Running Search and Restore Operations
■ Perform a Search for files and folders within the virtual machines which were configured for File System Indexing.
■ Select the files and folders in a retention set and restore on the recovery site.
The virtual machines on the protected site remain protected and live.
(vCloud Director only) When the recovery site, where the retention sets are stored, is managed by a cloud service provider using vCloud Director, only the cloud service provider can initiate the restore. When you restore a VPG to a recovery vCD site, the VMs are created in a vCenter Server and have to be manually imported into vCD.
Considerations:
■ When running multiple Search operations, make sure to monitor the ZVM resources during these operations.
To run a search for files and folders:
1. In the Zerto User Interface select ACTIONS > SEARCH AND RESTORE.
The Search and Restore window is displayed.
Only VMs that were successfully indexed appear in the VM in a VPG search field.
2. You can specify the following values, which are then applied to the Search:
■ VM in VPG: | Type the name of the virtual machine. |
■ Retention Set Date: | Specify the date range of the search. The default range is the last 7 days. |
■ File/folder name: | Type the file or folder name to search for. You can use the wildcard * at the end, middle or the beginning of a word. |
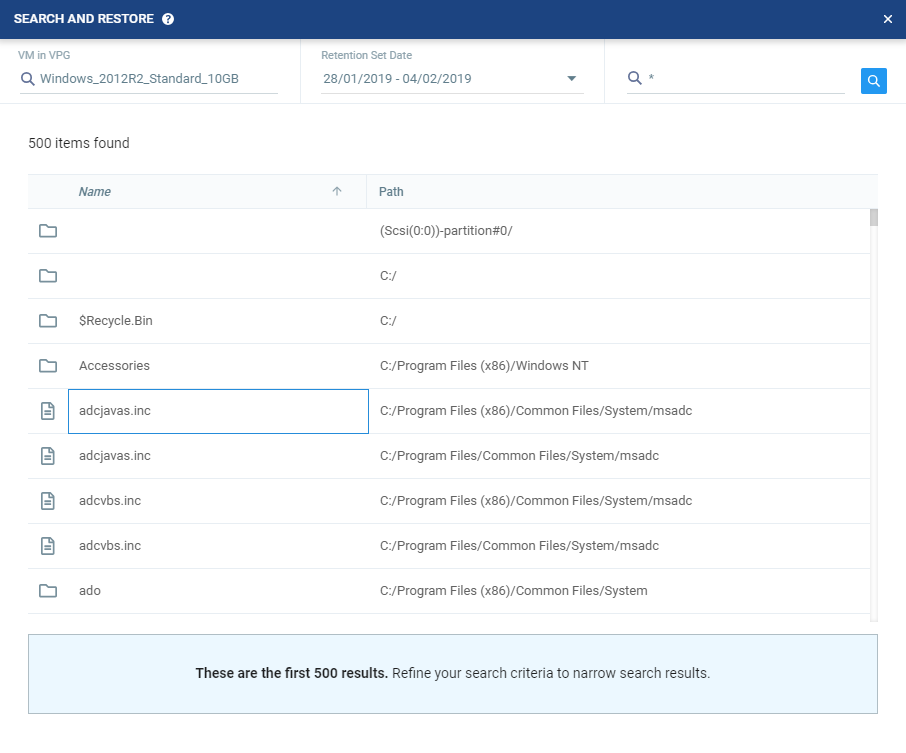
3. Click the Search Icon.
The Search results appear. The Search is limited to 500 results at a time.
The Search results specify the name of the file or folder and the path.
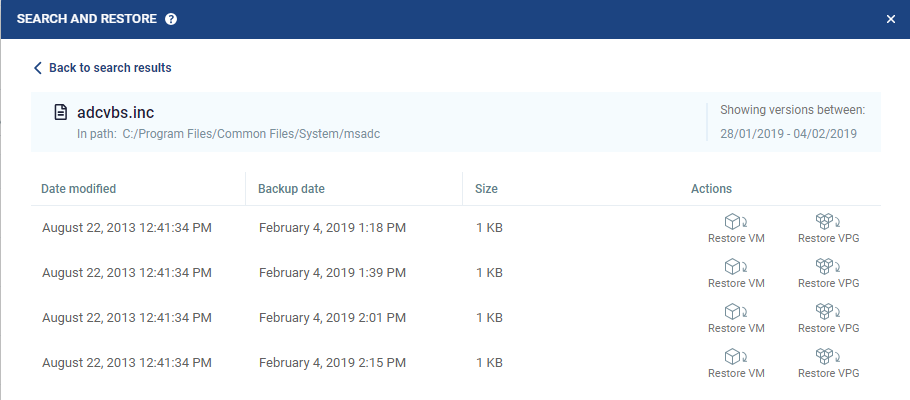
4. Select the file or folder. A list of revisions of that file or folder is displayed according to the retention set date previously selected.
The revisions display a list of restore points of the retention sets. The revisions view specifies the following:
■ Date Modified: | The date in which the file or folder was modified. |
■ Retention Set Date: | The date of the restore point. |
■ Size: | The size of the file. The size of a folder is not displayed. |
■ Actions: | Select either Restore VM or Restore VPG. |
5. Choose a restore point and click the Restore VM or Restore VPG icon.
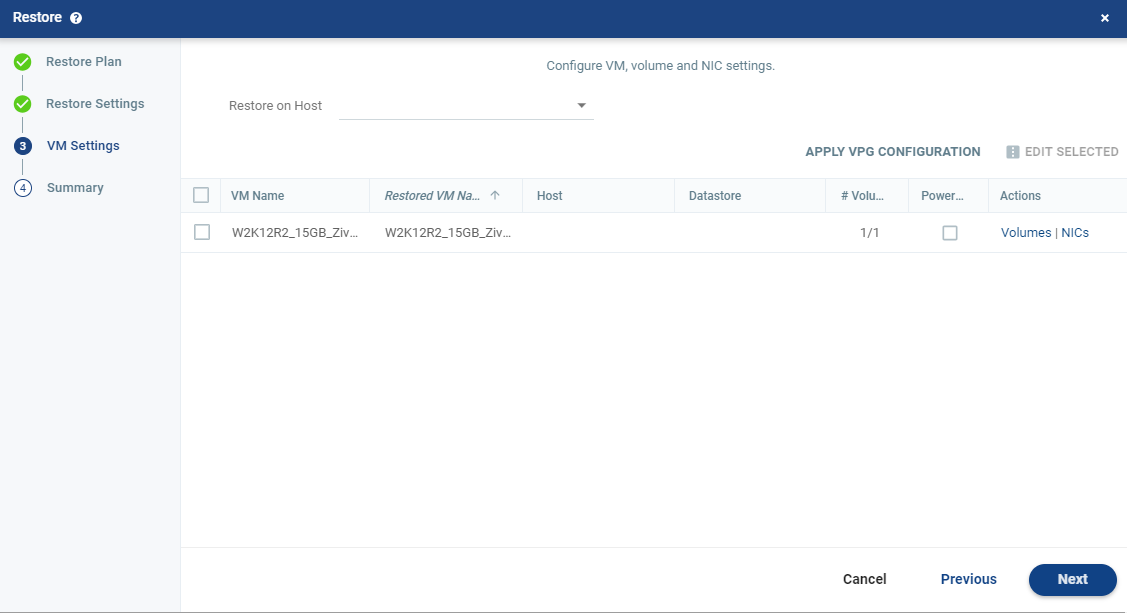
The Restore window is displayed on the VM SETTINGS step.
The list of virtual machines that can be restored is displayed.
6. You can specify the following which are then applied to all the virtual machines to be restored:
■ Restore on Host: The IP address of the host where you want the VPG restored.
After selecting a host, the Restore on Datastore field is displayed.
■ Restore on Datastore: The datastore to use for the restored VPG files.
- Or -
■ Alternatively, you can use the recovery host and storage specified for each virtual machine in the VPG definition by clicking APPLY VPG CONFIGURATION. To use this option, the VPG must still be available.
7. To change the information in a field, click the field and update the information.
8. To change the host or datastore information for several virtual machines at the same time, select the virtual machines and click EDIT SELECTED.
The Configure VM Settings window is displayed.
If one or more of the volumes which was retained, was deleted after the retention set was created, or if one of the volumes failed, the entire retention process for that VM will fail.
You can specify the following values, which are then applied to all the selected virtual machines:
■ Restore on Host: The IP address of the host where you want the virtual machines restored.
■ Restore on Datastore: The datastore to use for the restored virtual machine files.
■ Power On: Select this if you want the restored virtual machines to be powered on.
- Or -
Alternatively, you can use the recovery host and storage specified for each virtual machine in the VPG definition by clicking APPLY VPG CONFIGURATION.
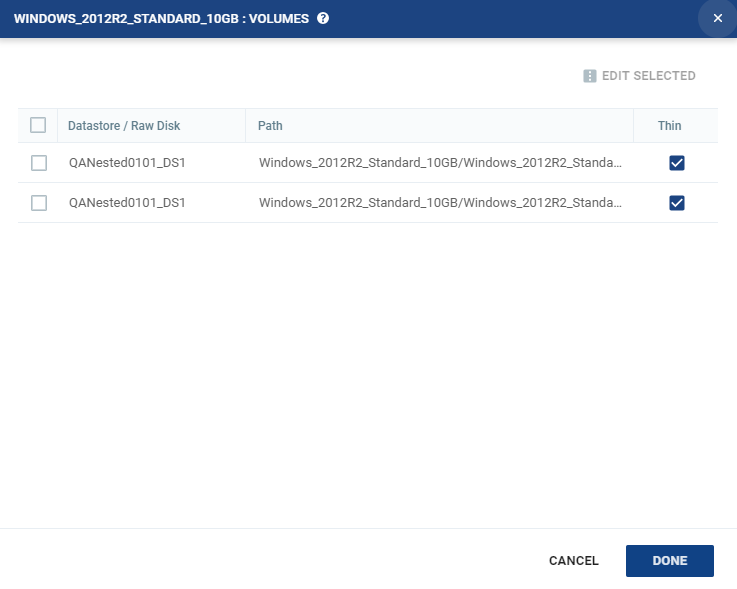
9. To specify the volume information for each virtual machine, from the Actions column, click Volumes.
The Volumes dialog is displayed:
10. To edit information in a field, click the field and update the information.
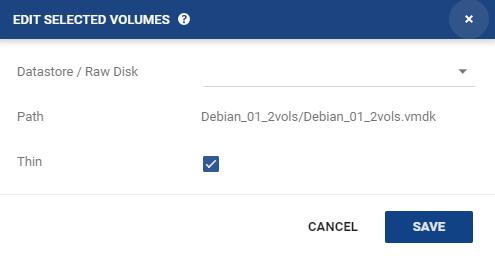
11. To edit information for several datastores at the same time, select the datastores and click EDIT SELECTED.
The Edit Selected Volumes dialog is displayed.
12. Specify the datastore settings.
■ Datastore / Raw Disk: The storage or RDM disk where the virtual machine files will be restored.
■ Path: This field cannot be edited in this window. The path to the datastore/storage/RDM disk. If more than one datastore is selected, the path is not displayed.
■ Thin: Whether the virtual machine disks will be thin‑provisioned or not.
13. Click Save to return to the Volumes dialog, then click DONE.
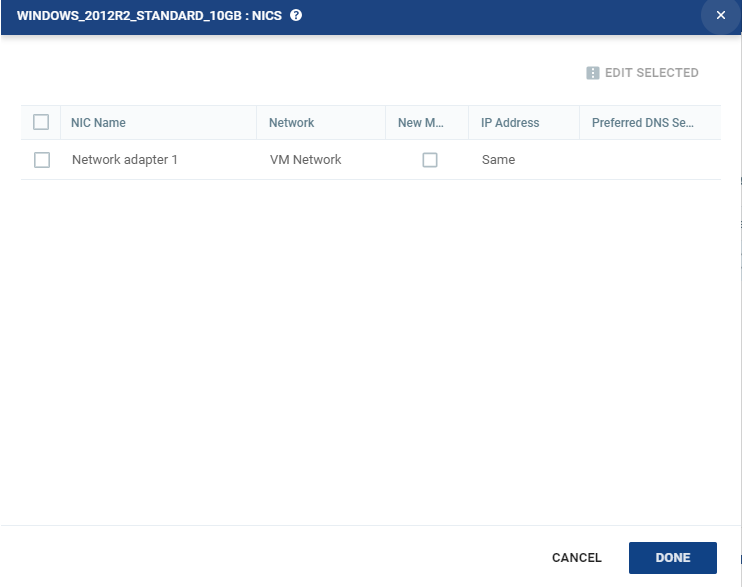
14. To specify the NIC information for each virtual machine, from the Actions column, click NICs.
The NICs window is displayed:
15. To edit information in one field, click the field and update the information.
16. To edit information for several virtual NICs at the same time, select the NICs and click EDIT SELECTED.
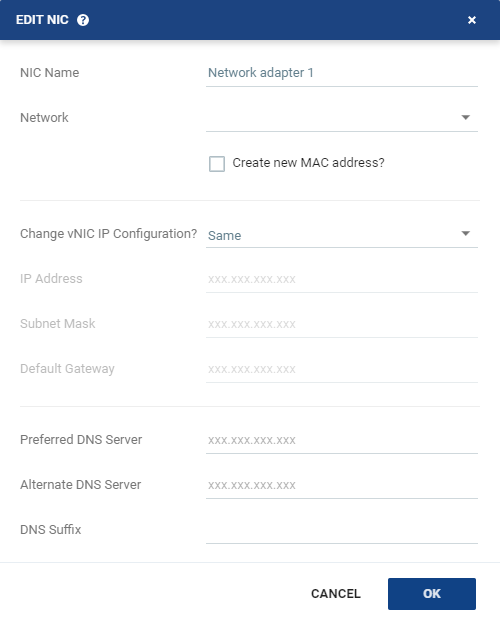
The Edit NIC dialog is displayed.
17. Specify the NIC settings.
■ NIC Name: | The name of the selected NIC. |
■ Network: | The network to use for the restored virtual machine. |
■ Create new MAC address: | The Media Access Control address (MAC address) to use. The default is to use the same MAC address for the restored virtual machine that was used in the protected site. Select the checkbox to create a new MAC address on the restore site. |
■ Change vNIC IP Configuration: | Whether or not to keep the default virtual NIC (vNIC) IP configuration. You can only change the vNIC IP after the restore has completed with VMware Tools installed. ■ If you select a static IP connection, you must set the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. Optionally, change the preferred and alternate DNS server IPs and the DNS suffix. ■ If you select DHCP, the IP configuration and DNS server configurations are assigned automatically, to match the protected virtual machine. You can change the DNS suffix. |
■ IP Address: | The IP for the restored virtual machine. This can be the same IP as the original protected virtual machine. |
■ Subnet Mask: | The subnet mask for the network. The default value is 255.255.255.0. |
■ Default Gateway: | The default mask for the network. |
■ Preferred DNS Server: | The IP address of the primary DNS server to handle Internet protocol mapping. |
■ Alternate DNS Server: | The IP address of the alternate DNS server. |
■ DNS Suffix: | The DNS name excluding the host. |
18. Click OK.
19. Click DONE.
20. Click NEXT.
The SUMMARY step is displayed. Review the details of the restore.
21. If this is the retention set which you want to restore, click RESTORE.
The virtual machines are created from the Repository at the recovery site.