Google BigQuery¶
Driverless AI allows you to explore Google BigQuery data sources from within the Driverless AI application. This section provides instructions for configuring Driverless AI to work with Google BigQuery. This setup requires you to enable authentication. If you enable the GCS and/or GBQ connectors, those file systems will be available in the UI, but you will not be able to use those connectors without authentication.
In order to enable the GBQ data connector with authentication, you must:
- Retrieve a JSON authentication file from GCP.
- Mount the JSON file to the Docker instance.
- Specify the path to the /json_auth_file.json in the GCS_PATH_TO_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON environmental variable.
Notes:
- The account JSON includes authentications as provided by the system administrator. You can be provided a JSON file that contains both Google Cloud Storage and Google BigQuery authentications, just one or the other, or none at all.
- Google BigQuery APIs limit the amount of data that can be extracted to a single file at 1GB. Any queries larger than this will fail.
GBQ with Authentication Example¶
This example enables the GBQ data connector with authentication by passing the JSON authentication file. This assumes that the JSON file contains Google BigQuery authentications.
nvidia-docker run \
--pid=host \
--init \
--rm \
--shm-size=256m \
-e DRIVERLESS_AI_ENABLED_FILE_SYSTEMS="file,gbq" \
-e DRIVERLESS_AI_GCS_PATH_TO_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON="/service_account_json.json" \
-u `id -u`:`id -g` \
-p 12345:12345 \
-v `pwd`/data:/data \
-v `pwd`/log:/log \
-v `pwd`/license:/license \
-v `pwd`/tmp:/tmp \
-v `pwd`/service_account_json.json:/service_account_json.json \
h2oai/dai-centos7-x86_64:1.4.2-9.0
After Google BigQuery is enabled, you can add datasets by selecting Google Big Query from the Add Dataset (or Drag and Drop) drop-down menu.
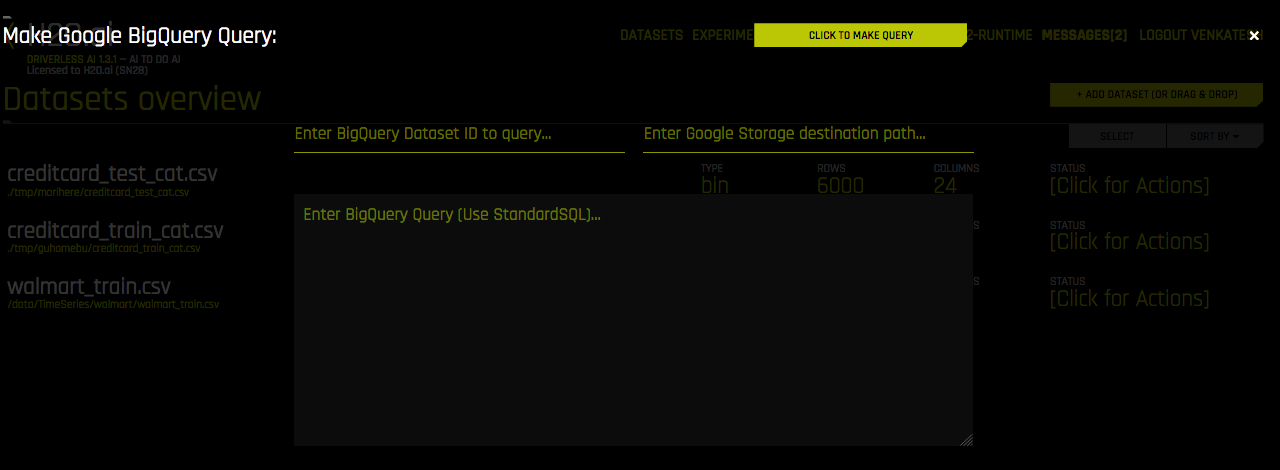
Specify the following information to add your dataset.
- Enter BigQuery Dataset ID to query. Enter a dataset from your user-owned Google Cloud project. Users will need read/write access to this dataset. BigQuery uses this dataset as the location for the new table generated by the query.
- Enter Google Storage destination path: Specify a destination path in Google Cloud Storage to store the dataset. Users will need read/write to the Google Storage bucket. BigQuery will export the new table created by the query to this path. This should be a full path, including the filename and file type extension. (For example, gs://mybucket/myfile.csv)
- Enter BigQuery Query (Use StandardSQL): Enter a StandardSQL query that you want BigQuery to execute. For example:
SELECT * FROM <my_dataset>.<my_table>. - When you are finished, select the Click to Make Query button to add the dataset.