Top Heating & Cooling Experts for hvac compressor Midland, AL. Call +1 334-298-1278. 24 Hour Calls. Guaranteed Services – Low Prices.
What We Do?
Residential
HVAC Service
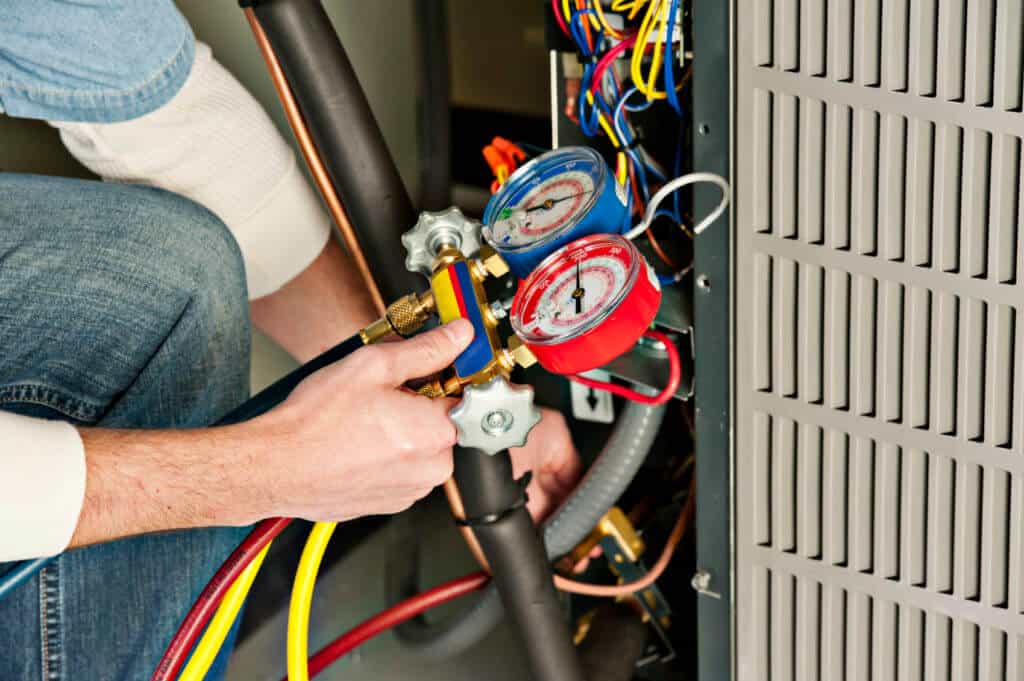
Are you searching for residential heating or cooling services that are centered on total home comfort remedies? The experts at Riley Heating & Air Conditioning sell, install, and fix HVAC systems of all makes and models. Get in touch with us today!
Commercial
HVAC Service
Commercial heating and cooling maintenance and repairs are unavoidable. At Riley Heating & Air Conditioning, we supply a comprehensive range of heating as well as cooling solutions to meet every one of your commercial HVAC installation, replacement, repair work, and servicing demands.
Emergency
HVAC Service
Emergencies may and do occur, and when they do, rest comfortably that we will will be there for you! Riley Heating & Air Conditioning is able to offer emergency assistance at any time of the day or night. Don’t hesitate to call us the minute an emergency happens!


24 Hour Service
We provide HVAC services 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year. One of our various service options guarantees that your comfort requirements are satisfied within your timespan and also even your trickiest heating or air conditioner concerns will be fixed today. Your time is valuable– and our team won’t keep you waiting!

25 YEARS EXPERIENCE
With over two decades of experience bringing our customer’s complete satisfaction, Riley Heating & Air Conditioning is a leading provider of HVAC services. Serving homes and businesses in , we complete routine servicing, repair work and also new installations modified to your needs and budget guidelines.
Testimonials
Contact Us
Riley Heating & Air Conditioning
1019 Knowles Rd, Phenix City, AL 36869, United States
Telephone
+1 334-298-1278
Hours
Mon-Sun, 8am – 9pm
We also provide hvac repair services in the following cities
- hvac contractors near me Fort Mitchell, AL
- heat pump hvac Fortson, AL
- emergency hvac repair Phenix City, AL
- hvac distributors Fortson, AL
- hvac contractors Seale, AL
- hvac contractors Smiths Station, AL
- commercial hvac services Cusseta, AL
- hvac air purifier Waverly Hall, AL
- hvac air filters Valley, AL
- hvac direct Phenix City, AL
- emergency hvac near me Columbus, AL
- commercial hvac services Smiths Station, AL
- hvac duct cleaning Opelika, AL
- hvac condensate pump Lumpkin, AL
- emergency hvac repair Cusseta, AL
- hvac air purifier Hurtsboro, AL
- commercial hvac services Fort Mitchell, AL
- emergency hvac services near me Hurtsboro, AL
- hvac emergency Lumpkin, AL
- emergency hvac services Seale, AL
More About Midland, AL
Multiple creations within this time frame preceded the starts of very first convenience cooling system, which was developed in 1902 by Alfred Wolff (Cooper, 2003) for the New York Stock Exchange, while Willis Carrier geared up the Sacketts-Wilhems Printing Business with the procedure A/C system the same year. Coyne College was the very first school to offer HVAC training in 1899.
Heating systems are devices whose purpose is to create heat (i.e. warmth) for the structure. This can be done via central heating. Such a system consists of a boiler, heating system, or heat pump to heat water, steam, or air in a main place such as a heating system space in a house, or a mechanical space in a large structure.
Heating systems exist for different kinds of fuel, including strong fuels, liquids, and gases. Another kind of heat source is electrical power, typically heating ribbons composed of high resistance wire (see Nichrome). This principle is likewise utilized for baseboard heating units and portable heaters. Electrical heating systems are typically utilized as backup or extra heat for heatpump systems.
Heatpump can extract heat from different sources, such as ecological air, exhaust air from a structure, or from the ground. Heat pumps transfer heat from outside the structure into the air inside. Initially, heatpump HEATING AND COOLING systems were just utilized in moderate environments, however with enhancements in low temperature level operation and reduced loads due to more efficient houses, they are increasing in popularity in cooler environments.


Many contemporary warm water boiler heater have a circulator, which is a pump, to move warm water through the distribution system (as opposed to older gravity-fed systems). The heat can be moved to the surrounding air utilizing radiators, hot water coils (hydro-air), or other heat exchangers. The radiators may be installed on walls or set up within the floor to produce floor heat.
The heated water can likewise supply an auxiliary heat exchanger to supply warm water for bathing and washing. Warm air systems disperse heated air through duct systems of supply and return air through metal or fiberglass ducts. Lots of systems use the very same ducts to distribute air cooled by an evaporator coil for cooling.
Insufficient combustion takes place when there is insufficient oxygen; the inputs are fuels consisting of various pollutants and the outputs are harmful by-products, many dangerously carbon monoxide gas, which is a tasteless and odor-free gas with major negative health impacts. Without proper ventilation, carbon monoxide can be deadly at concentrations of 1000 ppm (0.1%).
Carbon monoxide binds with hemoglobin in the blood, forming carboxyhemoglobin, decreasing the blood’s ability to carry oxygen. The primary health concerns associated with carbon monoxide direct exposure are its cardiovascular and neurobehavioral results. Carbon monoxide can cause atherosclerosis (the hardening of arteries) and can likewise set off heart attacks. Neurologically, carbon monoxide direct exposure reduces hand to eye coordination, watchfulness, and constant performance.
Ventilation is the procedure of changing or changing air in any area to manage temperature level or eliminate any combination of moisture, odors, smoke, heat, dust, air-borne bacteria, or carbon dioxide, and to replenish oxygen. Ventilation consists of both the exchange of air with the outdoors as well as blood circulation of air within the building.
Methods for ventilating a building might be divided into mechanical/forced and natural types. HVAC ventilation exhaust for a 12-story building Mechanical, or forced, ventilation is offered by an air handler (AHU) and used to manage indoor air quality. Excess humidity, odors, and pollutants can often be controlled via dilution or replacement with outside air.
Bathroom and kitchens usually have mechanical exhausts to manage odors and often humidity. Consider the design of such systems consist of the flow rate (which is a function of the fan speed and exhaust vent size) and noise level. Direct drive fans are available for numerous applications, and can reduce upkeep requirements.
Since hot air rises, ceiling fans might be used to keep a space warmer in the winter by flowing the warm stratified air from the ceiling to the floor. Natural ventilation is the ventilation of a structure with outdoors air without utilizing fans or other mechanical systems. It can be via operable windows, louvers, or drip vents when spaces are little and the architecture allows.
Natural ventilation plans can use really little energy, but care must be taken to ensure comfort. In warm or damp climates, keeping thermal convenience exclusively by means of natural ventilation may not be possible. A/c systems are utilized, either as backups or supplements. Air-side economizers likewise use outside air to condition areas, however do so using fans, ducts, dampers, and control systems to present and distribute cool outside air when suitable.
