Adding Virtual Machines to a VPG
You can add virtual machines that are not already included in a VPG, to an existing VPG.
Note: You cannot edit the VPG to add a virtual machine while a backup job is running.
Only virtual machines with a maximum of 60 disks can be protected.
60 disks requires 4 SCSI controllers each with a maximum of 15 disks.
When the recovery site is AWS
Only virtual machines that are supported by AWS can be protected by Zerto Virtual Replication. Refer to AWS documentation for the supported operating systems.
Each machine that you intend to protect must have at least 250MB free space because AWS adds files to the recovered machines during failover, move, test failover, and clone operations.
Protected volumes are recovered in EC2 as EBS disks with magnetic disk type. Virtual machines with disks that are less than 1GB are recovered with disks of 1GB. Additional volumes might be created in the recovered instance, dependent on the instance type used for the recovery. These volumes can be ignored.
Note: By default, every m3.xlarge instance is created with two SSD disks. These disks are in addition to the disks associated with each protected virtual machine.
A VPC must exist, and a security group and subnet must be assigned to it and to all other VPCs you want to use for recovered virtual machines.
The following limitations apply when protecting to AWS:
■ You cannot protect machines that have a disk larger than 1TB.
■ AWS supports virtual machines running a Windows operating system with up to 26 volumes, including the boot disk.
■ AWS supports virtual machines running a Linux operating system with up to 40 volumes, including the boot disk.
To add a virtual machine to a VPG:
1. In the VPGs tab in the Zerto User Interface, select the VPG and click MORE > Edit VPG. You can also select the VPG to display the VPG details and click EDIT VPG.
The Edit VPG wizard is displayed, enabling you to edit the VPG, including adding and removing virtual machines from the VPG.
In the VMs step, select the virtual machines to add and click the arrow pointing right to include these machines in the VPG. If you want to define the boot order of the VPGs, click DEFINE BOOT ORDER.
2. Configure the settings for the new virtual machines in the same way that you configured the other virtual machines in the VPG, when you created the VPG.
3. Click DONE.
The virtual machines are added to the VPG. This process may take a few minutes. While the VPG definition is being updated, you cannot perform any operation on the VPG, such as adding a checkpoint, editing its properties, or recovering it.
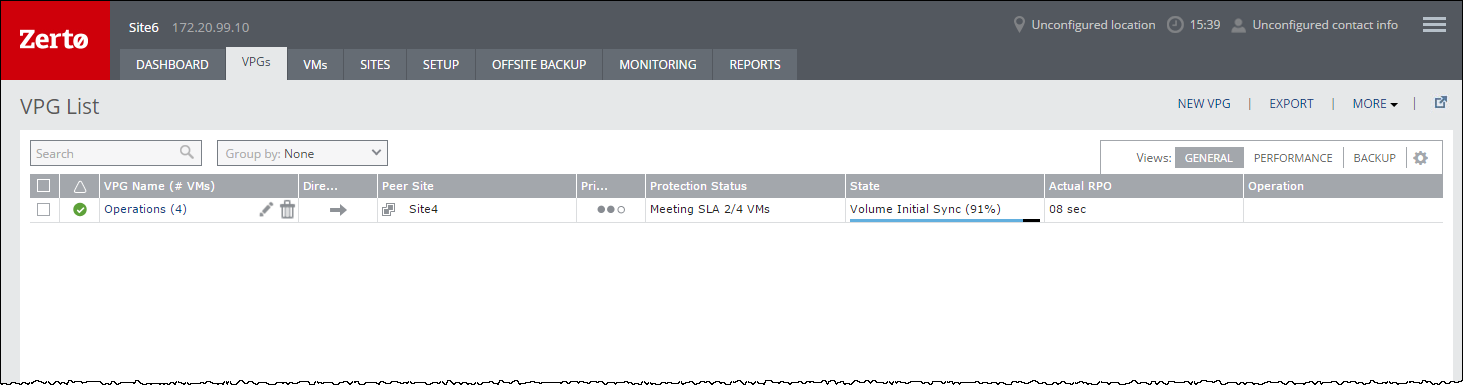
After the VPG definition has been updated, the protected and recovery sites are then synchronized. During the synchronization period, the Protection Status displayed in the VPGs tab of the Zerto User Interface is: Meeting SLA n/m VMs
where n is the number of virtual machines that were originally in the VPG, and m is the total number of virtual machines in the VPG, including the virtual machines that are currently being synced. While the virtual machines that were added are being synced, the VPG can be failed over but the failover only includes the original virtual machines in the VPG.
For example, in the following screen shot, 2 virtual machines were added to the VPG, Operations, that originally contained 2 other virtual machines.
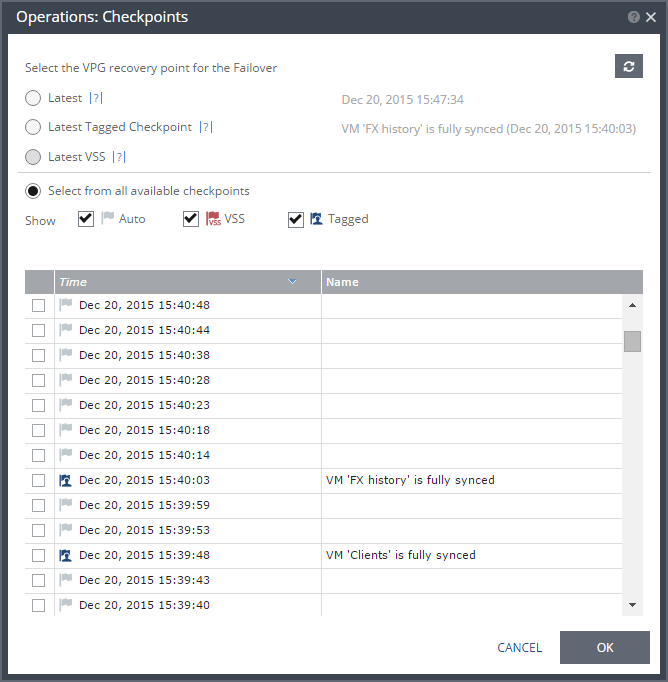
When the sync process for a virtual machine is complete, Zerto Virtual Manager tags the first checkpoint that includes a new virtual machine with: VM ’XXX’ is fully synced
where XXX is the name of the virtual machine that was synced.
When you perform a recovery operation using one of these checkpoints, or any later checkpoint, all the virtual machines that have completed syncing will be recovered.
For example, in the following screen shot, 2 virtual machines were added to the VPG Operations. When the sync process for each machine completed, a checkpoint was added to show this. If you use the checkpoint written on Dec 20, 2015 at 15:39:48, the recovery will include the virtual machine Clients but not FX history. If you select the checkpoint at 15:40:03 or a later checkpoint, a recovery operation will also include the virtual machine FX history.
If the virtual machine is added to a VPG replicating to a resource pool in VMware vSphere environments, Zerto Virtual Replication checks that the additional virtual machine doesn’t exceed the resource pool capacity, such that the sum of the virtual machine reservation is less than or equal to the resource pool CPU and storage settings.