General ArcGIS GIS Server or GeoAnalytics Server or RasterAnalytics Server Site.
Provision a highly available ArcGIS GIS Server or GeoAnalytics Server site.
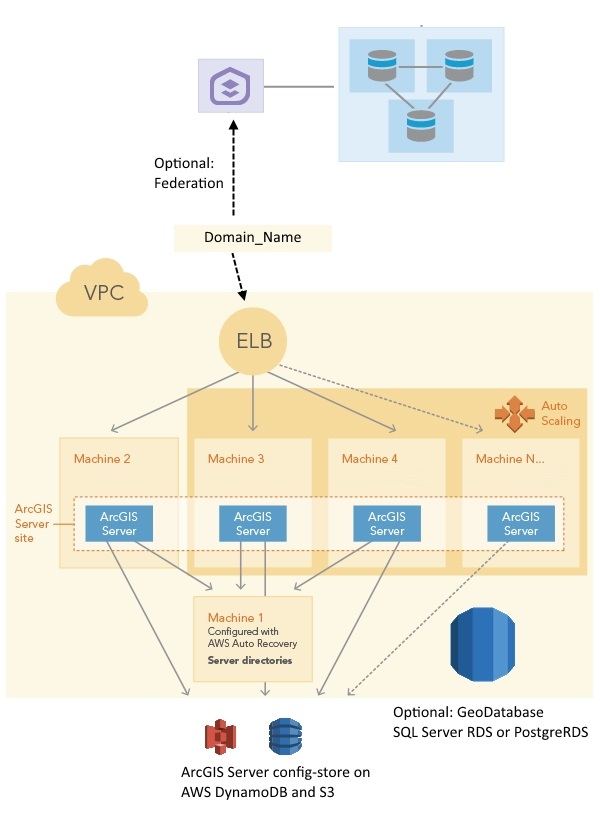
This template provisions a GIS Server or ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server site. You can optionally include geodatabases in AWS RDS for SQL Server or AWS RDS for PostgreSQL. One geodatabase is registered with the ArcGIS Server site, the other is registered as a managed database. This template will set up an architecure as shown in the graphic.
To deploy this template, follow the steps below:
- Create an S3 bucket in your account to store Esri authorization files.
- Create an S3 bucket in your AWS account. This bucket is called DeploymentBucket in the Parameters in the sample template.You will specify this name in the Parameters object when you launch the stack.
- Upload your ArcGIS Server license file to the DeploymentBucket. The ArcGIS Server license role will determine the type of site you create: a GIS Server site or ArcGIS GeoAnayltics Server site.
- Upload your SSL certificate to the DeploymentBucket.
- Run the template to create a CloudFormation stack.
Click Launch Stack for this template. There are a number of properties in the Parameters object that you can set when launching the stack using the template, such as the following:- ASInstanceType: The instance type for the EC2 instances that participate in the ArcGIS Server site. In this site, the primary machine in the site (machine 2 in the graphic) is the first EC2 instance created for the site, and it will be configured with AWS Auto Recovery. If the instance crashes, AWS can restore it in the same AWS Availability Zone to the stage before it crashed. The rest of the EC2 instances (machine 3, machine 4, and machine N...... in the graphic) are created in an AWS Auto Scaling group. These machines join the ArcGIS Server site through accessing the ArcGIS Server config-store. Only certain instance types are allowed.
- DBEngine:
- none: No geodatabases are created.
- sqlserver-se: Geodatabases created in AWS RDS for SQL Server, standard version.
- postgres: Geodatabases created in AWS RDS for PostgreSQL.
- DBAllocatedStorage: Define the size of the RDS storage space. This value is ignored if you choose "none" for the DBEngine variable.
- DBInstanceClass: The AWS RDS instance class. This value is ignored if you choose "none" for the DBEngine variable.
- DeploymentBucket: The S3 bucket you created, which has Esri authorization files uploaded to it.
- DriveSizeData: The size of the data drive. It's the D: drive on Windows and the /gisdata drive on Ubuntu Linux.
- DriveSizeRoot: The size of the root drive. It's the C: drive on Windows and the root drive on Ubuntu Linux.
- FSInstanceType: The instance type for the file server machine. This is machine 3 in the graphic. This machine hosts the server directories for the GIS Server site (and, possibly ArcGIS Server config-store if you choose "CloudStore" for the "StoreType" parameter). This machine is configured with AWS Auto Recovery. If the instance crashes, AWS can restore it in the same AWS Availability Zone to the stage before it crashed. Only certain instance types are allowed.
- KeyName: The EC2 Key Pair to allow you remote access to the instances.
- RunAsUserPassword: This is the password for the account used to run the ArcGIS Server service. (Windows only)
- SecondaryInstances: The number of EC2 instances in the ArcGIS Server site to include in an AWS Auto Scaling group. This number is the number of machines you want in your ArcGIS Server site minus 1. They are machine 2, machine 3, and machine N...... in the graphic.
- ServerLicenseFile: The authorization file for ArcGIS Server that you obtained from Esri (either an ArcGIS GIS Server license or ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server license). It must be in the S3 deployment bucket.
- SiteAdmin: ArcGIS Server primary site administrator account.
- SiteAdminPassword: Password for SiteAdmin.
- SSLCertificateARN: Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the certificate in your AWS certificate manager. For example: "arn:aws:acm:us-east-1:123456789012:certificate/12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789012". This certificate will be deployed to the ELB created in this stack.
- StoreType:
- FileSystem: ArcGIS Server config-store stored on the file system in the same machine.
- CloudStore: ArcGIS Server config-store is stored in AWS DynamoDB and an S3 bucket created by this stack.
- Subnet1: The ID of the subnet to which you want this site deployed.
- Subnet2: The ID of another subnet to which you want this site deployed.
- VPCId: The ID of the VPC where you want to deploy. The subnets you entered above must belong to this VPC.
-
Map your domain name to the ELB created with this stack.
After the stack is created successfully, the output of this stack shows the URLs to ArcGIS Server Manager and the REST page containing the ELB URL. You need to map your domain to the ELB, e.g., mapservergis.domain.comtoarcgis-serverhadynamodb-2116864963.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.comthrough CNAME mapping. Your ArcGIS Server site URL is in the format https:///arcgis. For example, https://servergis.domain.com/arcgis. - Read Capacity units to 250 tables
- Write Capacity units to 25 tables
Notes:
In this template, if you choose "CloudStore" for the "StoreType" variable, the DynomoDB's provision capacity is set to:Steps to complete the deployment
If you created a stand-alone ArcGIS Server site or ArcGIS Image Server site, sign in to ArcGIS Server Manager and configure users and security for the site.
If you created a GeoAnalytics Server site, or the ArcGIS Server site or ArcGIS Image Server site you deployed is intended to be used as a federated server with your base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment, you must manually federate. Note that ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server sites can only be used as federated servers, not as stand-alone ArcGIS Server sites.
- Open "All traffic" in the security groups between the ArcGIS Server stack and base ArcGIS Enterprise stack. Add "All traffic" in each security group to the other security group.
- As a portal administrator, sign in to the Portal for ArcGIS organization you created with your base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment. Follow steps in the Portal for ArcGIS administrator guide that are appropriate for the type of ArcGIS Server site you created. You can use the ArcGIS Server site URL for both Server URL and Server Admin URL during federation, e.g.,
https://gisserver.domain.com/server. The following links go to instructions for Windows operating systems; use the drop-down list at the top of each topic to change to Linux instructions.