposes. It is located on the Appomattox River (a tributary of the longer larger James River flowing east to meet the southern mouth of the Chesapeake Bay at the Hampton Roads harbor and the Atlantic Ocean). The city is just 21 miles (34 km) south of the historic commonwealth (state) capital city of Richmond. The city’s unique industrial past and its location as a transportation hub combined to create wealth for Virginia and the Middle Atlantic and Upper South regions of the nation.
Early in the colonial era of the 18th century, Petersburg was the final destination on the Upper Appomattox Canal Navigation System because of its location on the Appomattox River with its connection to the James River to the east at the Atlantic Seaboard fall line (the head of navigation of rivers on the U.S. East Coast) and the tying in with the James River shipping traffic was a strategic place for transportation and commercial activities. It connected commerce as far inland as Farmville, Virginia at the foothills of the Blue Ridge and the Appalachian Mountains chain, to shipping further east into the Chesapeake Bay and North Atlantic Ocean.[6] For similar reasons, 17th century era Fort Henry was built at the order of the Virginia House of Burgesses at Petersburg in 1645 to protect the river traffic.
Space pressure can be either positive or unfavorable with respect to outside the room. Favorable pressure happens when there is more air being provided than tired, and is typical to decrease the infiltration of outdoors impurities. Natural ventilation is a key aspect in reducing the spread of air-borne diseases such as tuberculosis, the acute rhinitis, influenza and meningitis.
Natural ventilation needs little upkeep and is low-cost. An a/c system, or a standalone a/c unit, offers cooling and humidity control for all or part of a building. Air conditioned buildings typically have actually sealed windows, because open windows would work versus the system meant to keep constant indoor air conditions.
The portion of return air comprised of fresh air can normally be controlled by adjusting the opening of this vent. Typical fresh air intake is about 10%. [] Cooling and refrigeration are provided through the removal of heat. Heat can be removed through radiation, convection, or conduction. Refrigeration conduction media such as water, air, ice, and chemicals are referred to as refrigerants.

It is vital that the cooling horsepower suffices for the area being cooled. Underpowered cooling system will lead to power waste and ineffective use. Adequate horsepower is required for any ac system installed. The refrigeration cycle utilizes 4 important elements to cool. The system refrigerant begins its cycle in a gaseous state.
From there it gets in a heat exchanger (in some cases called a condensing coil or condenser) where it loses energy (heat) to the outside, cools, and condenses into its liquid stage. An (also called metering gadget) regulates the refrigerant liquid to stream at the appropriate rate. The liquid refrigerant is gone back to another heat exchanger where it is enabled to vaporize, thus the heat exchanger is frequently called an evaporating coil or evaporator.
In the process, heat is taken in from indoors and moved outdoors, resulting in cooling of the structure. In variable climates, the system might include a reversing valve that switches from heating in winter season to cooling in summertime. By reversing the flow of refrigerant, the heat pump refrigeration cycle is altered from cooling to heating or vice versa.
Free cooling systems can have extremely high effectiveness, and are sometimes integrated with seasonal thermal energy storage so that the cold of winter can be used for summer season air conditioning. Common storage mediums are deep aquifers or a natural underground rock mass accessed through a cluster of small-diameter, heat-exchanger-equipped boreholes.
The heat pump is added-in because the storage acts as a heat sink when the system remains in cooling (as opposed to charging) mode, causing the temperature to gradually increase during the cooling season. Some systems include an “economizer mode”, which is often called a “free-cooling mode”. When economizing, the control system will open (fully or partially) the outdoors air damper and close (totally or partially) the return air damper.
When the outdoors air is cooler than the demanded cool air, this will enable the need to be fulfilled without utilizing the mechanical supply of cooling (usually cooled water or a direct growth “DX” system), therefore conserving energy. The control system can compare the temperature level of the outside air vs.
In both cases, the outdoors air must be less energetic than the return air for the system to enter the economizer mode. Central, “all-air” air-conditioning systems (or package systems) with a combined outdoor condenser/evaporator unit are often set up in North American residences, workplaces, and public structures, but are difficult to retrofit (install in a building that was not created to receive it) due to the fact that of the large duct required.
An option to packaged systems is the use of different indoor and outdoor coils in split systems. Split systems are preferred and commonly used around the world except in North America. In The United States and Canada, divided systems are frequently seen in domestic applications, however they are gaining popularity in little commercial structures.
The advantages of ductless air conditioning systems consist of simple setup, no ductwork, greater zonal control, versatility of control and quiet operation. [] In space conditioning, the duct losses can represent 30% of energy usage. Making use of minisplit can result in energy cost savings in space conditioning as there are no losses associated with ducting.
Indoor units with directional vents install onto walls, suspended from ceilings, or suit the ceiling. Other indoor systems install inside the ceiling cavity, so that brief lengths of duct deal with air from the indoor unit to vents or diffusers around the rooms. Split systems are more effective and the footprint is generally smaller sized than the package systems.
